|
Tumbler Ridge
Tumbler Ridge is a district municipality in the foothills of the B.C. Rockies in northeastern British Columbia, Canada, and a member municipality of the Peace River Regional District. With a population of 2,399 (2021) living in a townsite, the municipality encompasses an area of of mostly Crown land. The townsite is located near the confluence of the Murray River and Flatbed Creek and the intersection of Highway 52 and Highway 29 and includes the site of the Tumbler Ridge Secondary School and Tumbler Ridge Airport. It is part of the Peace River South provincial electoral district and the Prince George—Peace River—Northern Rockies federal riding. Tumbler Ridge is a planned community with the housing and infrastructure construct built simultaneously in 1981 by the provincial government to service the coal industry as part of the British Columbia Resources Investment Corporation's Northeast Coal Development. In 1981, a consortium of Japanese steel mills agreed to purchase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumbler Ridge Secondary School
Tumbler Ridge Secondary School (or TRSS) is a public High school#Canada, high school in Tumbler Ridge, British Columbia, Canada. TRSS is operated by School District 59 Peace River South and is the designated secondary school for the town's primary school. TRSS is a participant in the school district's International Student Study Program. , retrieved 2012-08-20 References External links Fraser Institute School Report Card 2010-2011 High schools in British Columbia 1982 establishments in British Columbia {{BritishColumbia-school-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, Android (operating system), Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro (computer science), macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft Office suite of software. Features Basic operation Microsoft Excel has the basic features of all spreadsheets, using a grid of ''cells'' arranged in numbered ''rows'' and letter-named ''columns'' to organize data manipulations like arithmetic operations. It has a battery of supplied functions to answer statistical, engineering, and financial needs. In addition, it can display data as line graphs, histograms and charts, and with a very limited three-dimensional graphical display. It allows sectioning of data to view its dependencies on various factors for different perspectives (using ''pivot tables'' and the ''sce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Highway 52
Highway 52, known locally as the ''Heritage Highway'', is a 243 km (151 mi) long alternate loop route between Arras, on the John Hart Highway just west of Dawson Creek, and Tupper, on the B.C.-Alberta boundary, via the community of Tumbler Ridge, 98 km (61 mi) south of Arras and 145 km (90 mi) south of Tupper. The highway to Arras was first given the number 52 in 1988, and the highway to Tupper received the same number in the late 1990s. In addition to Tumbler Ridge, the Heritage Highway provides access to Bearhole Lake Provincial Park and Protected Area and One Island Lake Provincial Park One Island Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. History The park was established 1963. Conservation Established between the Kiskatinaw River and the West Kiskatinaw River, the park provides representation of t .... The highway is mainly chip-seal, except for a 36km section which is gravel. It has many steep grades and sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Energy
Walter Energy, Inc. was a publicly traded "pure play" metallurgical coal producer for the global steel industry. The company also produced natural gas, steam coal and industrial coal, anthracite, metallurgical coke, and coal bed methane gas. Corporate and U.S. headquarters were located in Birmingham, Alabama, and its Canadian & UK headquarters in Vancouver, British Columbia. Walter Energy filed for bankruptcy in 2015 and its assets were purchased by Warrior Met Coal. Divisions U.S. The company's U.S. underground mines produced high-quality coal from Alabama's Blue Creek seam. Jim Walter Resources, the Company's U.S. underground coal mining unit, has grown from a small producer of less than 1 million tons of coal per year, produced solely for use in its sister company's coke ovens, into one of the 25 largest coal metallurgical coal producers in the United States, with 2010 metallurgical coal sales of approximately 6.0 million metric tons and plans to expand sales to 8.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian Financial Crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid and worries of a meltdown subsided. The crisis started in Thailand (known in Thailand as the ''Tom Yam Kung crisis''; th, วิกฤตต้มยำกุ้ง) on 2 July, with the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to float the baht due to lack of foreign currency to support its currency peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt. As the crisis spread, most of Southeast Asia and later South Korea and Japan saw slumping currencies, devalued stock markets and other asset prices, and a precipitous rise in private debt. South Korea, Indonesia and Thailand were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teck Cominco
Teck may refer to: * Teck Castle (Burg Teck) in Württemberg, Germany * Teckberg, mountain on which it is located * Duke of Teck, a title of nobility, associated with Teck Castle * Teck Railway, Germany * Teck Resources, a Canadian mining company formerly known as Teck Cominco * CCL25, a cytokine also known as "Teck" * Katherine Teck, an American author and composer * Lai Teck Lai Teck (real name Phạm Văn Đắc; 1901–1947) was a leader of the Communist Party of Malaya and Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army. A person of mixed Sino-Vietnamese descent, prior to his arrival in Malaya, Lai Teck was believed to ha ..., a Malayan communist leader * Lim Koon Teck, a Singaporean politician See also * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denison Mines
Denison Mines Corp. is a Canadian uranium exploration, development, and production company. Founded by Stephen B. Roman, and best known for its uranium mining in Blind River and Elliot Lake, it later diversified into coal, potash, and other projects. History About 1,000 workers at Denison's Elliot Lake mines went on strike in 1974, protesting unhealthy working conditions. The protest led to immediate improvements in safety conditions, and prompted Bill Davis to commission James Milton Ham to lead the Royal Commission on the Health and Safety of Workers in Mines. Denison served as manager for Uranium Participation Corporation, a Toronto-based investment fund which holds no license to deal in uranium until 2021 before it was sold to Sprott Asset Management and WMC Energy. Ownership and leadership 15% of the company is owned by Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). The CEO is David D. Cates, and Ron F. Hochstein is the chair of the board. Operations Denison's prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Resources Investment Corporation
The British Columbia Resources Investment Corporation, or BCRIC (pronounced "brick"), was a holding company formed under the government of William R. Bennett. The company took over ownership of various sawmills and mines that had been bought and bailed out by the government. The name was eventually changed to Westar Group Ltd. The most famous aspect of the company were the five free bearer shares, dated August 7, 1979, which were distributed to all British Columbians, to promote investment in the province, and earn back a profit to the buyer. British Columbians and investors were encouraged to buy more. The company expanded and bought numerous mining and logging installations. Because of significant investment in a North Sea oil play by a subsidiary, Westar Petroleum, and bad timing in a mining investment by another subsidiary, Westar Mining, the company ran into financial trouble. Investors saw their thousands of dollars dwindle to pennies. In 1995, the shares were consolida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
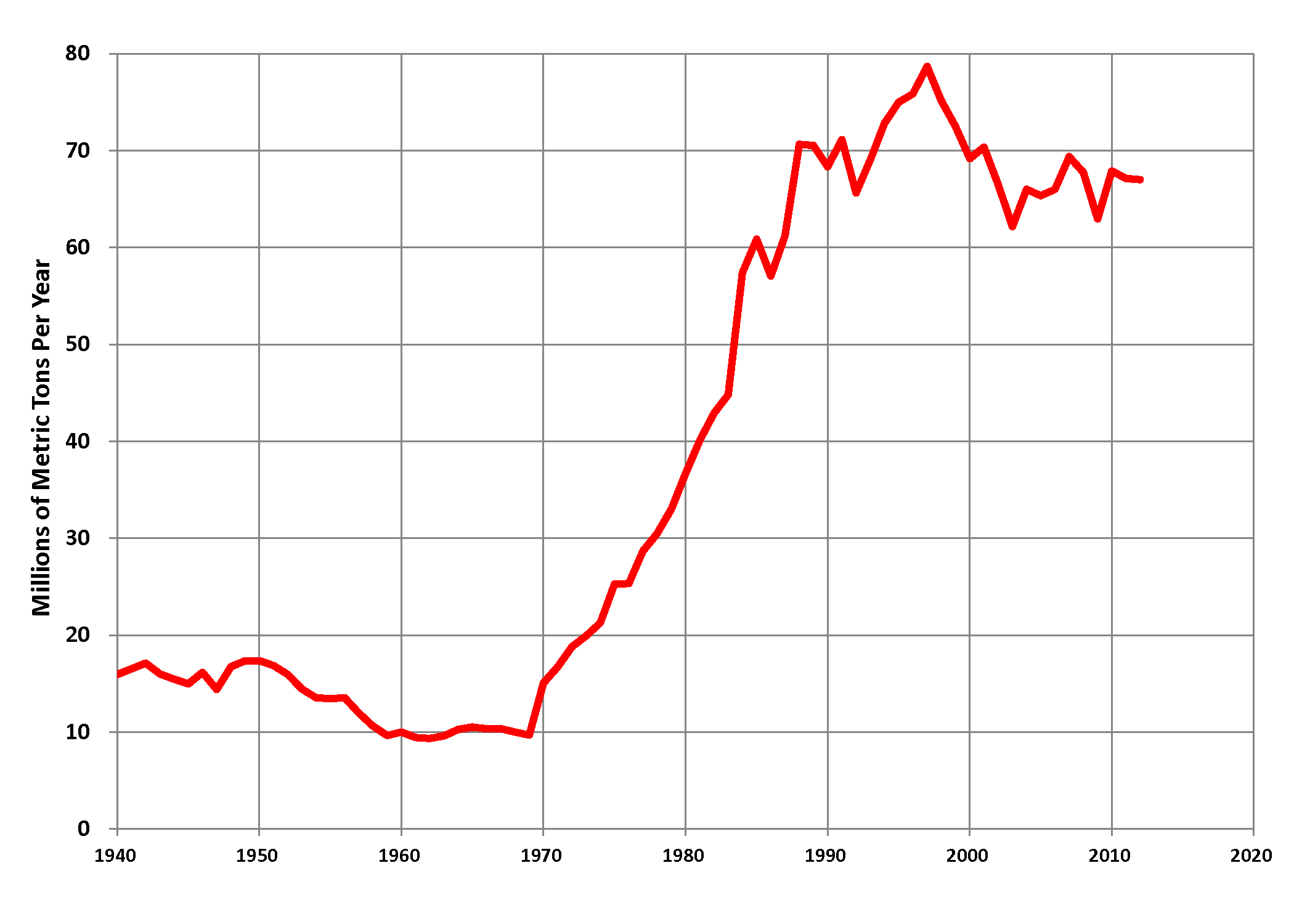
Coal In Canada
Coal reserves in Canada rank 13th largest in the world (following the former Soviet Union, the United States, the People's Republic of China and Australia) at approximately 10 billion tons, 0.6% of the world total. This represents more energy than all of the oil and gas in the country combined. The coal industry generates CDN$5 billion annually. Most of Canada's coal mining occurs in the West of the country. British Columbia operates 9 coal mines, Alberta nine, Saskatchewan three and New Brunswick one. Nova Scotia operates several small-scale mines, Westray having closed following the 1992 disaster there. In 2005, Canada produced 67.3 million tons of coal and its consumption was 60 million tons. Of this 56 million tons were used for electricity generation. The remaining four million tons was used in the steel, concrete and other industries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planned Community
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve in a more ''ad hoc'' and organic fashion. The term ''new town'' refers to planned communities of the new towns movement in particular, mainly in the United Kingdom. It was also common in the European colonization of the Americas to build according to a plan either on fresh ground or on the ruins of earlier Native American villages. Planned capitals A planned capital is a city specially planned, designed and built to be a capital. Several of the world's national capitals are planned capitals, including Canberra in Australia, Brasília in Brazil, Belmopan in Belize, New Delhi in India, Abuja in Nigeria, Islamabad in Pakistan, Naypyidaw in Myanmar (Burma) and Washington, D.C. in the United States, and the modern parts of Astana in Kaza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince George—Peace River—Northern Rockies
Prince George—Peace River—Northern Rockies (previously Prince George—Peace River) is a federal electoral district in northern British Columbia, Canada. It has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1968. Geography It consists of all of the province of British Columbia east of the Great Divide and some communities west of the divide. It contains large areas of uninhabited wilderness. Communities include the oil-and-gas exploration centre of Fort St. John; Fort Nelson, with the province's biggest wood products plant; Dawson Creek; Large Coal Mining operations in Tumbler Ridge and the part of Prince George north of the Nechako River and east of the Fraser River. History This electoral district was originally created in 1966 from parts of Cariboo and Kamloops ridings. It was abolished in 1976 when it was redistributed into Fort Nelson—Peace River riding and a part of Prince George—Bulkley Valley ridings. In 1978, Fort Nelson—Peace River was renam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |