|
Tropical Eosinophilia
Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia (TPE, tropical eosinophilia, or Weingarten's syndrome), is characterized by cough, bronchospasm, wheezing, abdominal pain, and an enlarged spleen. Occurring most frequently in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, TPE is a clinical manifestation of lymphatic filariasis, a parasitic infection caused by filarial roundworms that inhabit the lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, and bloodstream. Three species of filarial roundworms, all from the Onchocercidae family, cause human lymphatic filariasis: ''Wuchereria bancrofti'', ''Brugia malayi'', and ''Brugia timori''. Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia is a rare syndrome characterised by pulmonary interstitial infiltrates and marked peripheral eosinophilia. This condition is more widely recognised and promptly diagnosed in filariasis-endemic regions, such as the Indian subcontinent, Africa, Asia and South America. In nonendemic countries, patients are commonly thought to have bronchial asthma. Chronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release (degranulation) of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylatoxins. It causes difficulty in breathing which ranges from mild to severe. Bronchospasms occur in asthma, chronic bronchitis and anaphylaxis. Bronchospasms are a possible side effect of some drugs: pilocarpine, beta blockers (used to treat hypertension), a paradoxical result of using LABA drugs (to treat COPD), and other drugs. Bronchospasms can present as a sign of giardiasis. Some factors that contribute to bronchospasm include consuming certain foods, taking certain medicines, allergic responses to insects, and fluctuating hormone levels, particularly in women. Bronchospasms are one of several conditions associated with cold housing. The overactivity of the bronchioles' muscle is a result of exposure to a stimulus which under normal circumstances wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filariasis
Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type. These are spread by blood-feeding insects such as black flies and mosquitoes. They belong to the group of diseases called helminthiases. These parasites exist in the wild in subtropical parts of southern Asia, Africa, the South Pacific, and parts of South America. One does not acquire them in temperate areas like Europe or the United States. Eight known filarial worms have humans as a definitive host. These are divided into three groups according to the part of the body they affect: * Lymphatic filariasis is caused by the worms ''Wuchereria bancrofti'', ''Brugia malayi'', and ''Brugia timori''. These worms occupy the lymphatic system, including the lymph nodes; in chronic cases, these worms lead to the syndrome of ''elephantiasis''. * Subcutaneous filariasis is caused by ''Loa loa'' (the eye worm), ''Mansonella streptocerca'', and ''Onchocerca volvulus''. These worms occupy the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), with hundreds of millions infected worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host, before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongyloides
''Strongyloides'' (from Greek ''strongylos'', round, + ''eidos'', resemblance), anguillula, or threadworm is a genus of small nematode parasites, belonging to the family Strongylidae, commonly found in the small intestine of mammals (particularly ruminants), that are characterized by an unusual lifecycle that involves one or several generations of free-living adult worms. Human infection, strongyloidiasis, is caused by * ''Strongyloides stercoralis'', widespread in all tropical regions * '' Strongyloides fuelleborni'', a parasite of primates in African and Asian tropics and of humans in African tropics and New Guinea * '' Strongyloides papillosus,'' found in cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, rabbits, and rats * '' Strongyloides ransomi,'' found in pigs * '' Strongyloides ratti'', found in rats *'' Strongyloides myopotami'', found in coypu (nutria), causes dermatitis similar to strongyloidiasis. The condition is also called nutria itch. Treatment for strongyloides infection is iverm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune response by secreting immunomodulatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfilaria
::''Microfilaria may also refer to an informal "collective group" genus name, proposed by Cobbold in 1882. While a convenient category for newly discovered microfilariae which can not be assigned to a known species because the adults are unknown, it is seldom used today.'' The microfilaria (plural microfilariae, sometimes abbreviated mf) is an early stage in the life cycle of certain parasitic nematodes in the family Onchocercidae. In these species, the adults live in a tissue or the circulatory system of vertebrates (the "definitive hosts"). They release microfilariae into the bloodstream of the vertebrate host. The microfilariae are taken up by blood-feeding arthropod vectors (the "intermediate hosts"). In the intermediate host the microfilariae develop into infective larvae that can be transmitted to a new vertebrate host. The presence of microfilariae in the host bloodstream is called "microfilaraemia". The success of filariasis eradication programs is typically gauged by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
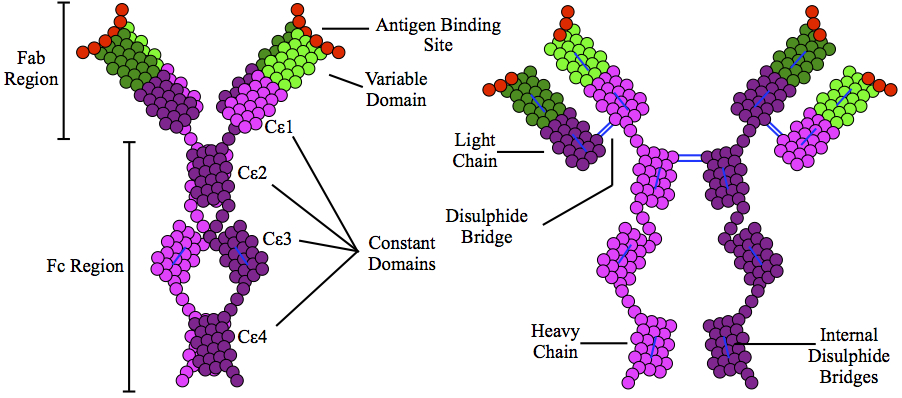
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isotype") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including ''Schistosoma mansoni'', ''Trichinella spiralis'', and ''Fasciola hepatica''. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as ''Plasmodium falciparum''. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms. IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity, which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, and specific types of chronic urticaria and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. They form about 2 to 3% of WBCs. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Criteria
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis. Diagnosis is often challenging because many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For example, redness of the skin (erythema), by itself, is a sign of many disorders and thus does not tell the healthcare professional what is wrong. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. This involves the correlation of various pieces of information followed by the recognition and differentiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |