|
Trzcianne
Trzcianne ( lt, Tžcianai) is a village in Mońki County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Trzcianne. It lies approximately south-west of Mońki and north-west of the regional capital Białystok. It is close to Biebrza National Park. The village has a population of 610. History First records of Trzcianne come from the 13th century. The name probably comes from reeds ( pl, trzcina) surrounding the river that flowed through the village. According to the records of Aleksander Jagiellon, Grand Duke of Lithuania, the first Catholic church in Trzcianne was built before 1496. It survived for ca. 100 years. The current, fourth church in Trzcianne was built in 1846 and consecrated in 1860. The vast majority of Trzcianne's population in the 20th century were Jewish.The first Jews arrived in Tzcianne in the 18th century. It was a shtetl, in the 1909 census, 98% of Trzcianne's population was Jewish. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Trzcianne
__NOTOC__ Gmina Trzcianne is a rural gmina (administrative district) in Mońki County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. Its seat is the village of Trzcianne, which lies approximately south-west of Mońki and north-west of the regional capital Białystok. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 4,701. Villages Gmina Trzcianne contains the villages and settlements of Boguszewo, Gmina Trzcianne, Boguszewo, Boguszki, Mońki County, Boguszki, Brzeziny, Podlaskie Voivodeship, Brzeziny, Budy, Mońki County, Budy, Chojnowo, Mońki County, Chojnowo, Dobarz, Giełczyn, Mońki County, Giełczyn, Gugny, Kleszcze, Podlaskie Voivodeship, Kleszcze, Korczak, Podlaskie Voivodeship, Korczak, Krynica, Mońki County, Krynica, Laskowiec, Podlaskie Voivodeship, Laskowiec, Milewo, Mońki County, Milewo, Mroczki, Mońki County, Mroczki, Niewiarowo, Nowa Wieś, Mońki County, Nowa Wieś, Pisanki, Stare Bajki, Stójka, Podlaskie Voivodeship, Stójka, Szorce, Trz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zubole
Zubole is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Trzcianne, within Mońki County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It lies approximately north-west of Trzcianne, south-west of Mońki, and north-west of the regional capital Białystok. History According to the 1921 census, the village was inhabited by 450 people, among whom 428 were Roman Catholic, 1 Orthodox, and 21 Mosaic. At the same time, 436 inhabitants declared Polish nationality, 14 Jewish. There were 81 residential buildings in the village.''Skorowidz miejscowości Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej: opracowany na podstawie wyników pierwszego powszechnego spisu ludności z dn. 30 września 1921 r. i innych źródeł urzędowych.'', t. T. 5, województwo białostockie, 1924, s. 17. During World War II, mass executions of Jews are perpetrated by Germans in Zubole. The Jews were kept in the gravel pit and then in a barn for almost a week before the series of shootings took place. From June 28 until July 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
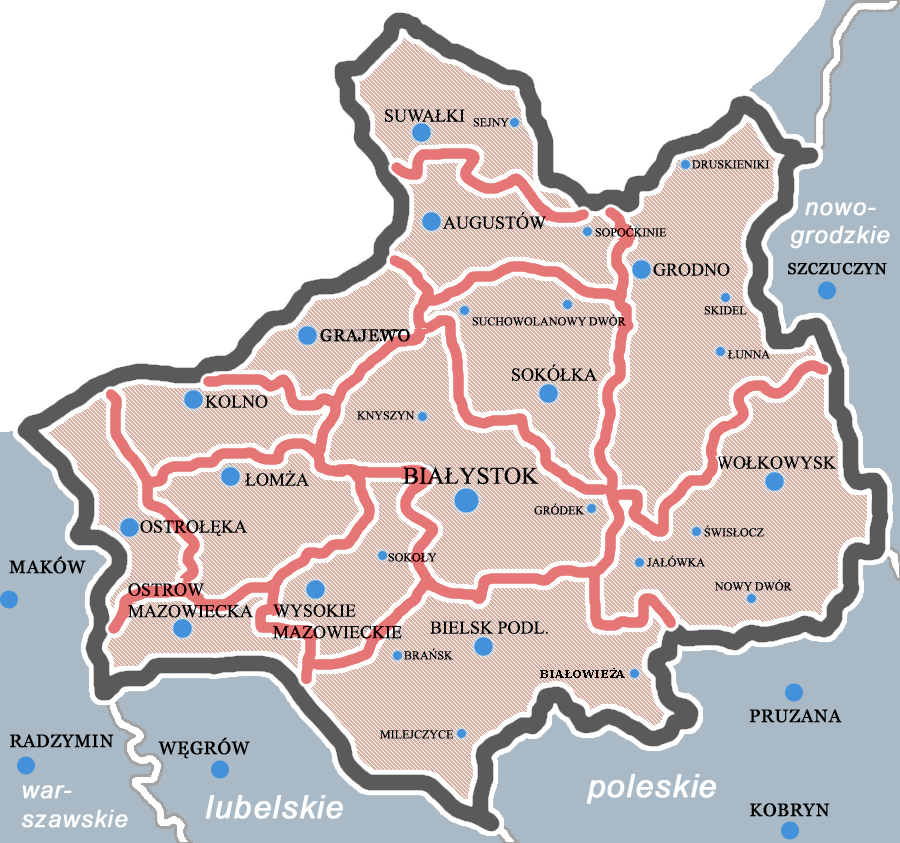
Mońki County
__NOTOC__ Mońki County ( pl, powiat moniecki) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, northeastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Mońki, which lies northwest of the regional capital Białystok. The county also contains the towns of Knyszyn, lying southeast of Mońki, and Goniądz, northwest of Mońki. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 40,518, out of which the population of Mońki is 9,986, that of Knyszyn is 2,748, that of Goniądz is 1,814, and the rural population is 25,970. Mońki County existed also between 1954 - 1975, but it was deleted after reform. Neighbouring counties Mońki County is bordered by Augustów County to the north, Sokółka County to the east, Białystok County to the south, Łomża County to the west and Grajewo County to the north-west. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belastok Region
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast ( be, Беластоцкая вобласць, Biełastockaja vobłasć, russian: Белостокская Область, pl, Obwód białostocki) was a short-lived territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) during World War II from September 1939 until Operation Barbarossa of 22 June 1941 and again for a short period in 1944. The administrative center of the newly created voblast was the pl, Białystok renamed Belastok ( be, Беласток). History Integration into the Soviet Union From 23 September to October 1939, the secretary of the central committee of the Belarusian SSR lived in Bialystok due to the protracted procedures for the transfer of the territories west of Bialystok by German troops to Białystok. While the leaders of provincial boards and were immediately established at the level of the Central Committee and the Military Front Council, the lower structures (poviat, gmina) were established "in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Białystok Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo białostockie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). The province's capital and its biggest city was Białystok with a population of over 91,000 people. Following the Nazi German and the Soviet invasion of Poland, the Voivodeship was occupied by both invading armies and divided according to Nazi-Soviet boundary treaty. Area and location In interwar Poland (1918–1939), Bialystok Voivodeship was located in the country's mid-northern part. It bordered Germany (East Prussia) to the north-west, Lithuania to the north-east, Wilno Voivodeship and Nowogródek Voivodeship to the east, Polesie Voivodeship and Lublin Voivodeship to the south and Warsaw Voivodeship to the west. Its area was 26 036 km². The landscape was flat, with the mighty Bialowieza Forest located right in the middle. Population Inhabited mostly by Poles (in 1931 they made up 66.9% of the population), it also had significant Belarusian (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belostoksky Uyezd , 0.2% Bashkir and 0.1% Lithuanian as their ...
Belostoksky Uyezd (''Белостокский уезд'') was one of the subdivisions of the Grodno Governorate of the Russian Empire. It was situated in the northwestern part of the governorate. Its administrative centre was Białystok. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Belostoksky Uyezd had a population of 206,615. Of these, 34.0% spoke Polish, 28.3% Yiddish, 26.1% Belarusian, 6.7% Russian, 3.6% German, 0.3% Ukrainian, 0.3% Chuvash, 0.3% Tatar The Tatars ()Tatar in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Mońki County
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviets
Soviet people ( rus, сове́тский наро́д, r=sovyétsky naród), or citizens of the USSR ( rus, гра́ждане СССР, grázhdanye SSSR), was an umbrella demonym for the population of the Soviet Union. Nationality policy in the Soviet Union During the history of the Soviet Union, different doctrines and practices on ethnic distinctions within the Soviet population were applied at different times. Minority national cultures were never completely abolished. Instead the Soviet definition of national cultures required them to be "socialist by content and national by form", an approach that was used to promote the official aims and values of the state. The goal was always to cement the nationalities together in a common state structure. In the 1920s and the early 1930s, the policy of national delimitation was used to demarcate separate areas of national culture and the policy of korenizatsiya (indigenisation) was used to promote federalism and strengthen non-Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekistan to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022. Almaty, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost Muslim-majority country by land area, and the ninth-largest country in the world. It has a population of 19 million people, and one of the lowest population densities in the world, at fewer than 6 people per square kilometre (15 people per square mile). The country dominates Central Asia economically and politically, generating 60 percent of the region's GDP, primarily through its oil and gas industry; it also has vast mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; around two-thirds of Europe's Jewish population. The murders were carried out in pogroms and mass shootings; by a policy of extermination through labor in concentration camps; and in gas chambers and gas vans in German extermination camps, chiefly Auschwitz-Birkenau, Bełżec, Chełmno, Majdanek, Sobibór, and Treblinka in occupied Poland. Germany implemented the persecution in stages. Following Adolf Hitler's appointment as chancellor on 30 January 1933, the regime built a network of concentration camps in Germany for political opponents and those deemed "undesirable", starting with Dachau on 22 March 1933. After the passing of the Enabling Act on 24 March, which gave Hitler dictatorial plenary powers, the government began isolating Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |