|
Tropical Peat
Tropical peat is a type of histosol that is found in tropical latitudes, including South East Asia, Africa, and Central and South America. Tropical peat mostly consists of dead organic matter from trees instead of spaghnum which are commonly found in temperate peat. This soils usually contain high organic matter content, exceeding 75% with dry low bulk density around . Areas of tropical peat are found mostly in South America (about 46% by area) although they are also found in Africa, Central America, Asia and elsewhere around the tropics. Tropical peatlands are significant carbon sinks and store large amounts of carbon and their destruction can have a significant impact on the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Tropical peatlands are vulnerable to destabilisation through human and climate induced changes. Estimates of the area (and hence volume) of tropical peatlands vary but a reasonable estimate is in the region of . Although tropical peatlands only cover about 0.25% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
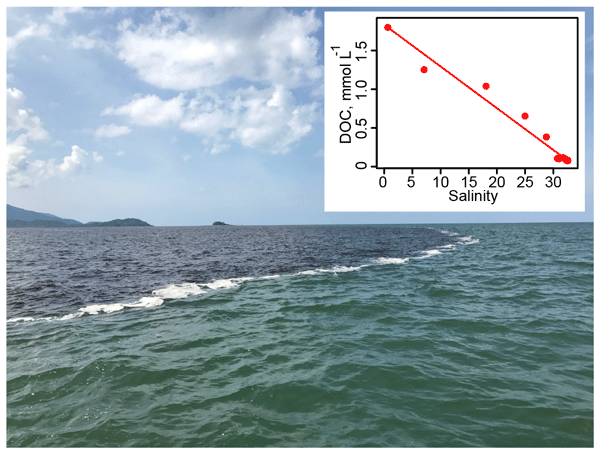
Interface Between Peatland Draining River Water And Coastal Waters
Interface or interfacing may refer to: Academic journals * ''Interface'' (journal), by the Electrochemical Society * ''Interface, Journal of Applied Linguistics'', now merged with ''ITL International Journal of Applied Linguistics'' * '' Interface: A Journal for and About Social Movements'' * ''Interfaces'' (journal), now ''INFORMS Journal on Applied Analytics'' Arts and entertainment * ''Interface'' (album), by Dominion, 1996 * Interface (band), an American music group * ''Interface'' (film), a 1984 American film * ''Interface'' (novel), by Stephen Bury (a pseudonym), 1994 * "Interface" (''Star Trek: The Next Generation''), an episode of the TV series * '' Interface series'', a science fiction horror story in short installments on Reddit Science, social science and technology Computing and electronics * Interface (computing), a shared boundary between system components ** Interface (Java) ** Interface (object-oriented programming) ** Application binary interface, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat Swamp Forests
Peat swamp forests are tropical moist forests where waterlogged soil prevents dead leaves and wood from fully decomposing. Over time, this creates a thick layer of acidic peat. Large areas of these forests are being logged at high rates. Peat swamp forests are typically surrounded by lowland rain forests on better-drained soils, and by brackish or salt-water mangrove forests near the coast. Tropical peatlands, which coexist with swamp forests within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, store and accumulate vast amounts of carbon as soil organic matter - much more than natural forests contain. Their stability has important implications for climate change; they are among the largest near-surface reserves of terrestrial organic carbon. Peat swamp forests, which have ecological importance, are one of the most threatened, yet least studied and most poorly understood biotypes. Since the 1970s, peat swamp forest deforestation and drainage have greatly increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedology
Pedology (from Greek: πέδον, ''pedon'', "soil"; and λόγος, ''logos'', "study") is a discipline within soil science which focuses on understanding and characterizing soil formation, evolution, and the theoretical frameworks for modeling soil bodies, often in the context of the natural environment. Pedology is often seen as one of two main branches of soil inquiry, the other being edaphology which is traditionally more agronomically oriented and focuses on how soil properties influence plant communities (natural or cultivated). In studying the fundamental phenomenology of soils, e.g. soil formation (aka pedogenesis), pedologists pay particular attention to observing soil morphology and the geographic distributions of soils, and the placement of soil bodies into larger temporal and spatial contexts. In so doing, pedologists develop systems of soil classification, soil maps, and theories for characterizing temporal and spatial interrelations among soils . There are a few note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat Swamp Forest
Peat swamp forests are tropical moist forests where waterlogged soil prevents dead leaves and wood from fully decomposing. Over time, this creates a thick layer of acidic peat. Large areas of these forests are being logged at high rates. Peat swamp forests are typically surrounded by lowland rain forests on better-drained soils, and by brackish or salt-water mangrove forests near the coast. Tropical peatlands, which coexist with swamp forests within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, store and accumulate vast amounts of carbon as soil organic matter - much more than natural forests contain. Their stability has important implications for climate change; they are among the largest near-surface reserves of terrestrial organic carbon. Peat swamp forests, which have ecological importance, are one of the most threatened, yet least studied and most poorly understood biotypes. Since the 1970s, peat swamp forest deforestation and drainage have greatly increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient carbon sink on the planet, because peatland plants capture carbon dioxide (CO2) naturally released from the peat, maintaining an equilibrium. In natural peatlands, the "annual rate of biomass production is greater than the rate of decomposition", but it takes "thousands of years for peatlands to develop the deposits of , which is the average depth of the boreal orthernpeatlands", which store around 415 gigatonnes (Gt) of carbon (about 46 times 2019 global CO2 emissions). Globally, peat stores up to 550 Gt of carbon, 42% of all soil carbon, which exceeds the carbon stored in all other vegetation types, including the world's forests, although it covers just 3% of the land's surface. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidise
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many state-owned by OPEC and Russia. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but it was consistent among all greenhouse gases (GHG). Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than ever before. Electricity generation and transport are major emitters; the largest single source, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, is transportation, accounting for 27% of all USA greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation and other changes in land use also emit carbon dioxide and methane. The largest source of anthropogenic methane emissions is agriculture, closely followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated deforestation occurs in tropical rainforests. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests at present. This is one-third less than the forest cover before the expansion of agriculture, a half of that loss occurring in the last century. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Bangladesh, are destroyed every year. On average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines deforestation as the conversion of forest to other land uses (regardless of whether it is human-induced). "Deforestation" and "forest area net change" are not the same: the latter is the sum of all forest losses (deforestation) and all forest gains (forest expansion) in a gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
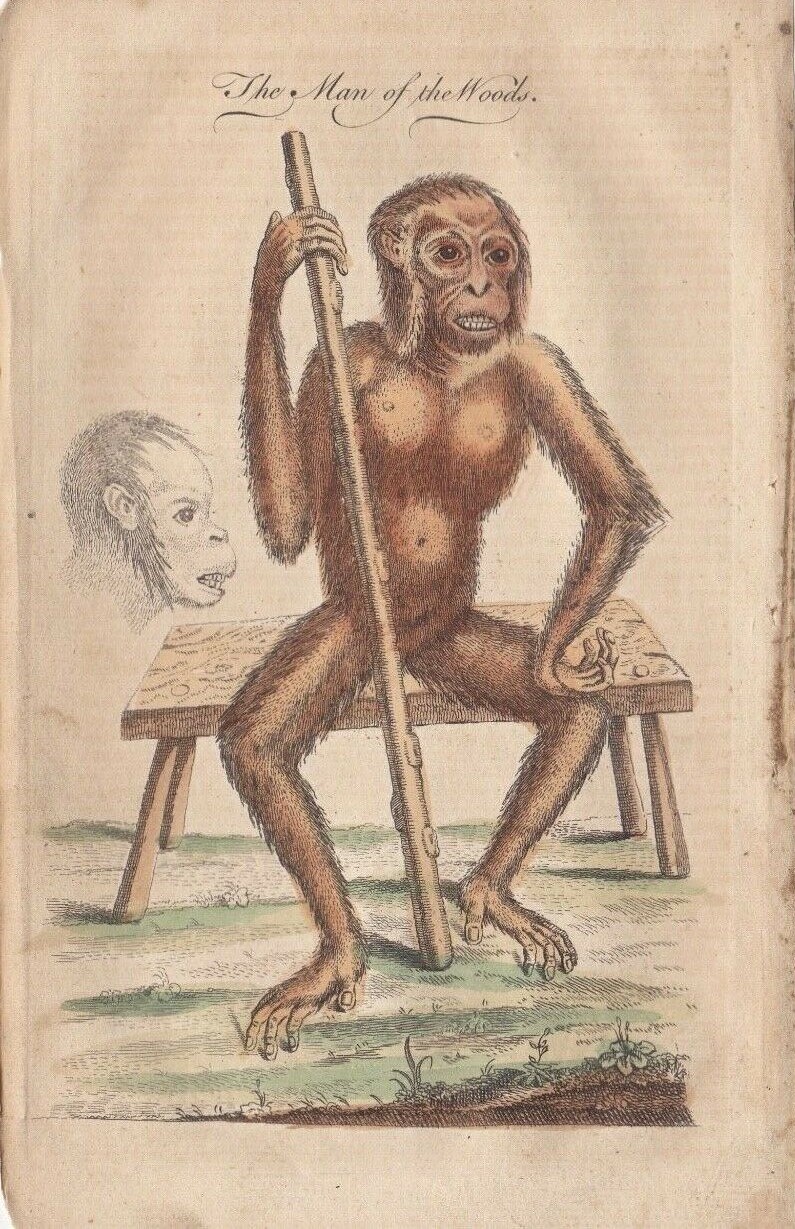
Orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genus ''Pongo'', orangutans were originally considered to be one species. From 1996, they were divided into two species: the Bornean orangutan (''P. pygmaeus'', with three subspecies) and the Sumatran orangutan (''P. abelii''). A third species, the Tapanuli orangutan (''P. tapanuliensis''), was identified definitively in 2017. The orangutans are the only surviving species of the subfamily Ponginae, which diverged genetically from the other hominids (gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans) between 19.3 and 15.7 million years ago. The most arboreal of the great apes, orangutans spend most of their time in trees. They have proportionally long arms and short legs, and have reddish-brown hair covering their bodies. Adult males weigh about , while female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histosol
In both the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) and the USDA soil taxonomy, a Histosol is a soil consisting primarily of organic materials. They are defined as having or more of organic soil material in the upper . Organic soil material has an organic carbon content (by weight) of 12 to 18 percent, or more, depending on the clay content of the soil. These materials include muck (sapric soil material), mucky peat (hemic soil material), or peat ( fibric soil material). Aquic conditions or artificial drainage are required. Typically, Histosols have very low bulk density and are poorly drained because the organic matter holds water very well. Most are acidic and many are very deficient in major plant nutrients which are washed away in the consistently moist soil. Histosols are known by various other names in other countries, such as peat or muck. In the Australian Soil Classification, Histosols are called Organosols. Histosols form whenever organic matter forms at a more r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



