|
Turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other Amniote, amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed Turtle shell#Carapace, carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scale (anatomy), scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley. Six of the seven sea turtle species, all but the flatback, are present in U.S. waters, and are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. They are listed as threatened with extinction globally on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The flatback turtle is found only in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be categorized as hard-shelled ( cheloniid) or leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. The only dermochelyid species of sea turtle is the leatherback. Description For each of the seven species of sea turtles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Depictions Of Turtles
Turtles are frequently depicted in popular culture as easygoing, patient, and wise creatures. Due to their long lifespan, slow movement, sturdiness, and wrinkled appearance, they are an emblem of longevity and stability in many cultures around the world.Cirlot, Juan-Eduardo, trans. Sage, Jack, 2002, ''A Dictionary of Symbols'', Courier Dover Publications, .Ball, Catherine, 2004, ''Animal Motifs in Asian Art'', Courier Dover Publications, . Turtles are regularly incorporated Reptiles in culture, into human culture, with painters, photographers, poets, songwriters, and sculptors using them as subjects.Lutz, Peter L., Musick, John A., and Wyneken, Jeanette, 2002, ''The Biology of Sea Turtles'', CRC Press, . They have an important role in mythologies around the world,Garfield, Eugene, 1986, The Turtle: A Most Ancient Mystery. Part 1. Its Role in Art, Literature, and Mythology, ''Towards Scientography: 9 (Essays of An Information Scientist)'', Isis Press, . and are often implicated in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
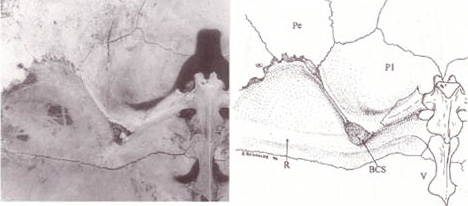
Plastron
The turtle shell is a shield for the ventral and dorsal parts of turtles (the Order (biology), order Testudines), completely enclosing all the turtle's vital organs and in some cases even the head. It is constructed of modified bony elements such as the ribs, parts of the pelvis and other bones found in most reptiles. The bone of the shell consists of both skeletal and dermal bone, showing that the complete enclosure of the shell likely evolved by including dermal armor into the rib cage. The turtle's shell is an important study, not just because of the apparent protection it provides for the animal but also as an identification tool, in particular with fossils, as the shell is one of the likely parts of a turtle to survive fossilization. Hence understanding the shell structure in living species provides comparable material with fossils. The shell of the hawksbill turtle, among other species, has been used as a material for a wide range of small decorative and practical items sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtling (hunting)
Turtling is the hunting of turtles. Turtling has been a part of human culture since as far back as the middle of the first millennium BC, where sea turtles such as the hawksbill sea turtle (''Eretmochelys imbricata'') were eaten as delicacies in countries such as China. While consumption and hunting of turtles is less common than it was in the past, this practice is still a part of communities throughout the globe, whether done legally or illegally. History In Melanesian societies, it was common during funeral ceremonies, for locals to partake in a feast of turtle meat and other delicacies. The deceased were sealed into a tomb, and several years later it was tradition to reopen the tomb and to indulge once more on turtle meat. Because turtle meat was relatively rare, hunting the turtle for others during this time was considered to be a display of public generosity. While turtle hunting within this culture is not as common as it was decades ago, locals on Murray Island, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Box Turtle
The common box turtle (''Terrapene carolina'') is a species of box turtle with five existing subspecies. It is found throughout the Eastern United States and Mexico. The box turtle has a distinctive hinged lower shell that allows it to completely enclose itself, like a box. Its upper jaw is hooked. The turtle is primarily terrestrial and eats a wide variety of plants and animals. The females lay their eggs in the summer. Turtles in the northern part of their range hibernate over the winter. Common box turtle numbers are declining because of habitat loss, roadkill, and capture for the pet trade. The species is classified as Vulnerable species, vulnerable to threats to its survival by the IUCN Red List. Three states have chosen subspecies of the common box turtle as their official state reptile: ''Eastern box turtle, T. c. carolina'' in North Carolina and Tennessee and ''Three-toed box turtle, T. c. triunguis'' in Missouri. Classification ''Terrapene carolina'' was first describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptodira
The Cryptodira (') are a suborder of Testudines that includes most living tortoises and turtles. Cryptodira is commonly called the "Hidden-Neck Turtles" or the "Inside-Neck Turtles". Cryptodira differ from Pleurodira (side-necked turtles) in that they lower their necks and pull the heads straight back into the shells, instead of folding their necks sideways along the body under the shells' marginals. They include among their species freshwater turtles, snapping turtles, tortoises, softshell turtles, and sea turtles. Neck retraction The Cryptodira are characterized by retraction of the head in the vertical plane, which permits for primarily vertical movements and restricted lateral movements outside of the shell. These motions are largely due to the morphology and arrangement of cervical vertebrae. In all recent turtles, the cervical column consists of nine joints and eight vertebrae. Compared to the narrow vertebrae and the closely positioned zygapophyses of the pleur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortoise
Tortoises ( ) are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin for "tortoise"). Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like other members of the suborder Cryptodira, they retract their necks and heads directly backward into the shell to protect them. Tortoises can vary in size with some species, such as the Galápagos giant tortoise, growing to more than in length, whereas others like the Speckled cape tortoise have shells that measure only long. Several lineages of tortoises have independently evolved very large body sizes in excess of , including the Galapagos giant tortoise and the Aldabra giant tortoise. They are usually diurnal animals with tendencies to be crepuscular depending on the ambient temperatures. They are generally reclusive animals. Tortoises are the longest-living land animals in the world, although the longest-living species of tortois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juveniles of the target species. The term "bycatch" is also sometimes used for untargeted catch in other forms of animal harvesting or collecting. Non- marine species ( freshwater fish not saltwater fish) that are caught (either intentionally or unintentionally) but regarded as generally "undesirable" are referred to as rough fish (mainly US) or coarse fish (mainly UK). In 1997, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defined bycatch as "total fishing mortality, excluding that accounted directly by the retained catch of target species". Bycatch contributes to fishery decline and is a mechanism of overfishing for unintentional catch. The average annual bycatch rate of pinnipeds and cetaceans in the US from 1990 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurodira
The Pleurodira are one of the two living suborders of turtles, the other being the Cryptodira. The division between these two suborders represents a very deep evolutionary divide between two very different types of turtles. The physical differences between them, although anatomical and largely internal, are nonetheless significant, and the zoogeographic implications of them are substantial. The Pleurodira are known more commonly as the side-necked turtles and the name Pleurodira quite literally translates to side neck, whereas the Cryptodira are known as hidden-necked turtles. The Pleurodira turtles are currently restricted to freshwater habitats in the Southern Hemisphere, largely to Australia, South America, and Africa. Within the Pleurodira, three living families are represented: Chelidae, also known as the Austro-South American side-necked turtles, the Pelomedusidae, also known as the African mud terrapins, and the Podocnemididae, also known as the American side-neck rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |