|
Tulip System-1
The Tulip System I is a 16-bit personal computer based on the Intel 8086 and made by Tulip Computers, formerly an import company for the Exidy Sorcerer, called ''Compudata Systems''. Its Motorola 6845-based video display controller could display 80×24 text in 8 different fonts for supporting different languages, including a (Videotex-based) font for 2×3 pseudo graphic symbols for displaying 160×72 pixel graphics in text mode. The video display generator could also display graphics with a 384×288 or 768×288 (color) or 768×576 (monochrome) pixel resolution using its built-in NEC 7220 video display coprocessor, which had hardware supported drawing functions, with an advanced set of bit-block transfers it could do line generating, arc, circle, ellipse, ellipse arc, filled arc, filled circle, filled ellipse, filled elliptical arc and many other commands. Its memory can be upgraded in units of 128 KB up to 896 KB (much more than the 640 KB of the original PC). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulip Computers
Tulip Computers NV was a Dutch computer manufacturer that manufactured PC clones. History It was founded in 1979 as ''Compudata'', as an importer of American microcomputers. Compudata was the distributor for Europe for the Exidy Sorcerer, a Zilog Z80 based home computer. When Exidy gave up on the Sorcerer in 1979, Compudata licensed the design and manufactured them locally for several years. In 1983 it launched its own PC, the Tulip PC. To achieve 100% compatibility it simply copied the IBM PC, including the BIOS. IBM sued, and after years of litigation, Tulip and IBM settled out of court for an undisclosed amount in 1989. It was listed on the Amsterdam Stock Exchange in 1984. In 1987, Compudata changed its name to Tulip Computers. Tulip made headlines among Commodore computer enthusiasts when it acquired the Commodore brand name in September 1997, and made headlines again in 2003 and 2004, when it tried to grab a share of the games and entertainment markets with Commodore br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC 7220
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of things (IoT) platform, and telecommunications equipment and software to business enterprises, communications services providers and to government agencies, and has also been the biggest PC vendor in Japan since the 1980s when it launched the PC-8000 series. NEC was the world's fourth-largest PC manufacturer by 1990. Its semiconductors business unit was the world's largest semiconductor company by annual revenue from 1985 to 1992, the second largest in 1995, one of the top three in 2000, and one of the top 10 in 2006. NEC spun off its semiconductor business to Renesas Electronics and Elpida Memory. Once Japan's major electronics company, NEC has largely withdrawn from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Pascal
Microsoft Pascal is a discontinued implementation of the Pascal programming language developed by the Microsoft Corporation for compiling programs for running on its MS-DOS and Xenix operating systems and, in later versions, on OS/2 (like many other Microsoft programming tools, albeit they are only capable of generating 16-bit programs for the latter). Overview Microsoft Pascal version 1.0 was released in 1980. The last version of Microsoft Pascal to be released was version 4.0 in 1988, when Microsoft Pascal was superseded by Microsoft QuickPascal, a cheaper development tool that Microsoft produced in order to compete with Borland's Turbo Pascal. Microsoft Pascal was priced at , whereas QuickPascal was priced between , and the differences between the two were similar to those between Microsoft BASIC Professional Development System and Microsoft QuickBASIC. Unlike the ISO compliant Microsoft Pascal product, QuickPascal went after the ultimate compatibility with Turbo Pascal. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft BASIC
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer. During the home computer craze during the late-1970s and early-1980s, BASIC was ported to and supplied with many home computer designs. Slight variations to add support for machine-specific functions, especially graphics, led to a profusion of related designs like Commodore BASIC and Atari Microsoft BASIC. As the early home computers gave way to newer designs like the IBM Personal Computer and Macintosh, Apple Macintosh, BASIC was no longer as widely used, although it retained a strong following. The release of Visual Basic (classic), Visual Basic reboosted its popularity and it remains in wide use on Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WordStar
WordStar is a word processor application for microcomputers. It was published by MicroPro International and originally written for the CP/M-80 operating system, and later written also for MS-DOS and other 16-bit PC OSes. Rob Barnaby was the sole author of the early versions of the program. Starting with WordStar 4.0, the program was built on new code written principally by Peter Mierau. WordStar dominated the market in the early and mid-1980s, succeeding the market leader Electric Pencil. WordStar was written with as few assumptions as possible about the operating system and machine hardware, allowing it to be easily ported across the many platforms that proliferated in the early 1980s. Because all of these versions had relatively similar commands and controls, users could move between platforms with equal ease. It was already popular when its inclusion with the Osborne 1 portable computer made the program the ''de facto'' standard for much of the small computer word-processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the booting process (power-on startup). The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on an IBM PC or IBM PC compatible's system board and exists in some UEFI-based systems to maintain compatibility with operating systems that do not support UEFI native operation. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by some companies (such as Phoenix Technologies) looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a ''de facto'' standard. The BIOS in modern PCs initializes and tests the system hardware components (Power-on self-test), and loads a boot loader from a mass storage device which then ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8087
The Intel 8087, announced in 1980, was the first x87 floating-point coprocessor for the 8086 line of microprocessors. The purpose of the 8087 was to speed up computations for floating-point arithmetic, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. It also computed transcendental functions such as exponential, logarithmic or trigonometric calculations, and besides floating-point it could also operate on large binary and decimal integers. The performance enhancements were from approximately 20% to over 500%, depending on the specific application. The 8087 could perform about 50,000 FLOPS using around 2.4 watts. Only arithmetic operations benefited from installation of an 8087; computers used only with such applications as word processing, for example, would not benefit from the extra expense (around $150) and power consumption of an 8087. The 8087 was an advanced IC for its time, pushing the limits of manufacturing technology of the period. Initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT (model 5160, often shortened to PC/XT) is the second computer in the IBM Personal Computer line, released on March 8, 1983. Except for the addition of a built-in hard drive and extra expansion slots, it is very similar to the original IBM PC model 5150 from 1981. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of "XT" on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some publications expanded the term as "''eXtended Technology''" or just "''eXTended''". Features The XT was regarded as an incremental improvement over the PC and a disappointment compared to the next-generation successor that some had anticipated. Compared to the original IBM PC, the XT has the following major differences: * The number of expansion slots is increased from five to eight * Base RAM is increased to at least 128 KB * 2x32KB ROM ICs replace the previous 6x8KB ROM ICs * A 10 MB hard drive is included as standard equipment * PC DOS 2.0 is included * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
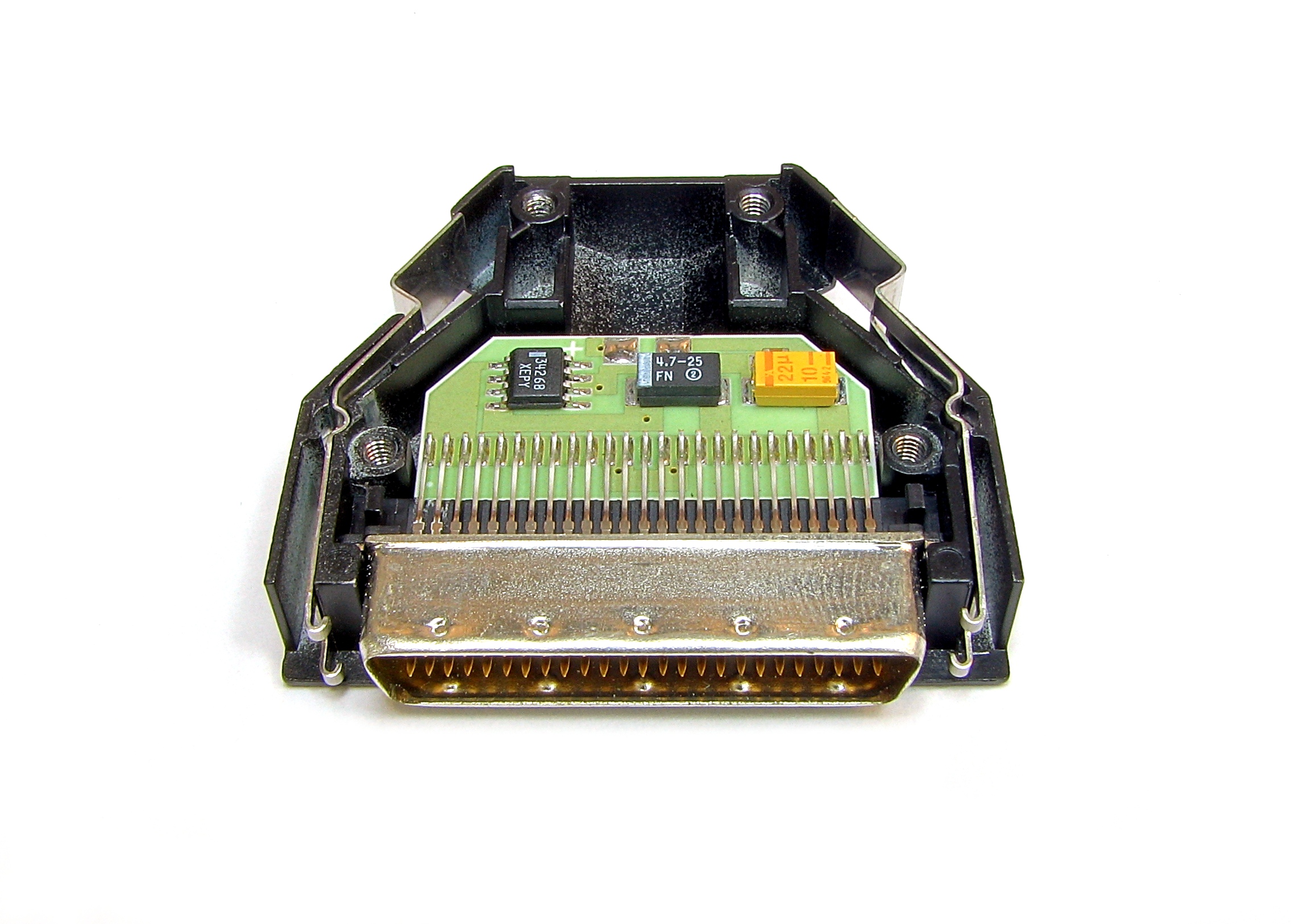
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shugart Associates System Interface
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)