|
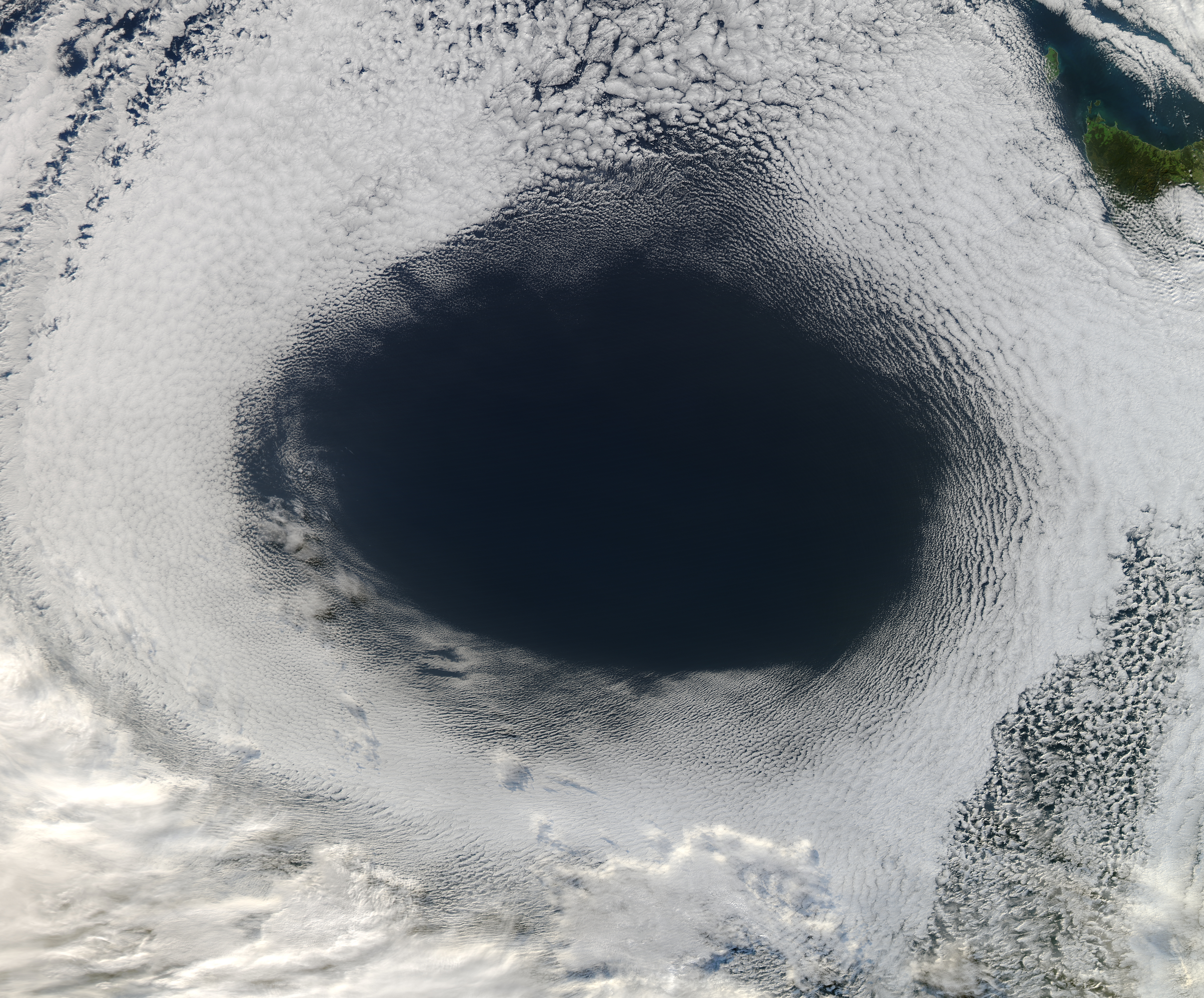
Tropical Storm Keith (1988)
Tropical Storm Keith struck the Continental United States later in the calendar year than any tropical cyclone since the 1925 Atlantic hurricane season. The nineteenth tropical depression and eleventh named storm of the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season, Keith developed out of a tropical wave in the Caribbean Sea on November 17. It tracked northwestward, and under generally favorable conditions, Keith reached a peak intensity of shortly before striking the northeastern tip of the Yucatán Peninsula. It turned northeastward in the Gulf of Mexico, and made landfall near Sarasota, Florida, on November 23. Keith accelerated its forward motion under the influence of a cold front, and became extratropical near Bermuda on November 24. The extratropical remnant persisted for two more days. Early in its duration, Keith produced moderate to heavy rainfall in Honduras, Jamaica, and Cuba. Minimal damage was reported in Mexico, which was still recovering from the effects of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern United States, Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
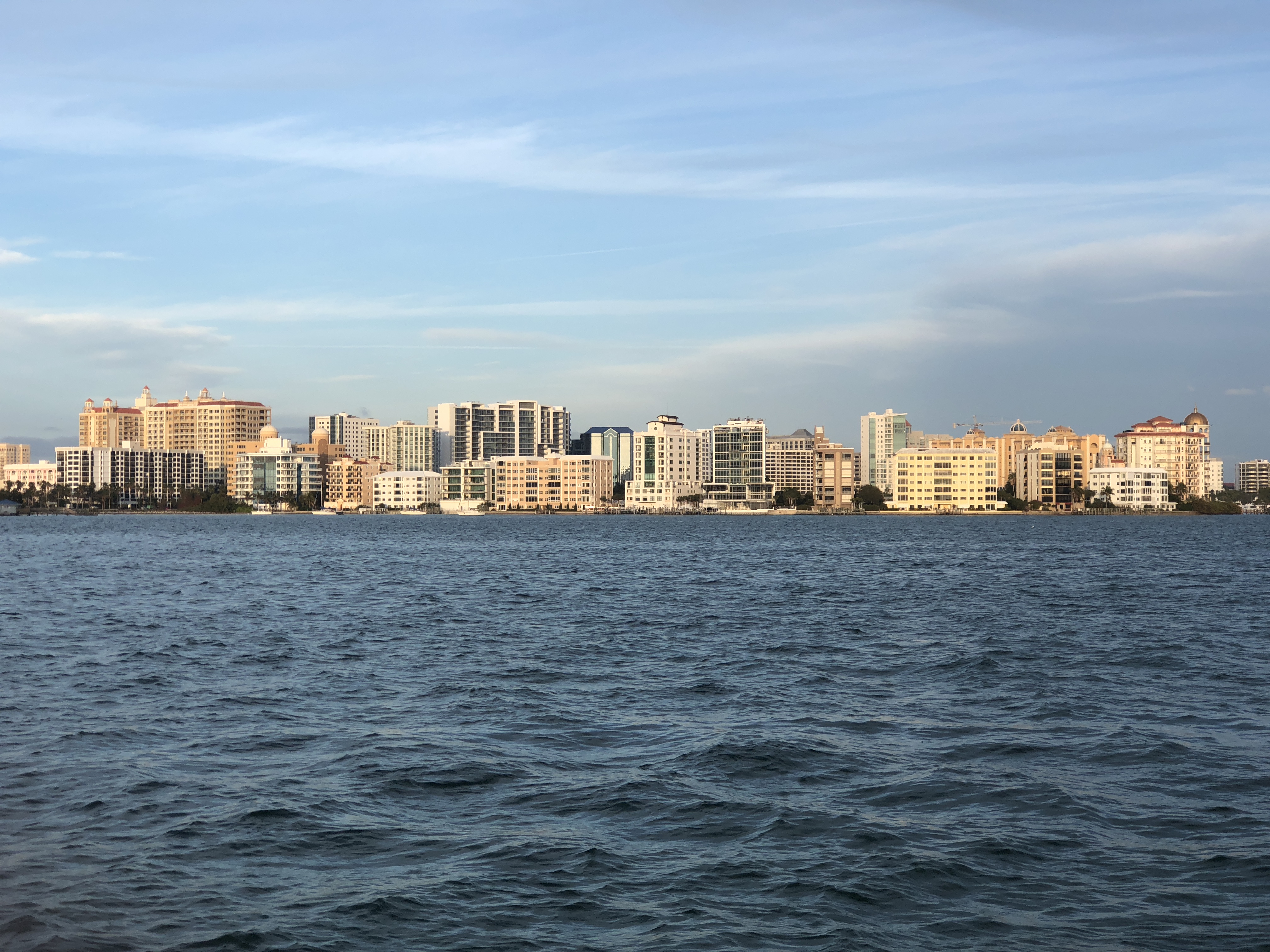
Sarasota, Florida
Sarasota () is a city in Sarasota County on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The area is renowned for its cultural and environmental amenities, beaches, resorts, and the Sarasota School of Architecture. The city is located in the southern end of the Greater Tampa Bay Area and north of Fort Myers and Punta Gorda. Its official limits include Sarasota Bay and several barrier islands between the bay and the Gulf of Mexico. Sarasota is a principal city of the Sarasota metropolitan area, and is the seat of Sarasota County. According to the 2020 U.S. census, Sarasota had a population of 54,842. The Sarasota city limits contain several keys, including Lido Key, St. Armands Key, Otter Key, Casey Key, Coon Key, Bird Key, and portions of Siesta Key. Longboat Key is the largest key separating the bay from the gulf, but it was evenly divided by the new county line of 1921. The portion of the key that parallels the Sarasota city boundary that extends to that new county line alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith (given Name)
Keith is a given name of Goidelic languages, Gaelic origin. It means "wood" or "from the battleground" and shares the same derivation as Clan Keith. The surname derives from a toponym, Keith Marischal in East Lothian, possibly containing the Brittonic languages, Brittonic element ''cet'' "woods, forest." Keith was the 298th most common name given to newborn boys in the United States in 2007. People with the given name *Keith Abbis (born 1932), English retired footballer *Keith Ablow (born 1961), American author and TV personality *Keith Ackerman (born 1946), American bishop *Keith Acton (born 1958), Canadian former ice hockey player *Keith Adams (other), several people *Keith Adamson (born 1945), English former footballer *Keith Agovida (born 1990), Filipino basketball player *Keith Ahlers (born 1955), British race car driver *Keith Aitken (born 1942), former Australian rugby league player *Keith Allan (actor) (born 1969), American actor and screenwriter *Keith Allan (lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure without a closed isobaric contour that would define it as a low pressure area. Since low pressure implies a low height on a pressure surface, troughs and ridges refer to features in an identical sense as those on a topographic map. Troughs may be at the surface, or aloft. Near-surface troughs sometimes mark a weather front associated with clouds, showers, and a wind direction shift. Upper-level troughs in the jet stream (as shown in diagram) reflect cyclonic filaments of vorticity. Their motion induces upper-level wind divergence, lifting and cooling the air ahead (downstream) of the trough and helping to produce cloudy and rain conditions there. Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a surface weather analysis chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked as a dashed line or bold line. In the UK, Hong Kong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection (meteorology)
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from abroad. The Chief, Aerial Reconnaissance Coordination, All Hurricanes (CARCAH) unit tasks planes, for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Observation
Tropical cyclone observation has been carried out over the past couple of centuries in various ways. The passage of typhoons, hurricanes, as well as other tropical cyclones have been detected by word of mouth from sailors recently coming to port or by radio transmissions from ships at sea, from sediment deposits in near shore estuaries, to the wiping out of cities near the coastline. Since World War II, advances in technology have included using planes to survey the ocean basins, satellites to monitor the world's oceans from outer space using a variety of methods, radars to monitor their progress near the coastline, and recently the introduction of unmanned aerial vehicles to penetrate storms. Recent studies have concentrated on studying hurricane impacts lying within rocks or near shore lake sediments, which are branches of a new field known as paleotempestology. This article details the various methods employed in the creation of the hurricane database, as well as reconstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process it redistributes the energy absorbed by the Earth's surface near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)