|
Trolleybuses In South Lancashire
The South Lancashire trolleybus system once served towns in South Lancashire, England, including Atherton, Bolton, Swinton and Leigh (all now in Greater Manchester) and St Helens (now in Merseyside). Opened on , it replaced the South Lancashire Tramways network. By the standards of the various now-defunct trolleybus systems in the United Kingdom, the South Lancashire system was of medium size, with four routes and a maximum fleet of 71 trolleybuses. It was closed on . None of the former South Lancashire trolleybuses has been preserved. History and background Trackless trolleybuses were first considered in 1922 by the independent South Lancashire Tramways Company - a subsidiary company of the Lancashire United Transport and Power Company - as substitute vehicles for its tramcar fleet. However the manager of the undertaking Mr E H Edwardes found the trackless trolleybuses of the time slow and rough-riding and deemed them unsuitable. By 1928 infrastructure renewals on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and keep clear of platforms, trackside buildings and structures. Classification systems vary between different countries, and gauges may vary across a network, even if the track gauge is uniform. The term loading gauge can also be applied to the maximum size of road vehicles in relation to tunnels, overpasses and bridges, and doors into automobile repair shops, bus garages, filling stations, residential garages, multi-storey car parks and warehouses. A related but separate gauge is the structure gauge, which sets limits to the extent that bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure can encroach on rail vehicles. The difference between these two gauges is called the clearance. The specified amount of clearance makes allowance for wobbling of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for International Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of all matters relating to Trade and Foreign Plantations, but is commonly known as the Board of Trade, and formerly known as the Lords of Trade and Plantations or Lords of Trade, and it has been a committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. The board has gone through several evolutions, beginning with extensive involvement in colonial matters in the 17th century, to powerful regulatory functions in the Victorian Era and early 20th century. It was virtually dormant in the last third of 20th century. In 2017, it was revitalised as an advisory board headed by the International Trade Secretary who has nominally held the title of President of the Board of Trade, and who at present is the only privy counsellor of the board, the other m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexborough And Swinton Traction Company
The Mexborough and Swinton Traction Company was the name adopted by the Mexborough & Swinton Tramways Company in 1929 following the introduction of trolleybuses on all its routes. It operated in the West Riding of Yorkshire, England, over routes serving Manvers Main Colliery, Wath upon Dearne and the towns of Rotherham, Rawmarsh, Swinton, Mexborough, Conisbrough and the estate at Conanby. The first opening took place in 1907 and was owned by the National Electric Construction Co., becoming part of the British Electric Traction Group in 1931. History A tramway connecting Rotherham, Mexborough, Swinton and Denaby had been authorised by an Act of Parliament obtained in 1902. It was constructed by the National Electric Construction Co Ltd, and operated by its subsidiary, the Mexborough and Swinton Tramways Company, from its opening in 1907, with the private company running its trams over Rotherham Corporation's tracks at the Rotherham end. The company's first attempt at rail-less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindley, Greater Manchester
Hindley is a town within the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan in Greater Manchester, England. Lying east of Wigan it covers an area of . Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, Hindley (which includes Hindley Green) borders the towns and villages of Ince-in-Makerfield, Aspull, Westhoughton, Atherton and Westleigh in the former borough of Leigh. In 2001, Hindley had a population of 23,457, increasing to 28,000 at the 2011 Census. It forms part of the wider Greater Manchester Urban Area. History Toponymy The name Hindley is derived from the Old English ''hind'' and ''leah'', meaning a "clearing frequented by hinds or does". The town is first recorded as ''Hindele'' in 1212 and then variously as "Hindeleye" 259 "Hyndeley" 285 and 1332''Hindelegh'' 301 "Hyndelegh" 303 and 1375 The first recorded use of its current spelling, Hindley, was in 1479. Early history Hindley was one of 15 berewicks of the royal manor of Newton before the Norman conquest in 1066. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boothstown
Boothstown is a suburban village in the City of Salford in Greater Manchester, England. Boothstown forms part of the Boothstown and Ellenbrook ward, which had a population at the 2011 Census of 9,599. The village is within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, west of the City of Salford, bordered to the north by the East Lancashire Road A580 and to the south by the Bridgewater Canal. Historically, it was a hamlet partly in Worsley township in the parish of Eccles, and partly in Tyldesley in the parish of Leigh. Boothstown lies northwest of Salford, northwest of Manchester and southeast of Wigan. Astley is to the west, to the north is Walkden and to the east is Worsley where there is a transport interchange between the M60, M62 and M602 motorways. Once known for its mining community, Boothstown is now a mainly residential area. History Evidence of the Romans in this area is that in 1947, workmen digging in Boothstown at discovered a hoard of over 550 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyldesley
Tyldesley () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan in Greater Manchester, England. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, it is north of Chat Moss near the foothills of the West Pennine Moors, southeast of Wigan and northwest of Manchester. At the United Kingdom Census 2001, the Tyldesley built-up area, excluding Shakerley, had a population of 16,142. The remains of a Roman road passing through the township on its ancient course between ''Coccium'' (Wigan) and ''Mamucium'' (Manchester) were evident during the 19th century. Following the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain, Tyldesley was part of the manor of Warrington, until the Norman conquest of England, when the settlement constituted a township called Tyldesley-with-Shakerley in the ancient parish of Leigh. The factory system and textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution triggered population growth and urbanisation, and by the early 20th century it was said that the mill town was "em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worsley
Worsley () is a village in the City of Salford, Greater Manchester, England, which in 2014 had a population of 10,090. It lies along Worsley Brook, west of Manchester. Within the boundaries of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire, there is evidence of Roman Britain, Roman and Anglo-Saxon activity, including two Roman roads. The completion in 1761 of the Bridgewater Canal allowed Worsley to expand from a small village of cottage industry, cottage industries to an important town based upon cotton manufacture, iron-working, brick-making and extensive coal mining. Later expansion came after the First World War, First and Second World Wars, when large urban estates were built. Worsley Delph is a scheduled monument and a significant part of the town's historic centre is now a conservation area. History Toponymy Worsley is first mentioned in a Pipe roll of 1195–96 as ''Werkesleia'', in the claim of a Hugh Putrell to a part of the fee of two knights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkden
Walkden is a town in the City of Salford in Greater Manchester, England, northwest of Salford, and of Manchester. Historically in the township of Worsley in Lancashire, Walkden was a centre for coal mining and textile manufacture. In 2014, the electoral wards of Walkden North, Walkden South and Little Hulton had a combined population of 35,616. History The name Walkden or ''Walkeden'' derives from the Old English ''denu'', a valley, belonging to a man possibly called Wealca ( fuller), an Old English personal name. It has been in existence since at least the 13th century. The name was recorded in documents dating to 1246. In the local dialect and accent, it is pronounced Wogden. A Roman road crossed the area roughly on the line of the present A6 road through Walkden and Little Hulton. In 1313, in a dispute involving land, a jury decided that Walkden was too small to be considered a hamlet or a town but was "only a place in Farnworth". In the 15th century Walkden appears t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosley Common
Mosley Common is a suburb of Tyldesley at the far-eastern edge of the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, in Greater Manchester, England. Historically part of Lancashire, it was anciently a hamlet in the east of the township of Tyldesley cum Shakerley, in the ancient parish of Leigh. The area of Mosley Common in 1747 was statute s. History The original name for the area was Hurst or Tyldesleyhurst (hyrst is Old English for "wooded hill") It was called Mosseld Yard in 1301. Mosley the clearing on mossy ground. In 1695 the Common was part of the Tyldesley Manor. In 1698 Parr Bridge or Mosley Bridge was rebuilt in stone Industry In 1831 R. Worthington of Mosley Common built a weaving shed with 60 pairs of looms.Lunn (1995), p. 80. Parr Bridge Mill built in 1859 was a weaving shed, it had several owners and continued working into the 1950s. In 1838 City Pit and Gatley Pit owned by the Bridgewater Trustees at New Manchester not far from the border with Worsley were working, New Manche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
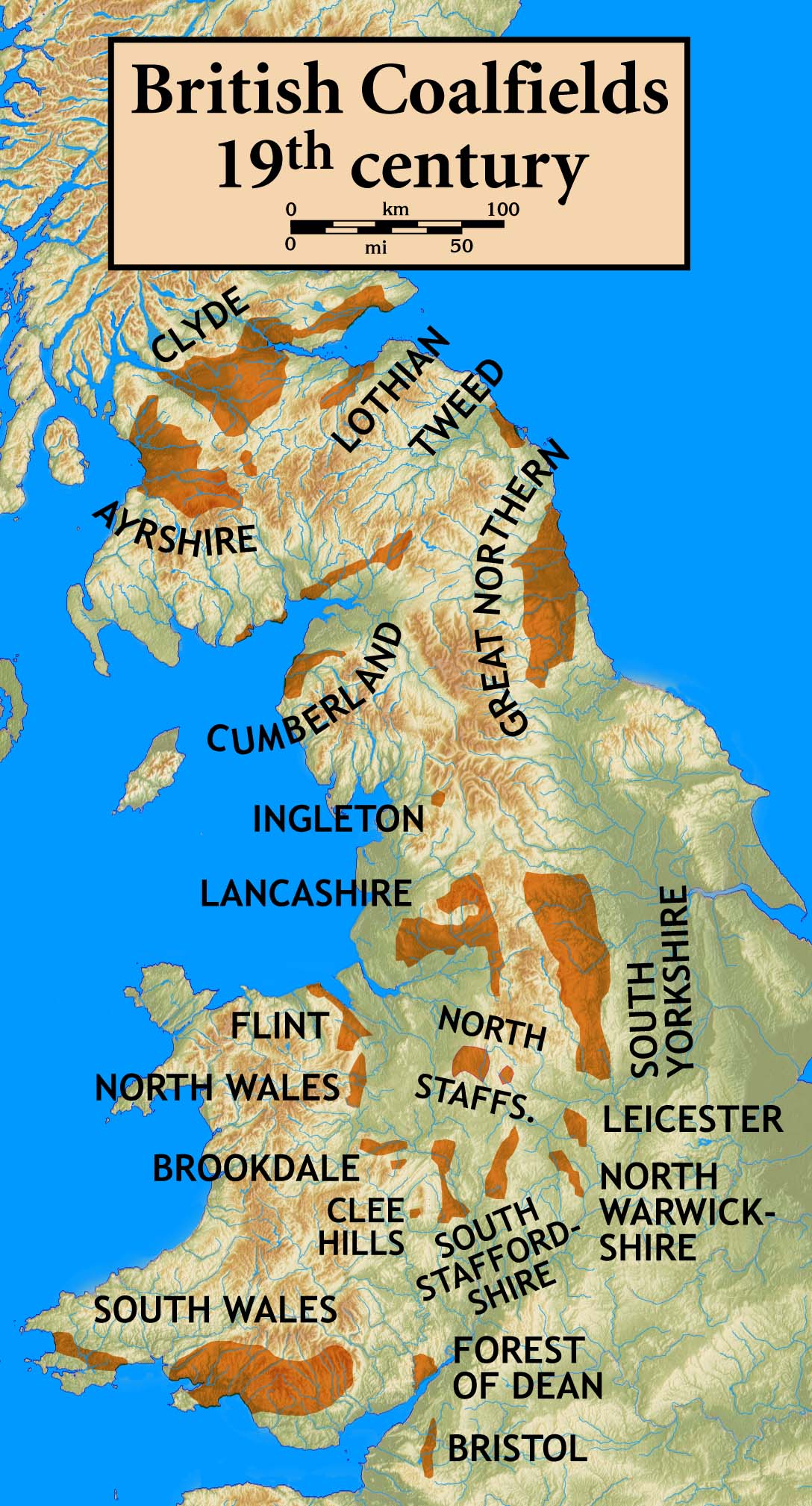
Lancashire Coalfield
The Lancashire Coalfield in North West England was an important British coalfield. Its coal seams were formed from the vegetation of tropical swampy forests in the Carboniferous period over 300 million years ago. The Romans may have been the first to use coal in Lancashire and its shallow seams and outcrops were exploited on a small scale from the Middle Ages and extensively after the start of the Industrial Revolution. The coalfield was at the forefront of innovation in coal mining, prompting the country's first canals, use of steam engines and creating conditions favourable for rapid industrialisation. The pits on the coalfield were at their most productive in 1907 when more than 26 million tons of coal were produced. By 1967 just 21 collieries remained. Parkside Colliery in Newton-le-Willows, St. Helens area, the last deep mine to be sunk on the coalfield, was closed in 1993. Geology The geology of the coalfield consists of the coal seams of the Upper, Middle and Lower Coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farnworth
Farnworth is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Bolton, Greater Manchester, England, southeast of Bolton, 4.3 miles south-west of Bury (7 km), and northwest of Manchester. Historically in Lancashire, Farnworth lies on the River Irwell and River Croal. At the 2011 Census, it had a population of 26,939. History Toponymy Farnworth derives from the Old English ''fearn'', fern and ''worth'' an enclosure. Farnworth was recorded as Farneworth and Farnewrth in 1278 and 1279 and Ffornword in a land survey of 1282. Middle Ages Farnworth was originally a hamlet in Barton. In the 13th century it was held by the Lords of Barton and Manchester. By 1320 Adam Lever, Richard Hulton and Richard Redford held the manor as tenants. Later the manor was acquired by the Hultons of Over Hulton. In 1666 there were 91 hearths in Farnworth liable to pay tax. The commons were enclosed in 1798. There was a watermill on the River Croal. Industrial Revolution The town expanded rapidly in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |