|
True Self
The true self (also known as real self, authentic self, original self and vulnerable self) and the false self (also known as fake self, idealized self, superficial self and pseudo self) are a psychological dualism conceptualized by English psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott. Winnicott used "true self" to denote a sense of self based on spontaneous authentic experience and a feeling of being alive, having a real self with little to no contradiction. "False self", by contrast, denotes a sense of self created as a defensive façade, which in extreme cases can leave an individual lacking spontaneity and feeling dead and empty behind an inconsistent and incompetent appearance of being real, such as in narcissism. Characteristics In his work, Winnicott saw the "true self" as stemming from self-perception in early infancy, such as awareness of tangible aspects of being alive, like blood pumping through veins and lungs inflating and deflating with breathing—what Winnicott called ''simply bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Winnicott
Donald Woods Winnicott (7 April 1896 – 25 January 1971) was an English paediatrician and psychoanalyst who was especially influential in the field of object relations theory and developmental psychology. He was a leading member of the British Independent Group of the British Psychoanalytical Society, President of the British Psychoanalytical Society twice (1956–1959 and 1965–1968), and a close associate of Marion Milner. Winnicott is best known for his ideas on the true self and false self, the "good enough" parent, and borrowed from his second wife, Clare Winnicott, arguably his chief professional collaborator, the notion of the transitional object. He wrote several books, including ''Playing and Reality'', and over 200 papers. Early life and education Winnicott was born on 7 April 1896 in Plymouth, Devon, to Sir John Frederick Winnicott and Elizabeth Martha, daughter of chemist and druggist William Woods, of Plymouth. Sir John Winnicott was a partner in the famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denial
Denial, in ordinary English usage, has at least three meanings: asserting that any particular statement or allegation is not true (which might be accurate or inaccurate); the refusal of a request; and asserting that a true statement is not true. In psychology, denialism is a person's choice to deny reality as a way to avoid a psychologically uncomfortable truth. In psychoanalytic theory, denial is a defense mechanism in which a person is faced with a fact that is too uncomfortable to accept and rejects it instead, insisting that it is not true despite what may be overwhelming evidence. The concept of denial is important in twelve-step programs where the abandonment or reversal of denial that substance dependence is problematic forms the basis of the first, fourth, fifth, eighth and tenth steps. People who are exhibiting symptoms of a serious medical condition sometimes deny or ignore those symptoms because the idea of having a serious health problem is uncomfortable or disturb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Foucault
Paul-Michel Foucault (, ; ; 15 October 192625 June 1984) was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationship between power and knowledge, and how they are used as a form of social control through societal institutions. Though often cited as a structuralist and postmodernist, Foucault rejected these labels. His thought has influenced academics, especially those working in communication studies, anthropology, psychology, sociology, criminology, cultural studies, literary theory, feminism, Marxism and critical theory. Born in Poitiers, France, into an upper-middle-class family, Foucault was educated at the Lycée Henri-IV, at the École Normale Supérieure, where he developed an interest in philosophy and came under the influence of his tutors Jean Hyppolite and Louis Althusser, and at the University of Paris (Sorbonne), where he earned degrees in philosophy and psychology. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Bertrand Pontalis
Jean-Bertrand Pontalis ibé(15 January 1924 – 15 January 2013) was a French philosopher, writer, editor and psychoanalyst. Career A student of Jean-Paul Sartre, Pontalis became a professor of philosophy in the forties, before undergoing an analysis with his associate Jacques Lacan the following decade. He was, however, one of the minority group of disciples/analysands who did not follow Lacan into the École Freudienne de Paris The École freudienne de Paris (EFP) was a French psychoanalytic professional body formed in 1964 by Jacques Lacan. It became 'a vital—if conflict-ridden—institution until its dissolution in 1980'. Early history In 1953 conflict within the ..., but rather stayed within the legitimist sphere as founding members of the Association Psychanalytique de France, of which he later became president. Together with Jean Laplanche, he wrote the influential work ''The Language of Psychoanalysis'' in 1967; while among his later, more literary writings we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
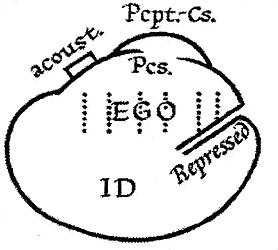
Id, Ego, And Super-ego
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neville Symington
Neville Symington (3 July 1937 - 3 December 2019) was a member of the Middle Group of British Psychoanalysts which argues that the primary motivation of the child is object-seeking rather than drive gratification. He published a number of books on psychoanalytic topics, and was President of the Australian Psychoanalytical Society from 1999 to 2002. Life and career Neville Symington was born in Portugal, and was a Catholic priest before becoming a psychoanalyst. He worked in England at the Tavistock Clinic, and the British Institute of Psycho-Analysis, before emigrating to Australia in 1986. On narcissism Symington was perhaps best known for his work on narcissism, which he considered to be the central psychopathology underlying all others. Symington introduced the concept of the 'lifegiver' as a kind of transitional object made up from the healthy part of the self combined with aspects of the motherer, and considered that narcissism emerged from the rejection of that object, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Rohr
Richard Rohr, (born 1943) is an American Franciscan priest and writer on spirituality based in Albuquerque, New Mexico. He was ordained to the priesthood in the Roman Catholic Church in 1970. In 2011, PBS called him "one of the most popular spirituality authors and speakers in the world". Life and ministry Rohr was born in Kansas in 1943. He received his Master of Theology degree in 1970 from the University of Dayton. He entered the Franciscans in 1961 and was ordained to the priesthood in 1970. Rohr founded the New Jerusalem Community in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1971 and the Center for Action and Contemplation (CAC) in Albuquerque, New Mexico, in 1986, where he serves as founding director and academic dean of the Living School for Action and Contemplation. The curriculum of Rohr's school is founded on seven themes developed by Rohr and explored in his book ''Yes, And....'' In his 2016 book ''The Divine Dance'', Rohr suggests that the top-down hierarchy of western Christianity s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Interpersonal World Of The Infant
''The Interpersonal World of the Infant'' (1985) is one of the most prominent works of psychoanalyst Daniel N. Stern, in which he describes the development of four interrelated senses of self. These senses of self develop over the lifespan, but make significant developmental strides during sensitive periods in the first two years of life. The mother or other primary attachment figure plays a critical role in helping the infant with this developmental process. Senses of self Emergent self At birth, the infant experiences the world as a barrage of seemingly unrelated sensory stimuli, which s/he gradually learns to "yoke" together using cues such as "hedonic tone" (emotional quality), and temporal and intensity patterns shared between stimuli. This process of integrating and organizing experience, called the emergent sense of self, continues until about two months. It serves as "the basis for the child's ability to learn and create," and is what Stern believes is the sense of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polly Young-Eisendrath
Polly Young-Eisendrath (born 1947) is an American psychologist, author, teacher, speaker, Jungian analyst, Zen Buddhist, and the founder of ''Dialogue Therapy'' and Real Dialogue' and creator of the podcast ''Enemies: From War to Wisdom''. She has been a featured speaker at the Aspen Ideas Festival, TED-X, and is the recipient of the Otto Weininger Award for Lifetime Achievement in Psychoanalysis. Young-Eisendrath is the originator of ''Dialogue Therapy'', designed to help couples and others transform chronic conflict into greater closeness and development. In 1983, she and her late husband, Ed Epstein, designed ''Dialogue Therapy'' as a new form of couples therapy that combined psychoanalysis, Jungian theory, psychodrama, and gender theory. She has published two books on ''Dialogue Therapy'' (1984 and 1993), detailing its theory and methods for clinicians and the general public. She has now re-visioned and updated ''Dialogue Therapy'' to include the distinctive combination of psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persona (psychology)
The persona, for Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, was the social face the individual presented to the world—"a kind of mask, designed on the one hand to make a definite impression upon others, and on the other to conceal the true nature of the individual." Jung's persona Identification According to Jung, the development of a viable social persona is a vital part of adapting to, and preparing for, adult life in the external social world. "A strong ego relates to the outside world through a flexible persona; identifications with a specific persona (doctor, scholar, artist, etc.) inhibits psychological development." For Jung, "the danger is that eoplebecome identical with their personas—the professor with his textbook, the tenor with his voice." The result could be "the shallow, brittle, conformist kind of personality which is 'all persona', with its excessive concern for 'what people think'"—an unreflecting state of mind "in which people are utterly unconscious of any distinctio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandiosity
In the field of psychology, the term grandiosity refers to an unrealistic sense of superiority, characterized by a sustained view of one's self as better than others, which is expressed by disdainfully criticising them (contempt), overinflating one's own capability and belittling them as inferior; and refers to a sense of personal uniqueness, the belief that few other people have anything in common with oneself, and that one can only be understood by a few, very special people. The personality trait of grandiosity is principally associated with narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), but also is a feature in the occurrence and expression of antisocial personality disorder, and the manic and hypomanic episodes of bipolar disorder. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fourth edition, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) American Psychiatric Association (2000) Narcissist-Grandiose (oblivious) Subtype Pathological grandiosity has been associated with one of the two subtype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confabulation
In psychology, confabulation is a memory error defined as the production of fabricated, distorted, or misinterpreted memories about oneself or the world. It is generally associated with certain types of brain damage (especially aneurysm in the anterior communicating artery) or a specific subset of dementias. While still an area of ongoing research, the basal forebrain is implicated in the phenomenon of confabulation. People who confabulate present with incorrect memories ranging from subtle inaccuracies to surreal fabrications, and may include confusion or distortion in the temporal framing (timing, sequence or duration) of memories. In general, they are very confident about their recollections, even when challenged with contradictory evidence. Description Confabulation is distinguished from lying as there is no intent to deceive and the person is unaware the information is false.Moscovitch M. 1995. "Confabulation". In (Eds. Schacter D.L., Coyle J.T., Fischbach G.D., Mesulum M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |