|
Troll Research Station
Troll is a Norwegian research station located at Jutulsessen, from the coast in the eastern part of Princess Martha Coast in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It is Norway's only all-year research station in Antarctica, and is supplemented by the summer-only station Tor (research station), Tor. Troll is operated by the Norwegian Polar Institute and also features facilities for the Norwegian Meteorological Institute and the Norwegian Institute for Air Research. Unlike most other research stations on the continent, Troll is constructed on the snow-free slope of solid rock breaking through the ice sheet at Jutulsessen, located above mean sea level. The station opened as a summer-only station in 1990 and was taken into use as an all-year station in 2005. It has an overwintering capacity of eight people and a summer capacity of 40. It is served by Troll Airfield, which is the base for the Dronning Maud Land Air Network (DROMLAN). Facilities Troll is located in the eastern part of Princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
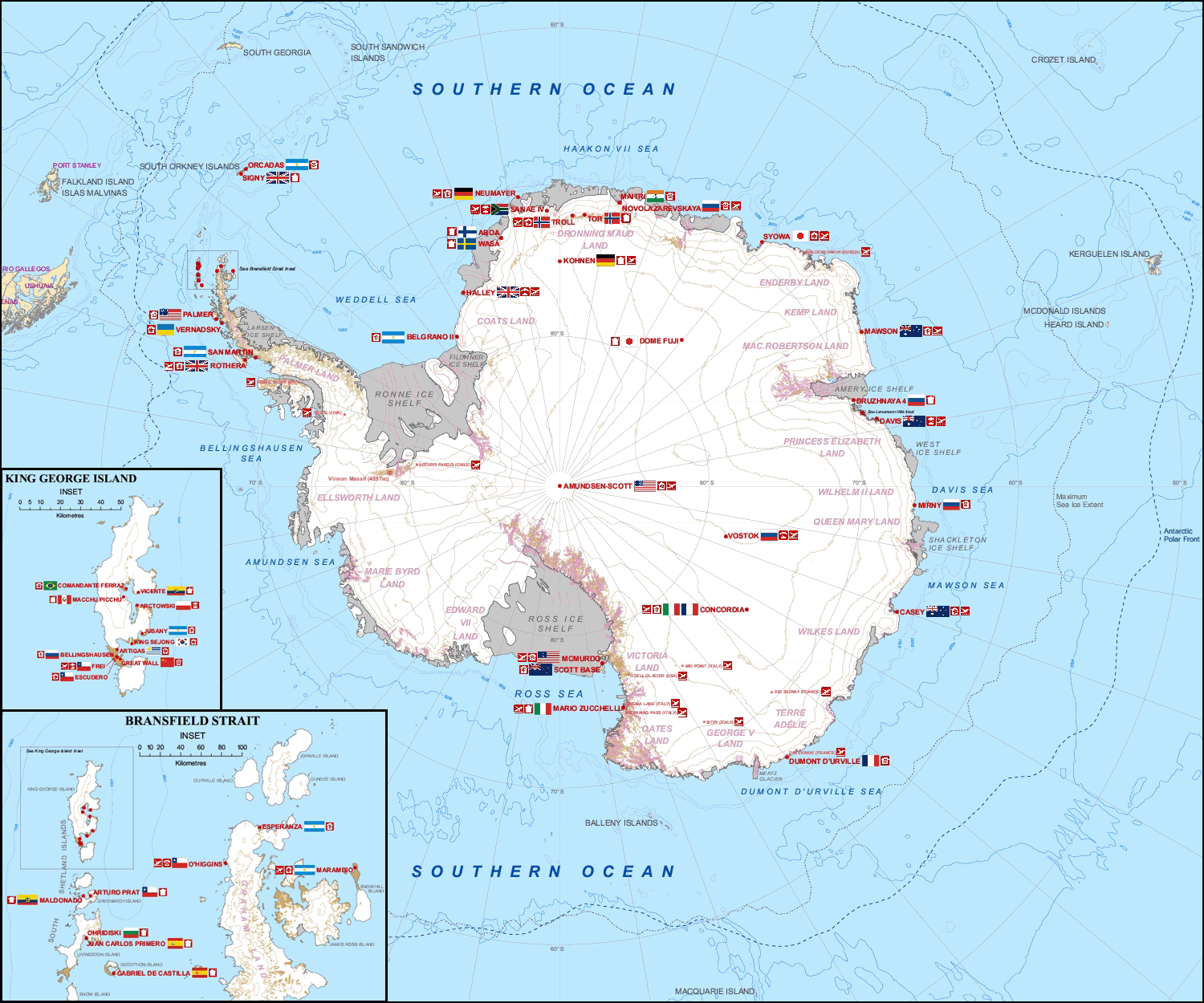
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. When rounded by glacial action, smaller rock promontories may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the nunataks protrude above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some nunataks are isolated, sometimes they form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, which hampers the formation of glacial ice on their tops, although snow can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is the widespread practice of collecting information and attempting to spot a pattern. In some fields of study, the term has more formally defined meanings. Although trend analysis is often used to predict future events, it could be used to estimate uncertain events in the past, such as how many ancient kings probably ruled between two dates, based on data such as the average years which other known kings reigned. Project management In project management, trend analysis is a mathematical technique that uses historical results to predict future outcome. This is achieved by tracking variances in cost and schedule performance. In this context, it is a project management quality control tool. Statistics In statistics, trend analysis often refers to techniques for extracting an underlying pattern of behavior in a time series which would otherwise be partly or nearly completely hidden by noise. If the trend can be assumed to be linear, trend analysis can be undertaken wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the latter, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odour is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetic. In standard conditions, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic temperatures to a dark blue liquid and finally a violet-black soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at Hydroelectric dam, hydroelectric dams, Irrigation, irrigation mist, Perfume, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, Pesticide, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic aerosol. The liquid or solid particles in an aerosol have diameters typically less than micrometre, 1 μm (larger particles with a significant settling speed make the mixture a Suspension (chemistry), suspension, but the distinction is not clear-cut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ny-Ålesund
Ny-Ålesund ("New Ålesund") is a small town in Oscar II Land on the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It is situated on the Brøgger peninsula ( Brøggerhalvøya) and on the shore of the bay of Kongsfjorden. The company town is owned and operated by Kings Bay, which provides facilities for permanent research activities by 19 institutions from 11 countries. The town is ultimately owned by the Ministry of Climate and Environment and is not incorporated (i.e. is not recognised as a town by the Norwegian government). Ny-Ålesund has an all-year permanent population of 30 to 35, with the summer population reaching 114. Its facilities include Ny-Ålesund Airport, Hamnerabben, Svalbard Rocket Range, a port and Ny-Ålesund Town and Mine Museum, as well as a number of buildings dedicated to research and environmental monitoring activities. It is the northernmost functional civilian settlement in the world. The town was founded in 1917 by Peter Brandal and his mining company, Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin (research Station)
The Zeppelin Observatory (''Zeppelinobservatoriet'') is a research station in Spitsbergen, Norway. It is located near the top of Zeppelinfjellet above Ny-Ålesund on the peninsula of Brøggerhalvøya. It is operated by the Norwegian Polar Institute. The research station at Zeppelinfjellet was built between 1988-1989 and officially opened in 1990. After 10 years of use, it was determined that the building no longer covered the needs that were required to operate advanced instrumentation. In the second half of 1999, the old building was demolished and a new and improved station was built at the same site. The new station building was officially opened on 2 May 2000. See also * |
Polar Night
The polar night is a phenomenon where the nighttime lasts for more than 24 hours that occurs in the northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth. This occurs only inside the polar circles. The opposite phenomenon, the polar day, or midnight sun, occurs when the Sun remains above the horizon for more than 24 hours. "Night" is understood as the center of the Sun being below a free horizon. Since the atmosphere refracts sunlight, the polar day is longer than the polar night, and the area that is affected by polar night is somewhat smaller than the area of midnight sun. The polar circle is located at a latitude between these two areas, at approximately 66.5°. While it is day in the Arctic Circle, it is night in the Antarctic Circle, and vice versa. Any planet or moon with a sufficient axial tilt that rotates with respect to its star significantly more frequently than it orbits the star (no tidal locking between the two) will experience the same phenomenon (a nighttime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midnight Sun
The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When the midnight sun is seen in the Arctic, the Sun appears to move from left to right, but in Antarctica the equivalent apparent motion is from right to left. This occurs at latitudes from 65°44' to 90° north or south, and does not stop exactly at the Arctic Circle or the Antarctic Circle, due to refraction. The opposite phenomenon, polar night, occurs in winter, when the Sun stays below the horizon throughout the day. Details Around the summer solstice (approximately 21 June in the Northern Hemisphere and 21 December in the Southern Hemisphere), in certain areas the Sun does not set below the horizon within a 24-hour period. Geography Because there are no permanent human settlements south of the Antarctic Circle, apart from research stations, the countries and territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Circle
The Antarctic Circle is the most southerly of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth. The region south of this circle is known as the Antarctic, and the zone immediately to the north is called the Southern Temperate Zone. South of the Antarctic Circle, the Sun is above the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year (and therefore visible at midnight) and the centre of the Sun (ignoring refraction) is below the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year (and therefore not visible at noon); this is also true within the equivalent polar circle in the Northern Hemisphere, the Arctic Circle. The position of the Antarctic Circle is not fixed and currently runs south of the Equator. This figure may be slightly inaccurate because it does not allow for the effects of astronomical nutation, which can be up to 10″. Its latitude depends on the Earth's axial tilt, which fluctuates within a margin of more than 2° over a 41,000-year period, due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

.jpg)
