|
Tulsi (Jain Monk)
Acharya Tulsi (20 October 1914 – 23 June 1997) was a prominent Jain religious leader. He was the founder of the Anuvrata movement and the Jain Vishva Bharti Institute, Ladnun, and the author of over one hundred books. Acharya Mahapragya, Acharya Mahashraman and Sadhvipramukha Kanakprabha were his disciples. Biography Acharya Tulsi was born on 20 October 1914 in Ladnun, in present Nagaur district of Rajasthan, to Vadana and Jhumarmal Khater. Acharya Kalugani, then the leader of the Svetambar Terapanth Sangh, greatly influenced Tulsi. Tulsi was initiated into monkhood at age 11 in 1925. In 1936, Kalugani nominated Tulsi to be his successor in Gangapur at Rang Bhawan-the house of Ranglal Hiran, making him the ninth Acharya of the Terapanth Sangha. During his leadership of the Sangha, he initiated more than 776 monks and nuns. Scholarship In the 1970s, Acharya Tulsi began researching, compiling translations and commentaries on the Jain Agamas. Acharya Tulsi, along with Yuvach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Vishva Bharati University
Jain Vishva Bharati Institute is a deemed university in Rajasthan. History JVBI was established with the inspiration of Acharya Tulsi, the 9th Head of the Jain Svetambar Terapanth religious sect, in Ladnun, Dist Nagaur, Rajasthan. In 20march 1991,Dimd university ka drja upon recommendation of the Government of India, University Grants Commission(UGC) notified JVBI as " Deemed University" under Section 3 of University Grants Commission Act, 1956. The Institute continues to be housed in the common campus of its parent body organization Jain Vishva Bharati. Acharya Tulsi remained its first constitutional Anushasta (moral and spiritual guide) followed by Acharya Mahapragya as its second Anushasta. Acharya Mahashraman is its present Anushasta. Campus The institute is in Ladnun, in Nagaur District Nagaur district is one of the 33 districts of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Panchayati Raj was introduced here. It is the fifth largest district in Rajasthan and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Religious Leaders In 2007
This is a list of the top-level leaders for religious groups with at least 50,000 adherents, and that led anytime since January 1, 2001. It should likewise only name leaders listed on other articles and lists. Buddhism *Cambodian buddhism — :*Tep Vong, Great Supreme Patriarch of Cambodia (2006–present) *Engaged Buddhism — :*Thích Nhất Hạnh, (1926–2022) *Sōka Gakkai — :*Einosuke Akiya, President (1981–2006) :*Minoru Harada, President (2006–present) *Thai Buddhism — :* Nyanasamvara Suvaddhana, 19th Somdet Phra and Supreme Patriarch (1989–2013) :* Ariyavongsagatanana IX, 20th Somdet Phra and Supreme Patriarch (2017–present) Tibetan Buddhism *Dalai Lama of the Gelug (Yellow Hat school) — :*Tenzin Gyatso, 14th Dalai Lama (1940–present) ;Mongolia *Jebtsundamba Khutuktu of the Gelug in Mongolia — :* Jambalnamdolchoyjijantsan, 9th Jebtsundamba Khutughtu (1991–2012) ;Russia *Buddhist Traditional Sangha of Russia — :* Damba Ayusheev, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acharya Tulsi Regional Cancer Institute And Research Centre
Acharya Tulsi Regional Cancer Institute and Research Centre is a cancer research institute in Bikaner, Rajasthan, India. It is the 13th Regional Cancer Centre in India. History Establishment of RCC, Bikaner Treatment of cancer patients in Bikaner has a very old and distinguished history. Even earlier than 1940, in the whole North-West India, Bikaner was the only place to provide Radiation Therapy by the deep and superficial X-ray to cancer patients. In pre independent era, cancer treatment by Radium was made available here. The first Tele Cobalt-60 machine for treatment of cancer patients was commissioned in 1965. Thereby keeping pace with the developments in the treatment of cancer around the world, Bikaner had become one of the oldest and prime centres of treatment of cancer in North West part of Ind ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acharya Bhikshu
Acharya Bhikshu (1726–1803) was the founder and first spiritual head of the Śvetāmbara Terapanth sect of Jainism. He was a Devotee of Mahavira. In the initial phase of his spiritual revolution, he moved out from the group of Sthanakvasi Acharya Raghunath. That time he had 13 saints, 13 followers and 13 the basic rules. This coincidence results in the name of "Terapanth" (Thirteen Path) and he referred it as "Hey Prabhu Yeh Terapanth". The various beliefs and teachings of the religious orders of those times greatly influenced his thinking. He studied and analysed the various disciplines of the Jain religion and on this basis he compiled his own ideologies and principles of the Jain way of life. Based on the doctrines propagated, Acharya Bhikshu rigorously followed the principles. It was this way of life that was demonstrated by Acharya Bhikshu which became the foundation principle of Terapanth. The Letter of Conduct was written by him is still followed in the same manne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
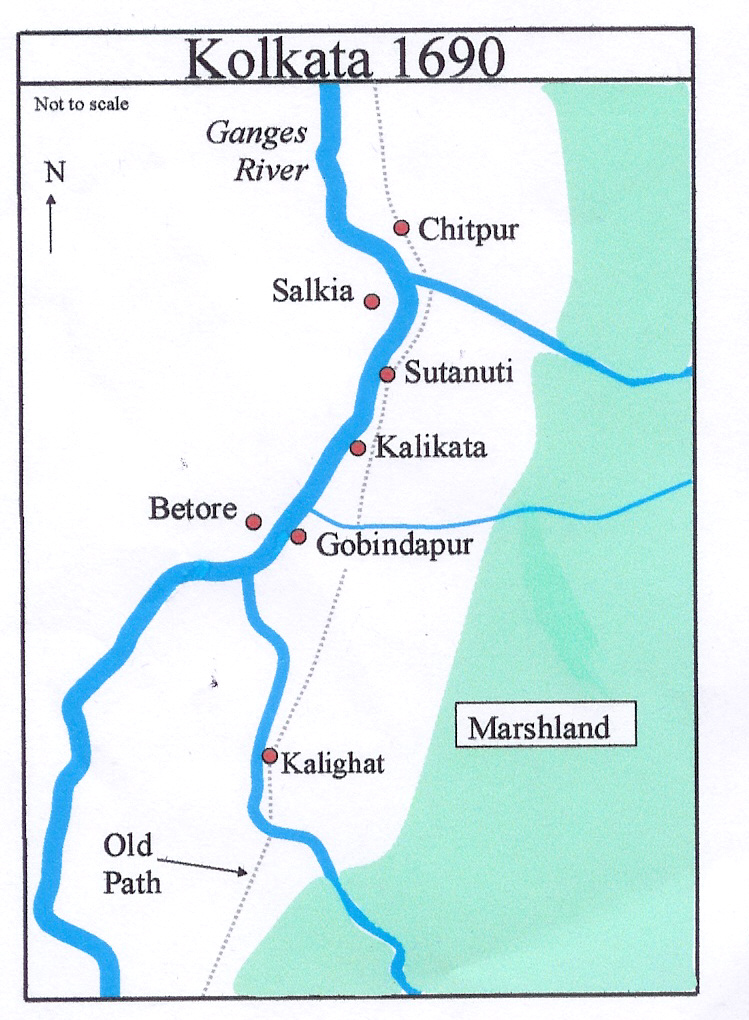
Salkia
Salkia is a neighbourhood of Howrah city in Howrah district, West Bengal, India and is administered by the Howrah Municipal Corporation. Salkia is under the jurisdiction of Golabari Police Station and Malipanchghara Police Station of Howrah City Police. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA). It comes under Howrah Uttar (Vidhan Sabha constituency). It has existed since the 19th century at least. The Postal code of Salkia is 711106. Location Salkia is located on the west bank of Hooghly River. Pilkhana is on its south, Liluah and Ghusuri are on its north and Bamangachi is on its west. Market and recreation Haragunge Bazaar is a century-old market, located at heart of North Howrah, on Aurobindo Road, Salkia. Aurobindo Road and Dobson Road are commercial streets in Salkia. Jelia Para Lane is one of the posh residential and commercial area of Salkia. Aurobindo Mall in Salkia (on Aurobindo Road) has a gross leasable area of 1.20 la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Bank Of India
The Reserve Bank of India, chiefly known as RBI, is India's central bank and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible for the control, issue and maintaining supply of the Indian rupee. It also manages the country's main payment systems and works to promote its economic development. Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran (BRBNM) is a specialised division of RBI through which it prints and mints Indian currency notes (INR) in two of its currency printing presses located in Nashik (Western India) and Dewas (Central India). RBI established the National Payments Corporation of India as one of its specialised division to regulate the payment and settlement systems in India. Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation was established by RBI as one of its specialised division for the purpose of providing insurance of deposits and guaranteeing of credit facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishan Kant
Krishan Kant (28 February 1927 – 27 July 2002) was an Indian politician who served as the tenth vice president of India from 1997 until his death 2002. Formerly, he was the governor of Andhra Pradesh from 1990 to 1997. He was a member of Lok Sabha from Chandigarh (1977-1980), and Member of Rajya Sabha from Haryana (1966-1972, 1972–1977). Early life Kant was born on 28 February 1927 in Kot Mohammad Khan a village of Tarn Taran district in the Punjab Province of British India. His parents were independence activists Lala Achint Ram and Satyavati Devi. Kant completed his MSc (Technology) from the Banaras Hindu University. He worked as a scientist with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi. Political career The son of noted Congress politician and later parliamentarian, Lala Achint Ram, Kant's first brush with politics came when he plunged into the Quit India movement, while he was still a student in Lahore. He took part in the Indian Independence Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice President Of India
The vice president of India (IAST: ) is the deputy to the head of state of the Republic of India, i.e. the president of India. The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the order of precedence and first in the line of succession to the presidency. The vice president is also a member of the Parliament of India as the ''ex officio'' chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Article 66 of the Constitution of India states the manner of election of the vice president. The vice president is elected indirectly by members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament and not the members of state legislative assembly by the system of proportional representation using single transferable votes and the voting is conducted by Election Commission of India via secret ballot. The vice president also acts as the chancellor of the central universities of India. Jagdeep Dhankhar of the Bharatiya Janata P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office from 25 July 2022. The office of president was created when India officially became a republic on 26 January 1950 after gaining independence on 15th August 1947, when its constitution came into force. The president is indirectly elected by an electoral college comprising both houses of the Parliament of India and the legislative assemblies of each of India's states and territories, who themselves are all directly elected by the citizens. Article 53 of the Constitution of India states that the president can exercise their powers directly or by subordinate authority (with few exceptions), though all of the executive powers vested in the president are, in practice, exercised by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
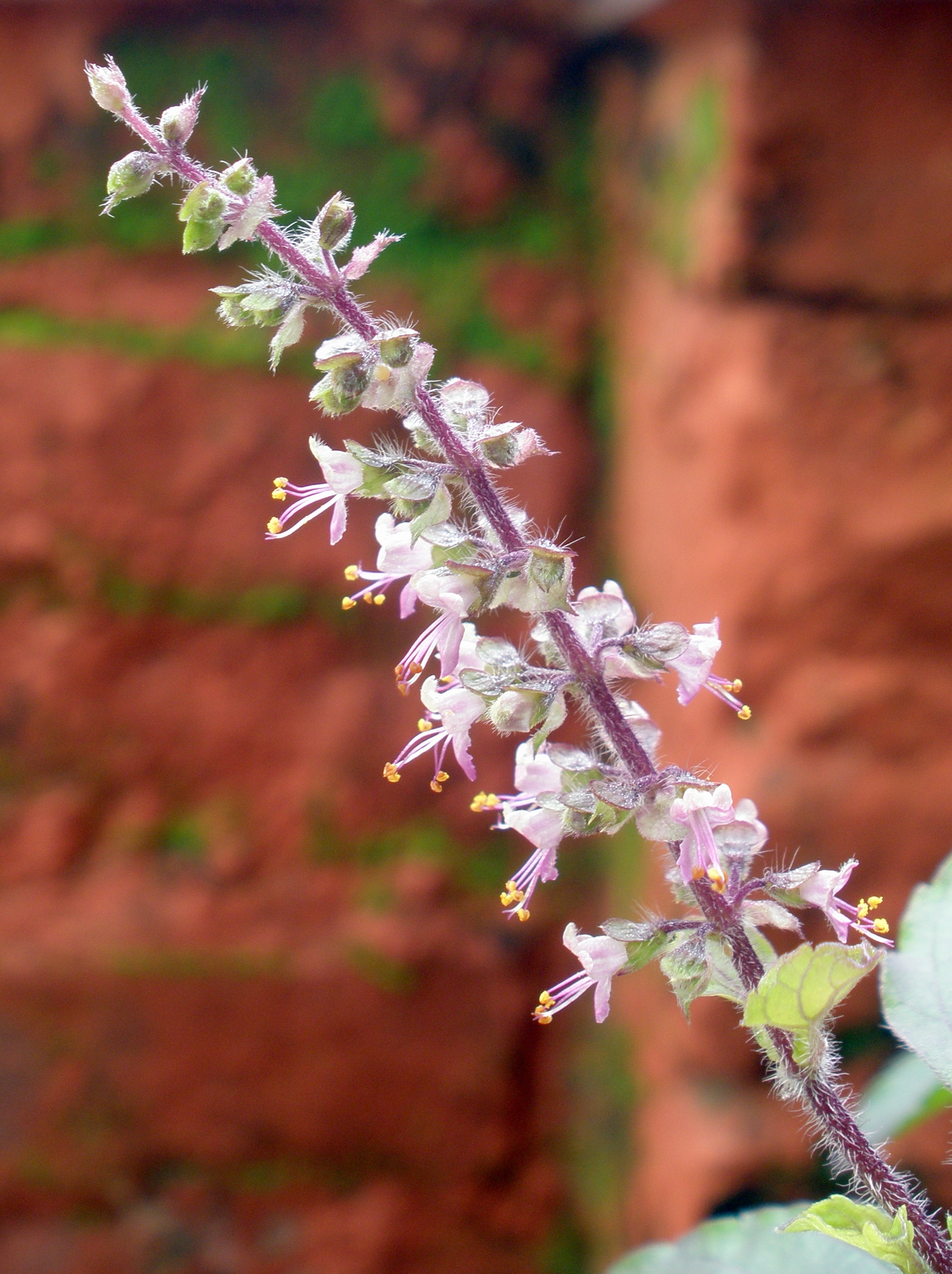
Tulsi 1998 Stamp Of India
''Ocimum tenuiflorum'', commonly known as holy basil, ''tulsi'' or ''tulasi'', is an aromatic perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and widespread as a cultivated plant throughout the Southeast Asian tropics. ''Tulsi'' is cultivated for religious and traditional medicine purposes, and also for its essential oil. It is widely used as a herbal tea, commonly used in Ayurveda, and has a place within the Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism, in which devotees perform worship involving holy basil plants or leaves. The variety of ''Ocimum tenuiflorum'' used in Thai cuisine is referred to as Thai holy basil ( th, กะเพรา ''kaphrao'') and is the key herb in phat kaphrao, a stir-fry dish; it is not the same as Thai basil, which is a variety of ''Ocimum basilicum''. In Cambodia, it is known as ''mreah-prov'' ( km, ម្រះព្រៅ). Morphology Holy basil is an erect, many-branched subshrub, tall with hairy stems. Leaves are gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |