|
Trucheosaurus
''Trucheosaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhytidosteid temnospondyl from the Late Permian period of the Sydney Basin, New South Wales, Australia. It is known from the holotype materials MMF 12697a, a partially complete skull, AMF 50977, an articulated postcranial skeleton and BMNHR 3728, the counterpart of both skull and postcranial skeleton, recovered from the Glen Davis Formation. This genus was named by Watson in 1956, and the type species is ''Trucheosaurus major''. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... from Dias-da-Silva and Marsicano (2011): References Permian temnospondyls Prehistoric amphibians of Australia Paleontology in New South Wales Fossil taxa described in 1956 {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriceps
''Bothriceps'' is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl. It is a member of the infraorder Trematosauria and is the most basal brachyopomorph known. It is one of the only brachyopomorph that lies outside the superfamily Brachyopoidea, which includes the families Brachyopidae and Chigutisauridae. It shares several similarities to ''Keratobrachyops'', another basal brachyopomorph, and may be closely related to or even synonymous with it. The genus was named in 1859 by Thomas Henry Huxley with the description of its type species ''B. australis'' from the Early Triassic Upper Parmeener Group of Tasmania, Australia. It was originally assigned to the family Brachyopidae and was not reassigned to a more basal position until 2000, when the clade Brachyopomorpha was constructed to accommodate for it. The genus ''Bothriceps'' once included several species, but the only species assigned to it now is the type. ''Bothriceps major'', named in 1909, was reassigned to the family Rhytid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhytidosteidae
Rhytidosteidae is a family of Temnospondyli that lived in the Permian and Triassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... from Dias-da-Silva and Marsicano (2011): References *Yates, AM (2000), A new tiny rhytidosteid (Temnospondyli: Stereospondyi) from the Early Triassic of Australia and the possibility of hidden temnospondyl diversity. J. Vert Paleontol. 20:484-489. External linksRhytidosteidae at Palaeos. Stereospondyls Permian temnospondyls Triassic temnospondyls Amphibian families Lopingian first appearances Early Triassic extinctions {{Temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Permian
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * Late (album), ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch (album), Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * Late (song), "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * Late (The Handmaid's Tale), "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Laivateollisuus, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzocephalus
''Luzocephalus'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of Russia. It is usually regarded as a member of the family Lydekkerinidae, although it has also been placed in the family Trematosauridae Trematosauridae are a family of large marine temnospondyl amphibians with many members. They first appeared during the Induan age of the Early Triassic, and existed until around the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic, although by then they wer .... References Trematosaurines Fossils of Russia Triassic temnospondyls Fossil taxa described in 1935 {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosaurus
''Trematosaurus'' is an extinct genus of trematosaurid temnospondyl amphibian found in Germany and Russia. It was first named by Hermann Burmeister in 1849 and the type species is ''Trematosaurus brauni''. History of study ''Trematosaurus'' was one of the first temnospondyls to be described. The type locality, called Merkel's Quarry, is in east-central Germany at Bernburg an der Saale within the Bausandstein (Olenekian) and was collected for several decades from the 1840s into the early 20th century, producing extensive cranial remains, although the majority of these are preserved as internal molds (steinkerns) or natural molds. The name ''Trematosaurus'' was in fact coined in 1842 by Carl von Braun, a frequent collector who used the Greek suffix ''trema'' ('hole') in reference to the pineal foramen to form the generic epithet, but as he provided no formal description, the name was not considered valid until the work of Burmeister, who named the type species after Braun. Burm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosauria
Trematosauria is one of two major groups of temnospondyl amphibians that survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event, the other (according to Yates and Warren 2000) being the Capitosauria. The trematosaurs were a diverse and important group that included many medium-sized to large forms that were semi-aquatic to totally aquatic. The group included long-snouted forms such as the Trematosauroidea, trematosauroids and short, broad-headed forms such as the Metoposauridae, metoposaurs.Brusatte, S. L., Butler R. J., Mateus O., & Steyer S. J. (2015). A new species of Metoposaurus from the Late Triassic of Portugal and comments on the systematics and biogeography of metoposaurid temnospondyls. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. e912988., 2015: Although most groups did not survive beyond the Triassic, one lineage, the Brachyopoidea, brachyopoids, continued until the Cretaceous period. Trematosauria is defined as all Stereospondyli, stereospondyls more closely related to ''Trematosauru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydekkerina
''Lydekkerina'' is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl. It is the type genus of the family Lydekkerinidae. Fossils have been collected from Early Triassic deposits in South Africa and Australia. The type species is '' L. huxleyi'', first described in 1889. While most other stereospondyls were semiaquatic, ''Lydekkerina'' was exclusively terrestrial. Description ''Lydekkerina'' was a relatively small temnospondyl, growing up to around in length. Skulls range in length from in the smallest known individual to up to in larger individuals. The skull is wedge-shaped and has a parabolic outline with convex lateral margins. Shallow pits cover the surface of the skull. Teeth line the palate as well as the jaws, and some skulls even bear large ectopterygoid tusks on the underside of the skull. ''Lydekkerina'' can be distinguished from other lydekkerinids on the basis of several skull characteristics. One such feature is the presence of vomerine shagreen, tiny bumps cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapillopsis
''Lapillopsis'' is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Lapillopsidae. Fossils belonging to the genus have been found in the Arcadia Formation ( Rewan Group) of Queensland, Australia. History of study The type species and only known species is ''Lapillopsis nana,'' named in 1990 by Australian scientists Anne Warren and Mark Hutchinson. The name is derived from the Latin ''lapillus'' (pebble) and Greek -''opsis'' (appearance) in reference to the material of this species being collected from within small rocky nodules. There are two known specimens, both nearly complete skulls with associated mandibles and associated postcranial elements. An additional fourteen specimens from the same locality were described by Australian paleontologist Adam Yates in 1999. Anatomy ''Lapillopsis'' was differentiated from the closely related '' Rotaurisaurus'' from Australia by several features: (1) a deep, semi-elliptical otic notch; (2) an abbreviated posterior sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhytidosteus
''Rhytidosteus'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of South Africa. In 2019, the remains were also discovered in the Astrakhan region, Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig .... References Early Triassic amphibians of Africa Triassic amphibians Taxa named by Richard Owen Fossil taxa described in 1884 {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australerpeton
''Australerpeton'' is an extinct genus of stereospondylomorph temnospondyl currently believed to belong to the family Rhinesuchidae. When first named in 1998, the genus was placed within the new family Australerpetontidae. However, studies published a few years later questioned the systematics used in the original description and included the genus within Archegosauridae.Schoch, R. R. and Milner, A. R. (2000). ''Stereospondyli. Stem-stereospondyli, Rhinesuchidae, Rhytidostea, Trematosauroidea, Capitosauroidea''. Handbuch der paläoherpetologie Part 3B. 203p A study by Dias & Schultz (2003) reassigned ''Australerpeton'' to the family Rhinesuchidae within the suborder Stereospondyli based on an earlier evaluation of the family. In this study, the close similarities between ''Australerpeton'' and archegosaurids were attributed to convergent evolution as a result of similar semi-aquatic lifestyles. A redescription of the skeleton of this genus was published by Eltink & Langer in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineceps
''Rhineceps'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian in the family Rhinesuchidae. ''Rhineceps'' was found in Northern Malawi (formerly Nyasaland) in Southern Africa known only from its type species ''R. nyasaensis''. ''Rhineceps'' was a late Permian (256-258 Mya) semi-aquatic carnivore that lived in streams, rivers, lakes or lagoons. ''Rhineceps'' is an early divergent Stereopondyl within the family Rhinesuchidae, which only existed in the late Permian (Lopingian) and failed to survive the Permian-Triassic extinction unlike other stereospondyl families. History ''Rhineceps'' was originally discovered in the “Upper Bone Beds” of the Chiweta Beds, North Waller Area in Northern Malawi. The fossil was first described and named by Haughton in 1926, whereby he describes the fossil of a left mandibular ramus of ''R. nyasaensis'' as within the genus ''Rhinesuchus'' due to its similarity with the fossils of ''Rhinesuchus whaitsi.'' Watson later determined in a letter to P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
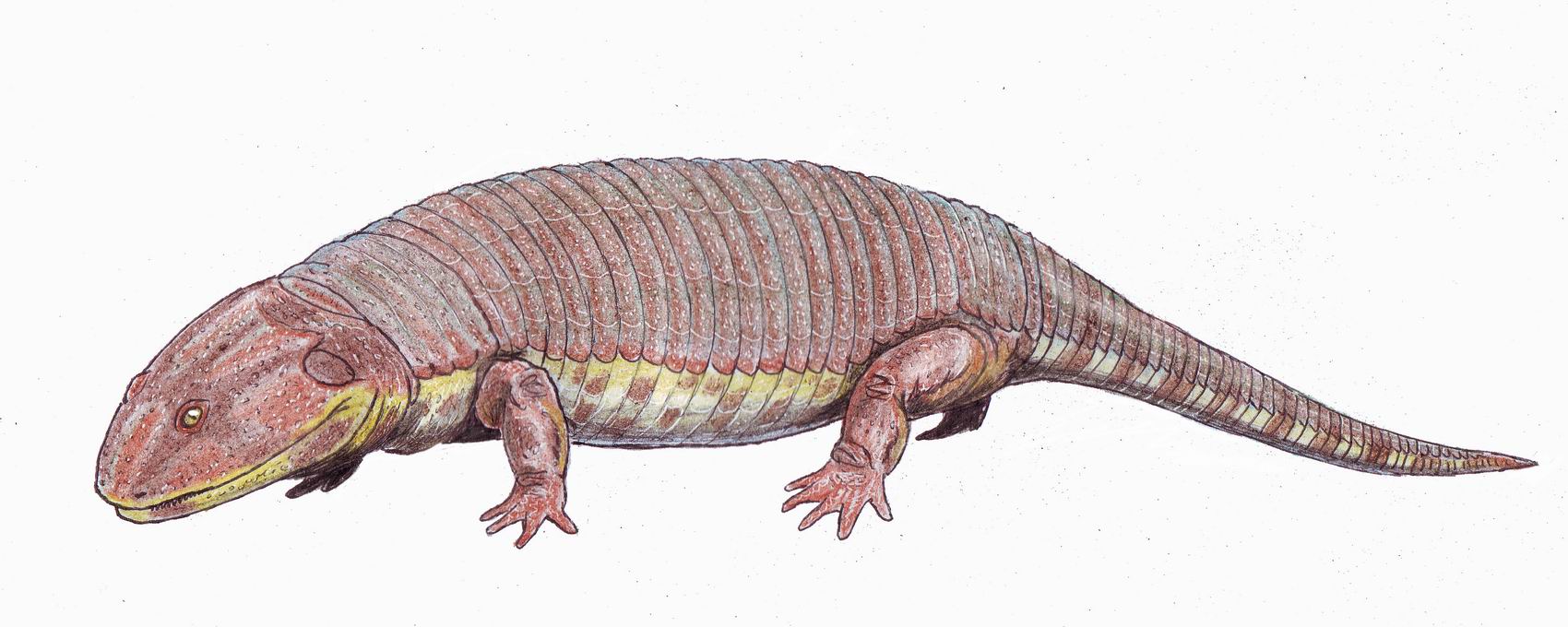
Peltobatrachus
''Peltobatrachus'' (from Greek ''pelte'', meaning shield and batrakhos, meaning frog) is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the late Permian period of Tanzania. The sole species, ''Peltobatrachus pustulatus'', is also the sole member of the family Peltobatrachidae. Description ''Peltobatrachus'' was a large, slow moving animal, up to in length. It was a fully terrestrial amphibian, only returning to the water to lay its eggs. To protect itself against predators such as the large gorgonopsid therapsids, it had developed an armadillo-like armored plating covering its body and tail. The armor consisted of broad plates on the shoulders and hips and narrower plates on the rest of the body. Although no teeth of the creature have been found, it probably fed on insects, worms, and snail A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |