|
Trolleybuses In Auckland
Trolleybuses in Auckland were part of the Auckland public transport system from 1938 until 1980. History On 19 December 1938, a one kilometre trolleybus route opened to service the Farmers Trading Company department store (now the Heritage Hotel) in Hobson Street, travelling via Queen, Wyndham, Hobson and Victoria Streets. It was operated by the Auckland Transport Board with four Leyland TB trolleybuses. In September 1949, a second route was introduced to Herne Bay. Between 1951 and 1961, further routes were added with the last trams replaced in 1956. The Meadowbank route closed in 1968, with the network contracting throughout the 1970s, with the last route ceasing on 26 September 1980. However the Auckland Regional Authority had placed an order for equipment to build a new system from Herne Bay to Newmarket prior to this. The proposal was abandoned in 1981 and the equipment, including 20 unused Volvo B10M bus chassis, was sold to Wellington.Trolley Buses ''Electric Tractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Street, Auckland
Queen Street is the major commercial thoroughfare in the Auckland CBD, Auckland, New Zealand's main population centre. The northern end is at Queens Wharf on the Auckland waterfront, adjacent to the Britomart Transport Centre and the Downtown Ferry Terminal. The road is close to straight, the southern end being almost three kilometres away in a south-southwesterly direction on the Karangahape Road ridge, close to the residential suburbs in the interior of the Auckland isthmus. Geography Named after Queen Victoria, Queen Street was an early development of the new town of Auckland (founded in 1840), although initially the main street was intended to be Shortland Street, running parallel to the shore of Commercial Bay. The early route of Queen Street led up the middle of a gully following the bank of the Waihorotiu Stream (later bounded in as the ' Ligar Canal'). This canal was culverted beneath the street from the 1870s onward, allowing for further development of the street to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit Australia
''Transit Australia'' was a Sydney based monthly magazine covering public transport in Australia and New Zealand New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count .... It was the in-house journal of the Australia Electric Traction Association. It was founded in 1946 as ''Tram Tracks'', being retitled ''Electric Traction'' in 1949 and ''Transit Australia'' in 1987. The final issue was published in June 2018. Transit Australia References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trolleybus Transport In New Zealand
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trolleyDunbar, Charles S. (1967). ''Buses, Trolleys & Trams''. Paul Hamlyn Ltd. (UK). Republished 2004 with or 9780753709702.) is an electric bus that draws power from dual overhead wires (generally suspended from roadside posts) using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires, and two trolley poles, are required to complete the electrical circuit. This differs from a tram or streetcar, which normally uses the track as the return path, needing only one wire and one pole (or pantograph). They are also distinct from other kinds of electric buses, which usually rely on batteries. Power is most commonly supplied as 600-volt direct current, but there are exceptions. Currently, around 300 trolleybus systems are in operation, in cities and towns in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Trolleybus Systems By City
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Park Royal Vehicles
Park Royal Vehicles was one of Britain's leading coachbuilders and bus manufacturers, based at Park Royal, Abbey Road, in west London. With origins dating back to 1889, the company also had a Leeds-based subsidiary, Charles H. Roe. Labour problems and slowness of production led to its closure in 1980.Ron Phillips. ''A History of the Leyland Bus'', Crowood Press, Ramsbury 2015. Associated Commercial Vehicles Associated with AEC from the 1930s in 1949 it became part of Associated Commercial Vehicles Ltd., which included AEC (the chassis manufacturer). This formidable combination of AEC and PRV supported the demanding requirements of London Transport and many other major fleet owners and operators. The famous AEC Routemaster bus was built at Park Royal. Leyland Motors In 1962 the ACV Group merged with the Leyland Motors group to form Leyland Motor Corporation. In 1968 Leyland Motor Corporation and British Motor Holdings merged, becoming British Leyland Motor Corporation. BL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders-Roe
Saunders-Roe Limited, also known as Saro, was a British aero- and marine-engineering company based at Columbine Works, East Cowes, Isle of Wight. History The name was adopted in 1929 after Alliott Verdon Roe (see Avro) and John Lord took a controlling interest in the aircraft and boat-builders S. E. Saunders. Prior to this (excepting for the Sopwith/Saunders Bat Boat) the products were Saunders, the A4 Medina for example dating from 1926. Sam Saunders the founder developed the Consuta material used in marine and aviation craft. The Saunders-Roe interest in aviation didn’t prevent the firm from continuing with the boatbuilding activities associated with S. E. Saunders Ltd Saunders Roe concentrated on producing flying-boats, but none were produced in very large quantities – the longest run being 31 Londons. They also produced hulls for the Blackburn Bluebird. During the Second World War Saro manufactured Supermarine Walrus and Supermarine Sea Otters. Their works at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BUT RETB/1
The BUT RETB/1 was a two-axle single deck trolleybus chassis manufactured by British United Traction between 1950 and 1964. Glasgow purchased one in 1950, followed by two batches of 10 in 1952 and 1958.; 18 units were bought for Montevideo, Uruguay for the first trolleybus lines of the municipal operator AMDET, these trolleybuses were finally scrapped in 1976 with the dissolution of AMDET. These buses ran on two New Zealand networks. Wellington purchased 109, the last 38 being assembled by Scammell's Watford plant in 1964. Dunedin initially ordered 31, its fleet growing to 79. Both trolleybus networks in Tasmania used this vehicle: Hobart Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-small ... ordered 38 and Trolleybuses in Launceston, Tasmania, Launceston ordered 30. Copenhagen place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metro Cammell Weymann
Metro Cammell Weymann Ltd. (MCW) was once a major contributor in transportation manufacturing in the UK and Europe. It was established in 1932 by Metro-Cammell's bus bodybuilding division and Weymann Motor Bodies to produce bus bodies. MCW bus bodies were built in Metro-Cammell's and Weymann's factories until 1966 when Weymann's factory in Addlestone was closed (the Metro-Cammell and Weymann brand names were discontinued in the same year). From 1977 onward MCW also built bus chassis. In 1989 the Laird Group decided to sell its bus and rail divisions. No buyer for all of the subdivisions could be found so each product was sold separately to various companies interested in its assets. The Metrorider was bought by Optare who relaunched it as the MetroRider; the Metrobus design was bought by DAF (chassis) and Optare (body), who jointly reworked it into the Optare Spectra. The Metroliner design was acquired by Optare though not pursued. The Metrocab was bought by Reliant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British United Traction
British United Traction (BUT) was a manufacturer of railway equipment and trolleybuses. It was established in 1946 as a joint venture between AEC and Leyland. History British United Traction was established in 1946 when AEC and Leyland amalgamated their trolleybus interests. Neither had produced trolleybuses since early years of World War II. With both forecasting that demand would return to pre-war levels as networks began to close, a joint venture was formed. The new company was organised so that AEC would design and produce vehicles for the UK market while Leyland looked after export markets, although there were some exceptions to this. The only noticeable difference between the manufacturers output was the wheels. Initially vehicles were produced at Leyland's Ham, London factory, with the first vehicles completed in 1947 for Johannesburg. After the factory closed 1948, production moved to AEC's Southall and Leyland's Leyland, Lancashire factories. Following AEC's acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
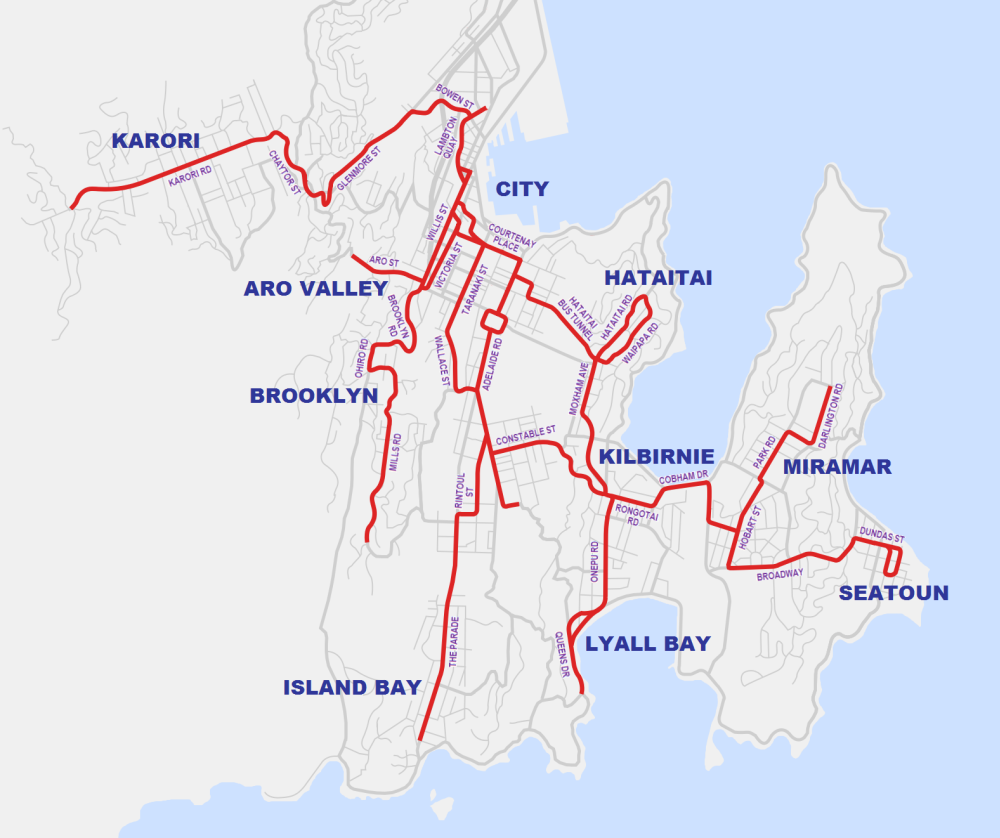
Trolleybuses In Wellington
Trolleybuses in Wellington were part of the Wellington public transport system from 1924 until 1932 and again from 1949 until 2017. It was the last trolleybus system operating commercially in Oceania and the last major system operating in a country where driving is on the left side of the road. History First era On 29 September 1924 the first trolleybus route was inaugurated with a single AEC 602 trolleybus running from Thorndon along Hutt Road to Kaiwharawhara (then known as Kaiwarra).A Brief History The Wellington Trolley Bus PageBlee, Ian (November 1978). "Under Two Wires in New Zealand, Part 3 – Wellington". ''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 103, pp. 137–140. National Trolleybus Association (UK). . A trolleybus was chosen over an extension to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |