|
Tunupa
Tunupa is a dormant volcano in the Potosí Department of southwestern Bolivia. It stands on the northern side of the Salar de Uyuni at an elevation of on the Bolivian Altiplano. Tunupa was active in the Pleistocene, with most of the volcano constructed by lava flows that erupted between 1.36 and 1.56 million years ago. Later glaciers developed on the mountain. There is a cave with several mummies about half way up and an ancient village at the foot with a modest "salt hotel". Geography and geomorphology Tunupa is located in Bolivia, at the centre of the Altiplano about east of the main volcanic arc. It forms a peninsula in the Salar de Uyuni, which surrounds the volcano on its southern side. The volcano is located within the Salinas de Garci-Mendoza municipality, and the towns of Ayque, Coquesa and Jirira lie on its southern slopes. Volcanism in the backarc of the Central Andes is represented by several types of volcanoes, including several monogenetic volcanoes, strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tauca
Lake Tauca is a former lake in the Altiplano of Bolivia. It is also known as Lake Pocoyu for its constituent lakes: Lake Poopó, Salar de Coipasa and Salar de Uyuni. The lake covered large parts of the southern Altiplano between the Eastern Cordillera and the Western Cordillera, covering an estimated of the basins of present-day Lake Poopó and the Salars of Uyuni, Coipasa and adjacent basins. Water levels varied, possibly reaching in altitude. The lake was saline. The lake received water from Lake Titicaca, but whether this contributed most of Tauca's water or only a small amount is controversial; the quantity was sufficient to influence the local climate and depress the underlying terrain with its weight. Diatoms, plants and animals developed in the lake, sometimes forming reef knolls. The duration of Lake Tauca's existence is uncertain. Research in 2011 indicated that the rise in lake levels began 18,500 BP, peaking 16,000 and 14,500 years ago. About 14,200 years ago, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
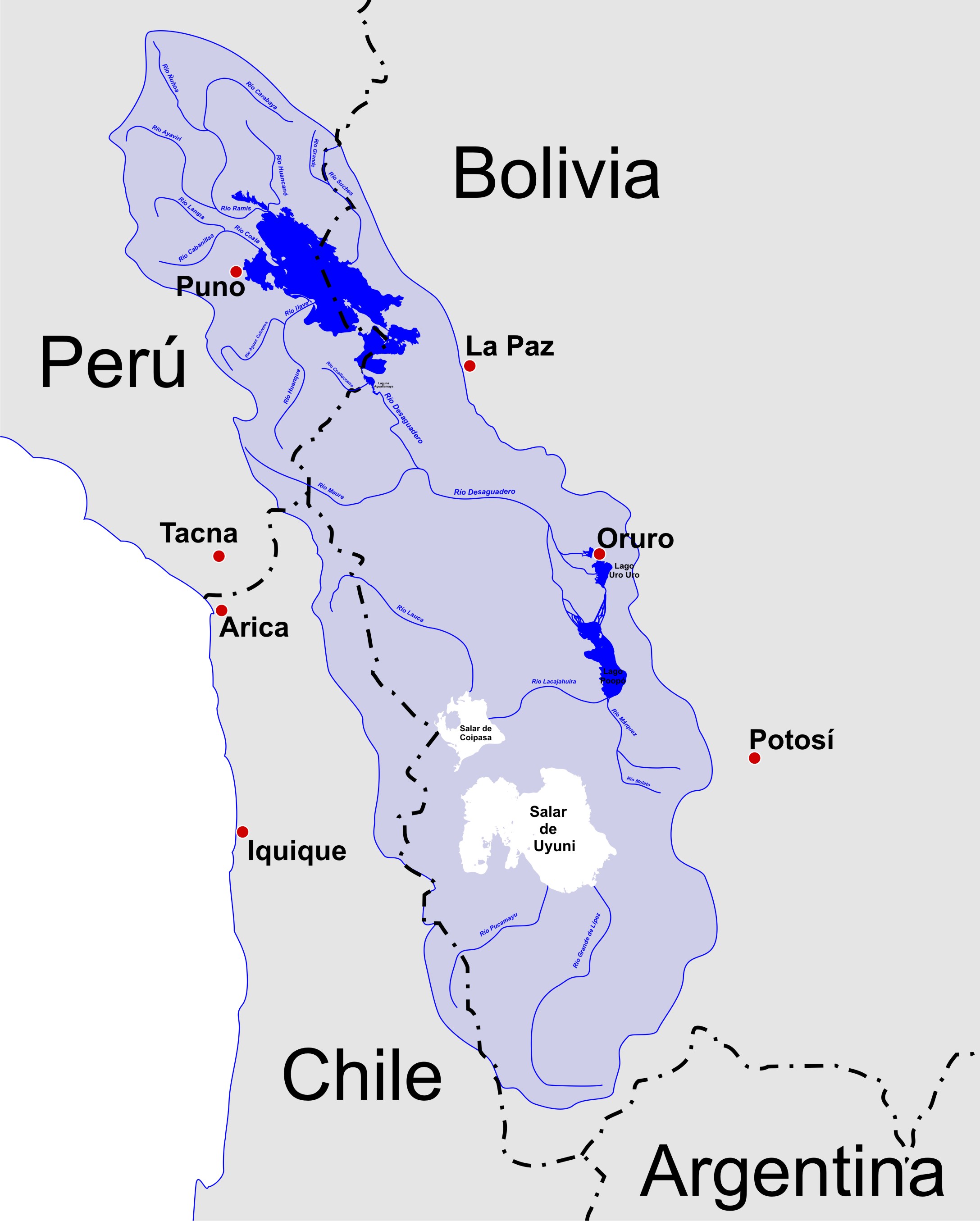
Salar De Uyuni
Salar de Uyuni (or "Salar de Tunupa") is the world's largest salt flat, or playa, at over in area. It is in the Daniel Campos Province in Potosí in southwest Bolivia, near the crest of the Andes at an elevation of above sea level. The Salar was formed as a result of transformations between several prehistoric lakes that existed around forty thousand years ago but had all evaporated over time. It is now covered by a few meters of salt crust, which has an extraordinary flatness with the average elevation variations within one meter over the entire area of the Salar. The crust serves as a source of salt and covers a pool of brine, which is exceptionally rich in lithium. The large area, clear skies, and exceptional flatness of the surface make the Salar ideal for calibrating the altimeters of Earth observation satellites. Following rain, a thin layer of dead calm water transforms the flat into the world's largest mirror, across. The Salar serves as the major transport route a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coquesa
Coqueza (also spelled Coquesa) is one of the cantons of the Tahua Municipality, the second municipal section of the Daniel Campos Province in the Potosí Department of Bolivia. During the census of 2001 it had 102 inhabitants.Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Bolivia (Spanish) Its seat is Coqueza. The village is situated at the and south of the volcano. See also * Inkawasi Island * |
Ultra Prominent Peak
An ultra-prominent peak, or Ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,524 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not Ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and therefore do not achieve enough topographic prominence. The term "Ultra" originated with earth scientist Steve Fry, from his studies of the prominence of peaks in Washington (state), Washington in the 1980s. His original term was "ultra major mountain", referring to peaks with at least of prominence. Distribution Currently, 1,518 Ultras have been identified above sea level: 639 in Asia, 356 in North America, 209 in South America, 120 in Europe (including 12 in the Caucasus), 84 in Africa, 69 in Oceania, and 41 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. and θέρμη, ''heat'' ). Hydrothermal circulation occurs most often in the vicinity of sources of heat within the Earth's crust. In general, this occurs near volcanic activity, but can occur in the shallow to mid crust along deeply penetrating fault irregularities or in the deep crust related to the intrusion of granite, or as the result of orogeny or metamorphism. Seafloor hydrothermal circulation Hydrothermal circulation in the oceans is the passage of the water through mid-oceanic ridge systems. The term includes both the circulation of the well-known, high-temperature vent waters near the ridge crests, and the much-lower-temperature, diffuse flow of water through sedim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galán
Cerro Galán is a caldera in the Catamarca Province of Argentina. It is one of the largest exposed calderas in the world and forms part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, one of the three volcanic belts found in South America. One of several major caldera systems in the Central Volcanic Zone, the mountain is grouped into the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex. Volcanic activity at Galán is the indirect consequence of the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South America Plate, and involves the infiltration of melts into the crust and the formation of secondary magmas which after storage in the crust give rise to the dacitic to rhyodacitic rocks erupted by the volcano. Galán was active between 5.6 and 4.51 million years ago, when it generated a number of ignimbrites known as the Toconquis group which crop out mainly west of the caldera. The largest eruption of Galán was 2.08 ± 0.02 million years ago and was the source of the Galán ignimbrite, which covere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Frailes Ignimbrite Plateau
Los Frailes is an ignimbrite plateau in Bolivia, between the city of Potosi and the Lake Poopo. It belongs to a group of ignimbrites that exist in the Central Andes and which includes the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex. The plateau covers a surface of – with about of ignimbrite. The plateau features several putative vents, including Cerro Condor Nasa, Cerro Livicucho, Cerro Pascual Canaviri, Cerro Villacollo and Nuevo Mundo. The plateau was emplaced starting from 25 million years ago to the Holocene, when the Nuevo Mundo vent was active. Geography and geomorphology Los Frailes lies in the Eastern Cordillera of Bolivia, between the southeastern shores of Lake Poopo and the city of Potosi. It is a little-studied volcanic system. Los Frailes belongs to the Central Andean ignimbrites, which cover parts of southern Peru, southwestern Bolivia, northwestern Argentina and northeastern Chile and which contains the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex. Ignimbrites do not cover al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morococala
Morococala is a volcanic field in Bolivia, in the Department Oruro. It is formed by ignimbrites and associated volcanic features. It is part of the chain of plutons that extends over the Cordillera Real and the Cordillera Occidental and are the sites of mining activity. Geography and geomorphology It lies in the Cordillera Occidental. The city of Oruro lies northwest of Morococala, and the town of Llallagua is just south. Morococala consists of a high plateau, and is a field consisting of ignimbrites and tuffs, which were deposited on top of the basement. These form sequences with thicknesses on average less than . This field covers a surface area of . The presence of two calderas has been inferred, one at Tankha Tankha in the northern part of the field and one at Condoriri in the southern part of the field. The Tankha Tankha caldera has a resurgent dome which has erupted domes and lava flows. Other volcanic landforms in the field are lava domes. Mines are located at San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of but is capable of reaching speeds up to . The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about . Pyroclastic flows are the most deadly of all volcanic hazards and are produced as a result of certain explosive eruptions; they normally touch the ground and hurtle downhill, or spread laterally under gravity. Their speed depends upon the density of the current, the volcanic output rate, and the gradient of the slope. Origin of term The word ''pyroclast'' is derived from the Greek (''pýr''), meaning "fire", and (''klastós''), meaning "broken in pieces". A name for pyroclastic flows which glow red in the dark is (French, "burning cloud"); this was notably used to describe the disastrous 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée on Martinique, a French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on Earth are lava dome forming. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt (e.g. Semeru, 1946) to rhyolite (e.g. Chaiten, 2010) although the majority are of intermediate composition (such as Santiaguito, dacite-andesite, present day) The characteristic dome shape is attributed to high viscosity that prevents the lava from flowing very far. This high viscosity can be obtained in two ways: by high levels of silica in the magma, or by degassing of fluid magma. Since viscous basaltic and andesitic domes weather fast and easily break apart by further input of fluid lava, most of the preserved domes have high silica content and consist of rhyolite or dacite. Existence of lava domes has been suggested for some domed structures on the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
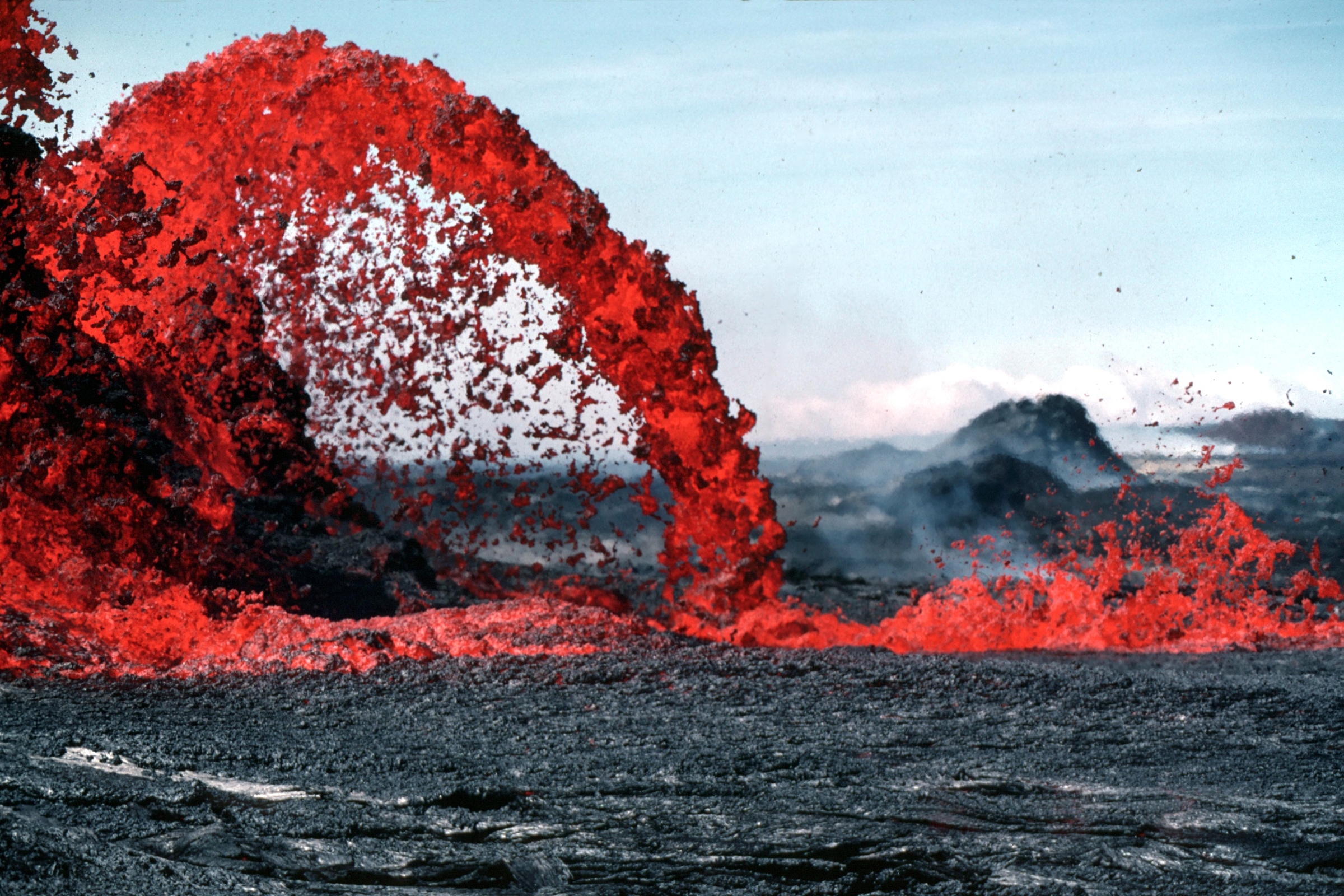
Lava Flow
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. The word ''lava'' comes from Italian and is probably derived from the Latin word ''labes'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



