|
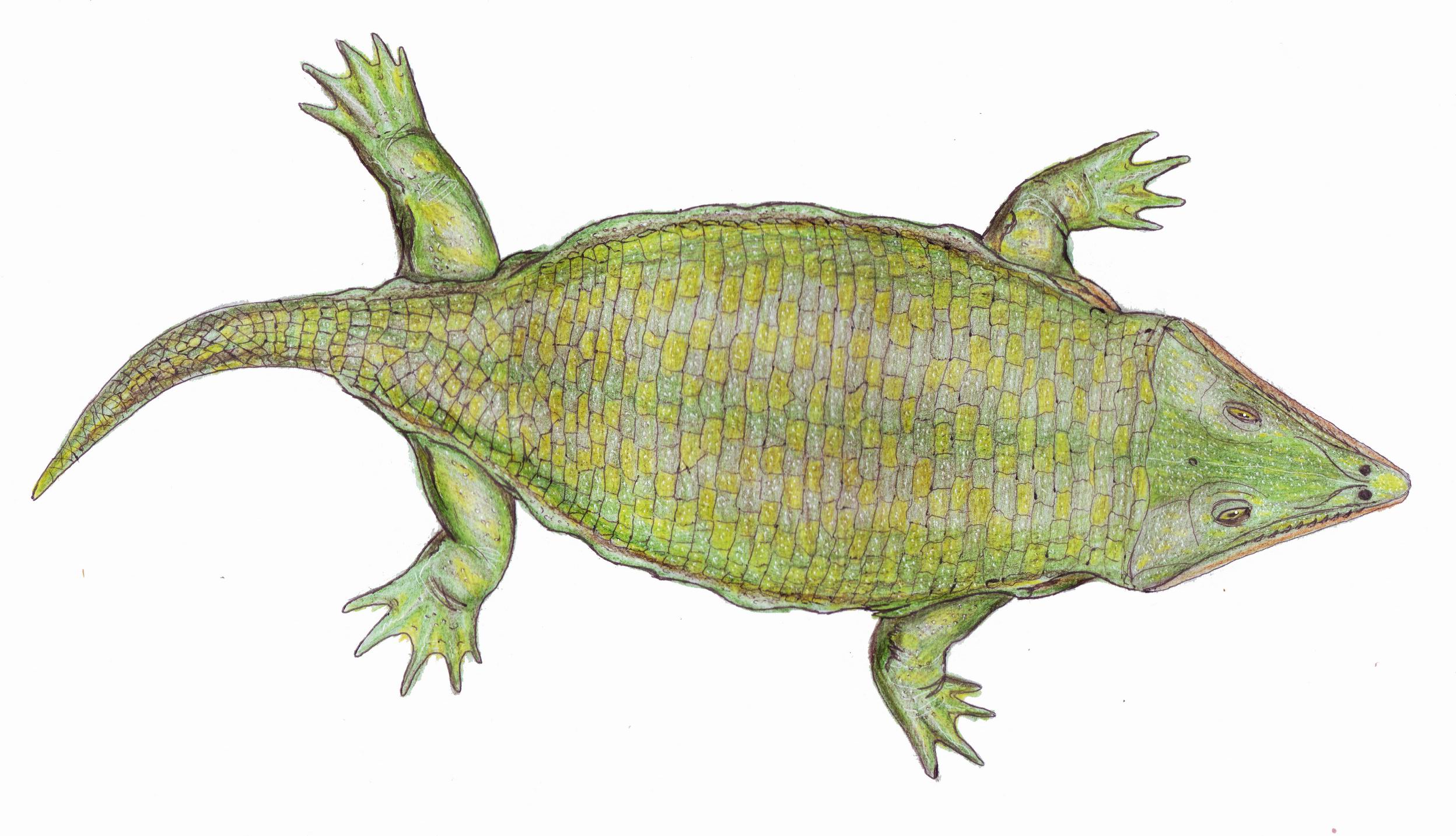
Tupilakosaurus
''Tupilakosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dvinosaurian temnospondyl within the family Tupilakosauridae. Two species are known: *''Tupilakosaurus heilmani'' Nielsen, 1954 — Wordie Creek Formation, Greenland *''Tupilakosaurus wetlugensis'' Shishkin, 1961 — Vokhma and Kopanskaya Formation, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Dvinosaurs Induan genera Triassic temnospondyls of Europe Fossils of Greenland Triassic Greenland Fossil taxa described in 1954 {{triassic-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupilakosauridae
Tupilakosauridae is an extinct family of dvinosaurian temnospondyls. It contains the genera ''Slaugenhopia'', '' Thabanchuia'', ''Tupilakosaurus'', and possibly ''Kourerpeton''. Tupilakosaurs are known from Texas, Greenland, Russia, and France. The earliest tupilakosaur, ''Slaugenhopia'', is Early Permian in age while the latest known tupilakosaurs are Early Triassic in age. Derived tupilakosaurs possess embolomerous centra in their vertebrae, which are diplospondylous. They also have a deep notch in the pterygoid bone of the palate. Tupilakosaurs were aquatic, and used an undulatory mode of swimming much like that of eels. References External linksTupilakosauridaein the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Dvinosaurs Amphibian fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Greenland
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Amphibian
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvinosauria
Dvinosaurs are one of several new clades of Temnospondyl amphibians named in the phylogenetic review of the group by Yates and Warren 2000. They represent a group of primitive semi-aquatic to completely aquatic amphibians, and are known from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Triassic, being most common in the Permian period. Their distinguishing characteristics are a reduction of the otic notch; the loss of a flange on the rear side of the pterygoid; and 28 or more presacral vertebrae. Trimerorhachidae is the most basal family of dvinosaurs. Most other dvinosaurs are placed in the superfamily Dvinosauroidea. Within Dvinosauroidea are two families, Eobrachyopidae and Tupilakosauridae, as well as dvinosaurs that cannot be placed in either family, such as '' Dvinosaurus'' and ''Kourerpeton''. A 2008 phylogenetic analysis found Eobrachyopidae to be paraphyletic, representing a grade of basal dvinosauroids. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic relationships of dvinos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Temnospondyls Of Europe
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvinosaurs
Dvinosaurs are one of several new clades of Temnospondyl amphibians named in the phylogenetic review of the group by Yates and Warren 2000. They represent a group of primitive semi-aquatic to completely aquatic amphibians, and are known from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Triassic, being most common in the Permian period. Their distinguishing characteristics are a reduction of the otic notch; the loss of a flange on the rear side of the pterygoid; and 28 or more presacral vertebrae. Trimerorhachidae is the most basal family of dvinosaurs. Most other dvinosaurs are placed in the superfamily Dvinosauroidea. Within Dvinosauroidea are two families, Eobrachyopidae and Tupilakosauridae, as well as dvinosaurs that cannot be placed in either family, such as '' Dvinosaurus'' and ''Kourerpeton''. A 2008 phylogenetic analysis found Eobrachyopidae to be paraphyletic, representing a grade of basal dvinosauroids. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic relationships of dvinosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium, nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum, nomina nuda''), as well as synonym (zoology), junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Synonym (zoology), Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type (zoology), type specimens are later assigned to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Greenland
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induan Genera
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian (latest Permian) and is followed by the Olenekian. The Induan is roughly coeval with the regional Feixianguanian Stage of China. Geology Stratigraphy The Triassic is the first period of the Mesozoic era. It is subdivided into the Lower, Middle, and Upper Triassic series, which are further subdivided into stages. The Induan is the first stage of the Lower Triassic, from 251.9 million to 251.2 million years ago, spanning the first 700,000 years after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Stages can be defined globally or regionally. For global stratigraphic correlation, the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian (latest Permian) and is followed by the Olenekian. The Induan is roughly coeval with the regional Feixianguanian Stage of China. Geology Stratigraphy The Triassic is the first period of the Mesozoic era. It is subdivided into the Lower, Middle, and Upper Triassic series, which are further subdivided into stages. The Induan is the first stage of the Lower Triassic, from 251.9 million to 251.2 million years ago, spanning the first 700,000 years after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Stages can be defined globally or regionally. For global stratigraphic correlation, the International Commission on Stratigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast (russian: link=no, Нижегородская область, ''Nizhegorodskaya oblast''), is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Nizhny Novgorod. It has a population of 3,310,597 as of the 2010 Census. From 1932 to 1990 it was known as Gorky Oblast. The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area (including Dzerzhinsk, Bor and Kstovo) the biggest city is Arzamas. Near the town of Sarov there is the Serafimo-Diveyevsky Monastery, one of the largest convents in Russia, established by Saint Seraphim of Sarov. The Makaryev Monastery opposite of the town of Lyskovo used to be the location of the largest fair in Eastern Europe. Other historic towns include Gorodets and Balakhna, located on the Volga to the north from Nizhny Novgorod. Geography The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republic. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1954 In Paleontology
Plants Angiosperms Arthropods Insects Archosauromorphs Phytosaurs Dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Synapsids Pelycosaurs Eutherians Cetaceans References {{portal, Paleontology 1950s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)