|
Tunica-Biloxi
The Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe, ( tun, Yoroniku-Halayihku) formerly known as the Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe of Louisiana, is a federally recognized tribe of primarily Tunica and Biloxi people, located in east central Louisiana. Descendants of Ofo (Siouan-speakers), Avoyel (a Natchez people), and Choctaw (Muskogean) are also enrolled in the tribe. In the 21st century, the people speak mostly English and French. Many live on the Tunica-Biloxi Indian Reservation () in central Avoyelles Parish, just south of the city of Marksville, Louisiana, and overlapping its boundaries. The Reservation is . The 2010 census lists 951 persons self-identified as at least partly of Tunica-Biloxi, with 669 of those identifying as solely of Tunica-Biloxi ancestry. History By the Middle Mississippian period, local Late Woodland peoples in the Central Mississippi Valley had developed or adopted a Mississippian lifestyle, with maize agriculture, hierarchical political structures, mussel shell- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica People
The Tunica people are a group of linguistically and culturally related Native American tribes in the Mississippi River Valley, which include the Tunica (also spelled Tonica, Tonnica, and Thonnica); the Yazoo; the Koroa (Akoroa, Courouais); and possibly the Tioux. They first encountered Europeans in 1541 – members of the Hernando de Soto expedition. The Tunica language is an isolate. Over the next centuries, under pressure from hostile neighbors, the Tunica migrated south from the Central Mississippi Valley to the Lower Mississippi Valley. Eventually they moved westward and settled around present-day Marksville, Louisiana. Since the early 19th century, they have intermarried with the Biloxi tribe, an unrelated Siouan-speaking people from the vicinity of Biloxi, Mississippi and shared land. Remnant peoples from other small tribes also merged with them. In 1981 they were federally recognized and now call themselves the Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe; they have a reservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biloxi People
The Biloxi tribe are Native Americans of the Siouan language family. They call themselves by the autonym ''Tanêks(a)'' in Siouan Biloxi language. When first encountered by Europeans in 1699, the Biloxi inhabited an area near the coast of the Gulf of Mexico near what is now the city of Biloxi, Mississippi. They were eventually forced west into Louisiana and eastern Texas. The Biloxi language--''Tanêksąyaa ade''--has been extinct since the 1930s, when the last known native semi-speaker, Emma Jackson, died. Today, remaining Biloxi descendants have merged with the Tunica and other remnant peoples. Together they were federally recognized in 1981; today they are called the Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe and share a small reservation in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana. Descendants of several other small tribes are enrolled with them. The two main tribes were from different language groups: the Biloxi were Siouan-speaking and the Tunica had an isolate language. Today the tribe members spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Language
The Tunica or Luhchi Yoroni (or Tonica, or less common form Yuron) language is a language isolate that was spoken in the Central and Lower Mississippi Valley in the United States by Native Americans in the United States, Native American Tunica people, Tunica peoples. There are no native speakers of the Tunica language, but , there are 32 second language speakers. Tunica-Biloxi tribal member William Ely Johnson worked with Swiss ethnologist Albert Samuel Gatschet, Albert Gatschet to help him document the language in 1886. This initial documentation was further developed by linguist John R. Swanton in the early 1900s. The last known native speaker, Sesostrie Youchigant, died in 1948. In the 1930s, linguist Mary Haas worked with him to describe what Youchigant remembered of the language, and the description was published in ''A Grammar of the Tunica Language'' in 1941. That was followed by ''Tunica Texts'' in 1950 and ''Tunica Dictionary'' in 1953. By the 17th century, the people h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marksville, Louisiana
Marksville is a small city in and the parish seat of Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana, United States. The population was 5,702 at the 2010 census, an increase of 165 over the 2000 tabulation of 5,537. Louisiana's first land-based casino, Paragon Casino Resort, opened in Marksville in June 1994. It is operated by the federally recognized Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe, which has a reservation in the parish. History The land where Marksville was founded on was once a meeting place, leading to the present day Marksville Prehistoric Indian Site. Marksville is named after Marc Eliche (Marco Litche or Marco de Élitxe, as recorded by the Spanish), a Venetian Jew who established a trading post after his wagon broke down in this area. He was a Sephardic Jewish trader believed to be from Venice. His Italian name was recorded by a Spanish priest as ''Marco Litche;'' French priests, who were with colonists, recorded his name as ''Marc Eliche'' or ''Mark Eliché'' after his trading post was establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana
Avoyelles (french: Paroisse des Avoyelles) is a parish located in central eastern Louisiana on the Red River where it effectively becomes the Atchafalaya River and meets the Mississippi River. As of the 2010 census, the population was 42,073. The parish seat is Marksville. The parish was created in 1807, with the name deriving from the French name for the historic Avoyel people, one of the local Indian tribes at the time of European encounter. Today the parish is the base of the federally recognized Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe, who have a reservation there. The tribe has a land-based gambling casino on their reservation. It is located in Marksville, the parish seat, which is partly within reservation land. History Native Americans occupied this area beginning around 300 BC. Varying indigenous cultures flourished there in the following centuries. Today on the banks of the old Mississippi River channel in Marksville, three large burial mounds have been preserved from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Federally Recognized Tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 231 are located in Alaska. Description  In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants
In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants
|
Avoyel
The Avoyel or Avoyelles were a small Native American tribe who at the time of European contact inhabited land near the mouth of the Red River at its confluence with the Atchafalaya River near present-day Marksville, Louisiana. Also called variously ''Shi'xkaltī'ni'' (Stone-Arrow-Point people) in Tunican and ''Tassenocogoula'', ''Tassenogoula'', ''Toux Enongogoula'', and ''Tasånåk Okla'' in the Mobilian trade language; all names (including the autonym ''Avoyel'') are said by early French chroniclers to mean either "Flint People" or "People of the Rocks". This is thought to either reflect their active trading of flint for tools from local sources on their land in the eponymously named modern Avoyelles Parish or more likely as their status as middlemen in trading flint from Caddoan peoples to their north to the stone deficit Atakapa and Chitimacha peoples of the Gulf Coast. The Avoyel were also known by the French as the ''petits Taensas'' (English: Little Taensa), who were m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
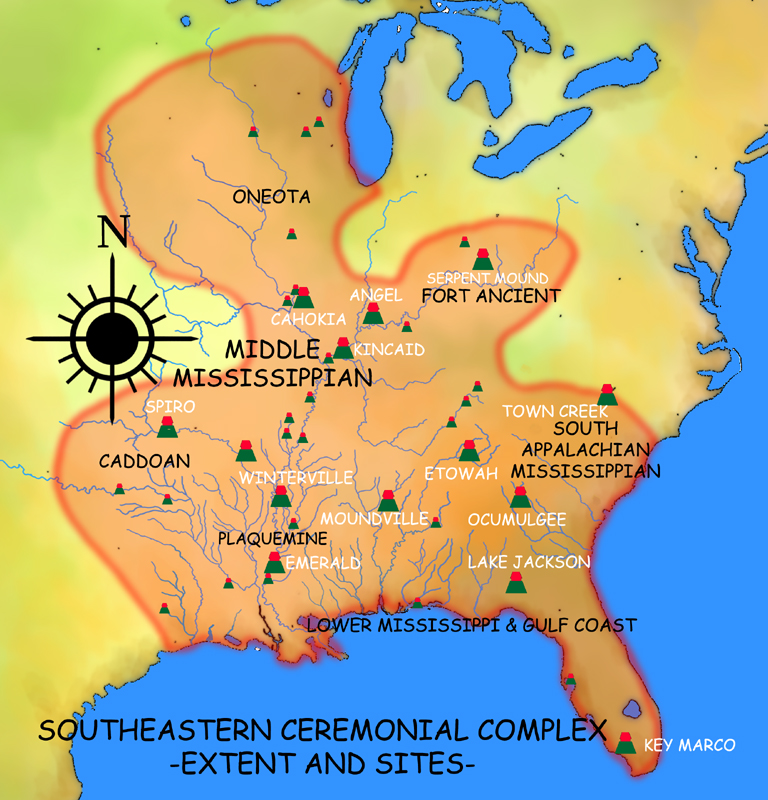
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. But, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that their civilizations developed independently. Obsolete names for this ceremonial complex, found in some anthropological sources, include Buzzard Cult and Southern Death Cult. Theories and names The complex operated as an exchange network. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosopelea
The Mosopelea, or Ofo, were a Siouan-speaking Native American people who historically inhabited the upper Ohio River. In reaction to Iroquois Confederacy invasions to take control of hunting grounds in the late 17th century, they moved south to the lower Mississippi River. They finally settled in central Louisiana, where they assimilated with the Tunica and the Siouan-speaking Biloxi. They are generally classified with the speakers of the Siouan Ofo language. History According to the 1684 French map of Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin, the Mosopelea had eight villages just north of the Ohio River, between the Muskingum and Scioto rivers, within the present-day state of Ohio, corresponding with the heart of Ohio Hopewell country. (The Miami-Illinois name ("river of the Mosopelea") referred to what is now called the Ohio River. Shortened in the Shawnee language, the name evolved to "Pelisipi" or "Pellissippi" and was also later applied to what is now called the Clinch River in V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biloxi Language
Biloxi was a Siouan language, which was once spoken by the Biloxi tribe in present-day Mississippi, Louisiana, and southeastern Texas. History The Biloxi tribe first encountered Europeans in 1699, along the Pascagoula River. By the mid-18th century, they had settled in central Louisiana. Some were also noted in Texas in the early 19th century. By the early 19th century, their numbers were already dwindling. By 1934, the last native speaker, Emma Jackson, was in her eighties. Morris Swadesh and Mary Haas spoke with her in 1934 and confirmed that she spoke the language. Classification Biloxi is an Ohio Valley, or Southeastern, Siouan language. It is related to Ofo and Tutelo. Phonology Multiple possible inventories have been suggested. This article follows that of Einaudi (1976). Vowels Along with contrastive nasalization, Biloxi also has phonemic vowel length. Notes: # May be either open-mid or close-mid. # Biloxi may have a phonetic schwa, but Dorsey-Swanton ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
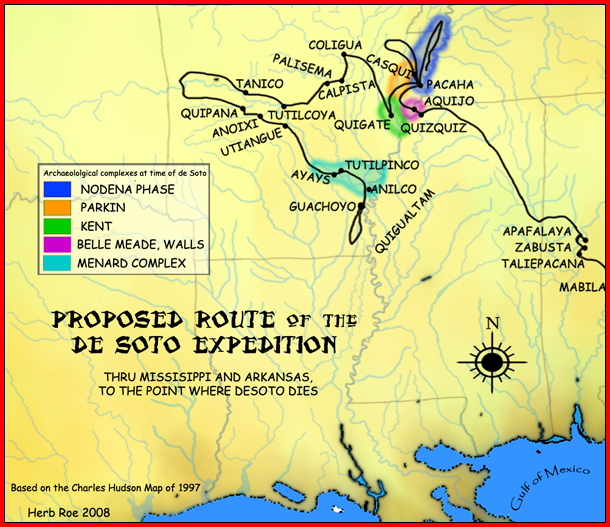
Menard–Hodges Site
The Menard–Hodges site ( 3AR4) (also known as Menard-Hodges Mounds and Osotouy), is an archaeological site in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It includes two large platform mounds as well as several house mounds. It is the type site for the Menard phase, a protohistoric Mississippian culture group. The Menard Mound was named for Frank Menard, on whose farm the mound was discovered. Description The site is considered as a possible candidate for the Province of Anilco encountered by the Hernando de Soto Entrada in 1540. It was contemporaneous with the Parkin site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Casqui, and the Nodena site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Pacaha. The site is also considered to be the location of the protohistoric Quapaw village of ''Osotouy'' (or ''Ossoteoue'') first encountered by French explorers in the late 17th century. The Quapaw at the time had four villages, Kappa, Ossoteoue, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |