|
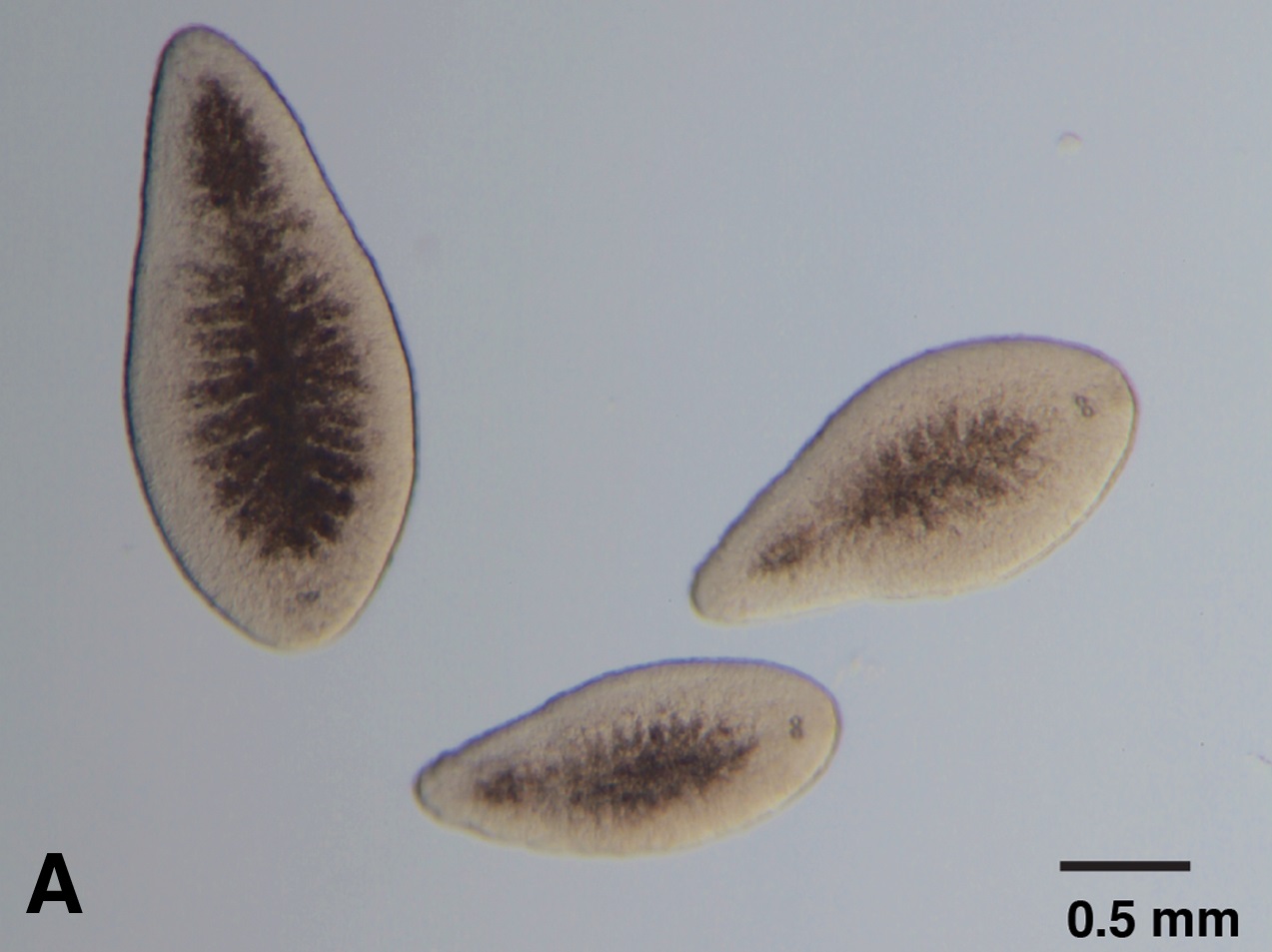
Turbellarians
The Turbellaria are one of the traditional sub-divisions of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), and include all the sub-groups that are not exclusively parasitic. There are about 4,500 species, which range from to large freshwater forms more than long or terrestrial species like ''Bipalium kewense'' which can reach in length. All the larger forms are flat with ribbon-like or leaf-like shapes, since their lack of respiratory and circulatory systems means that they have to rely on diffusion for internal transport of metabolites. However, many of the smaller forms are round in cross section. Most are predators, and all live in water or in moist terrestrial environments. Most forms reproduce sexually and with few exceptions all are simultaneous hermaphrodites. The Acoelomorpha and the genus ''Xenoturbella'' were formerly included in the Turbellaria, but are no longer regarded as Platyhelminthes. All the exclusively parasitic Platyhelminthes form a monophyletic group Neodermat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthes
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no coelom, body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory system, respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenea
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.L.A. Tubbsa et al. (2005). "Effects of temperature on fecundity in vitro, egg hatching and reproductive development of ''Benedenia seriolae'' and ''Zeuxapta seriolae'' (Monogenea) parasitic on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi". ''International Journal for Parasitology''(35), 315–327. Some monogeneans are oviparous (egg-laying) and some are viviparous (live-bearing). Oviparous varieties release eggs into the water. Viviparous varieties release larvae, which immediately attach to another host. The genus ''Gyrodactylus'' is an example of a viviparous variety, while the genus ''Dactylogyrus'' is an example of an oviparous variety. Signs and symptoms Freshwater fish that become infected with this parasite become let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
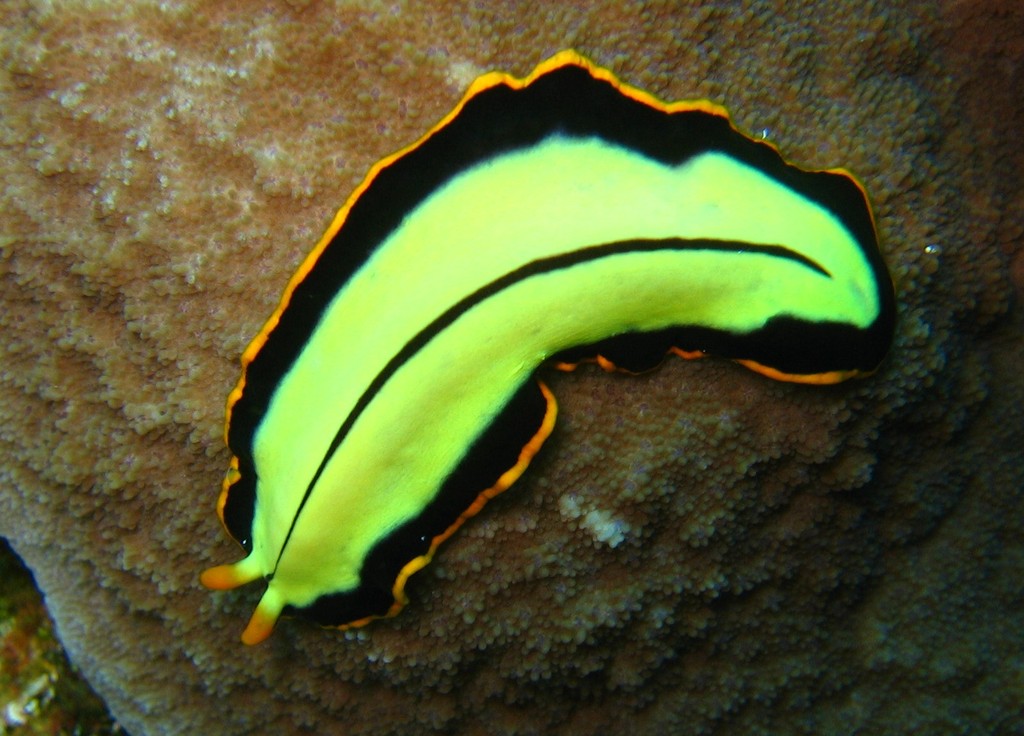
Pseudobiceros Bedfordi
''Pseudobiceros bedfordi'' (common names Persian carpet flatworm and Bedford's flatworm) is a species of flatworm in the family Pseudocerotidae. This species has two penises, which it uses to engage in penis fencing, attempting to inject sperm into its opponent in order to fertilize it, while simultaneously avoiding being fertilized by their opponent. Description ''Pseudobiceros bedfordi'' is a large polyclad flatworm approximately 8–10 cm in length. It has a distinctive pattern consisting of a brown to black background, with multiple transverse, bilateral pink lines around thousands of tightly spaced, bright yellow spots,Richmond, Matthew D. (1997), ''A Field Guide to the Seashores of Eastern Africa and the Western Indian Ocean Islands'', IDA/Department for Research Cooperation, SAREC, , p. 154 pink undulating spots with stripes on the sides of the body. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow, diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment. Gases are constantly consumed and produced by Metabolism, cellular and metabolic reactions in most living things, so an efficient system for gas exchange between, ultimately, the interior of the cell(s) and the external environment is required. Small, particularly unicellular organisms, such as bacterium, bacteria and protozoa, have a high Surface-area-to-volume ratio, surface-area to volume ratio. In these creatures the gas exchange membrane is typically the cell membrane. Some small multicellular organisms, such as flatworms, are also able to perform sufficient gas exchange across the skin or cuticle that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoelomate
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it remains undifferentiated. In the past, and for practical purposes, coelom characteristics have been used to classify bilaterian animal phyla into informal groups. Etymology The term ''coelom'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'cavity'. Structure Development The coelom is the mesodermally lined cavity between the gut and the outer body wall. During the development of the embryo, coelom formation begins in the gastrulation stage. The developing digestive tube of an embryo forms as a blind pouch called the archenteron. In Protostomes, the coelom forms by a process known as schizocoely. The archenteron initially forms, and the mesoderm splits into two layers: the first attaches to the body wall or ectoderm, formin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triploblastic
Triploblasty is a condition of the gastrula in which there are three primary germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Germ cells are set aside in the embryo at the blastula stage, which are incorporated into the gonads during organogenesis. The germ layers form during gastrulation of the blastula. The term ''triploblast'' may refer to any egg cell in which the blastoderm splits into three layers. All bilaterians, the animals with bilaterally symmetrical embryos, are triploblastic. Other animal taxa, the Ctenophora, ctenophores, placozoans and cnidarians, are diploblasty, diploblastic, meaning their embryos contain only two germ layers. Sponges are even less developmentally specialized, lacking both true Tissue (biology), tissues and Organ (anatomy), organs. The earliest triploblasts are thought to have evolved from the diploblasts some time in the Proterozoic, establishing themselves as a group prior to the diversification of them during the Cambrian explosion. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateria
The Bilateria or bilaterians are animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other. This also means they have a head and a tail (anterior-posterior axis) as well as a belly and a back (ventral-dorsal axis). Nearly all are bilaterally symmetrical as adults as well; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical during embryonic development. Most animals are bilaterians, excluding sponges, ctenophores, placozoans and cnidarians. For the most part, bilateral embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Except for a few phyla (i.e. flatworms and gnathostomulids), bilaterians have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities ( acoelomates, i.e. Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha and Gnathostomulida), while others display primary body cavities (de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemertodermatida
Nemertodermatida is a class of Acoelomorpha, comprising 18 species of millimetre-sized turbellariform, mostly interstitial worms. Taxonomy The order ''Nemertodermatida'' contains two families with 6 genera. The high level of cryptic diversity in this meiofauna group however implies that the number of nemertodermatid taxa may be underestimated. Ascopariidae The family Ascopariidae Sterrer, 1998 contains two genera. * '' Ascoparia'' Sterrer, 1998 * '' Flagellophora'' Faubel & Dorjes, 1978 There are 3 species in the family ''Ascopariidae''. Nemertodermatidae The family Nemertodermatidae Nemertodermatidae is a family of wormlike animals in the phylum Acoelomorpha. They are similar to the flatworms of the phylum Platyhelminthes, and were traditionally classified as such. These are hermaphroditic marine worms with ciliated bodies ... Steinböck, 1930 contains four genera. * '' Meara'' * '' Nemertinoides'' * '' Nemertoderma'' * '' Sterreria'' There are 15 species in the fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoela
Acoela, or the acoels, is an order of small and simple invertebrates in the subphylum Acoelomorpha of phylum Xenacoelomorpha, a deep branching bilaterian group of animals, which resemble flatworms. Historically they were treated as an order of turbellarian flatworms. The etymology of "acoel" is from the Ancient Greek words (), the ''alpha privative'', expressing negation or absence, and (), meaning "cavity". This refers to the fact that acoels have a structure lacking a fluid-filled body cavity. Description Acoels are very small flattened worms, usually under in length, but some larger species, such as '' Symsagittifera roscoffensis'', may reach up to . They are bilaterally symmetric and microscopic. They are found worldwide in marine and brackish waters, usually having a benthic lifestyle, although some species are epibionts. Two species, ''Limonoposthia polonica'' and ''Oligochoerus limnophilus'', lives in freshwater. Members of the class Acoela lack a conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |