|
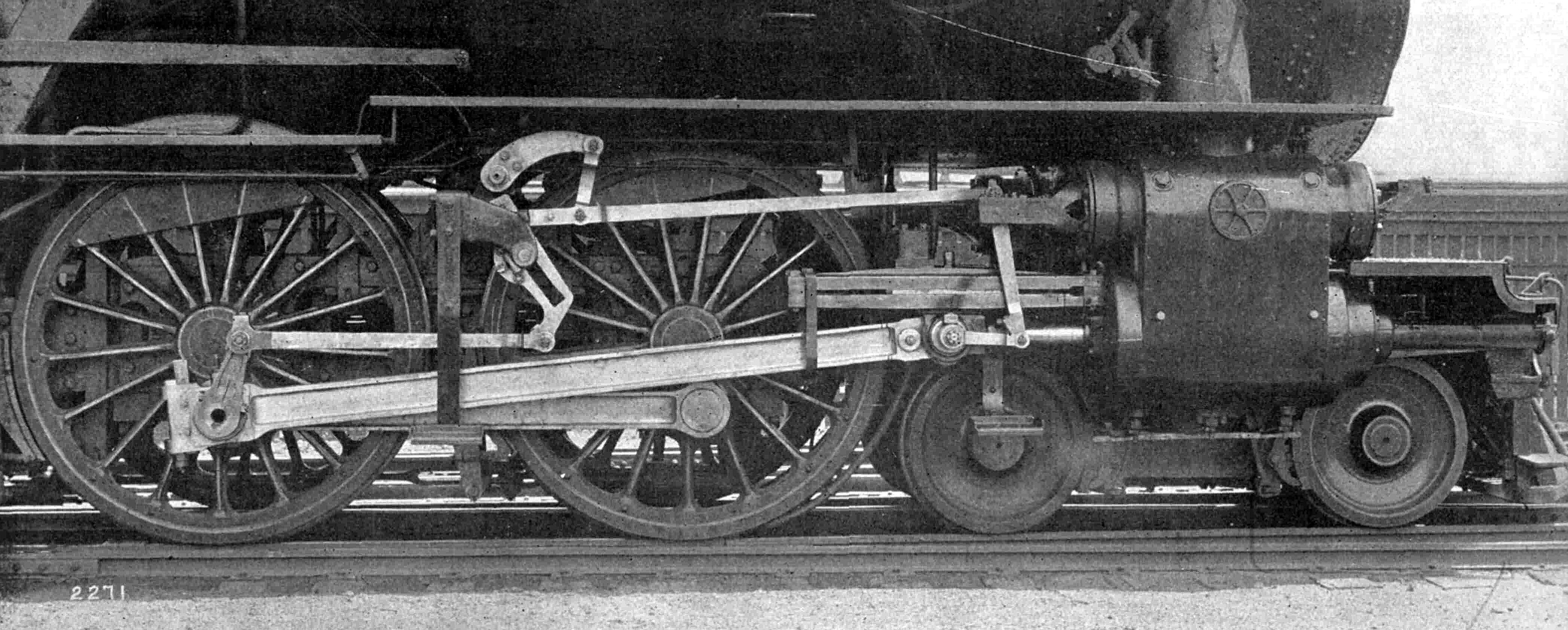
Trofimoff Piston Valve
The Trofimoff valve (german: Trofimoff-Schieber) (also ''Trofimov'', ''Troffimoff'' or ''Trofimof'') is a springless pressure-compensation piston valve for steam locomotives. Overview The function of the valve is to improve efficiency when running light, with the regulator closed, such as when descending hills. The valve consists of the usual parts of a piston valve: two valve pistons with sealing rings, carried on a valve spindle driven by the valve gear The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing .... The difference with a Trofimoff valve is that the piston heads are free to slide on the spindle. When steam pressure is applied, under normal operating conditions, steam is admitted to the centre of the valve chest. This forces the valve heads apart against end stops on the spind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Valve
A "piston valve" is a device used to control the motion of a fluid along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder. Examples of piston valves are: * The valves used in many brass instruments * The valves used in pneumatic cannons * The valves used in many stationary steam engines and steam locomotives Brass instruments Cylindrical piston valves called Périnet valves (after their inventor François Périnet) are used to change the length of tube in the playing of most brass instruments, particularly the trumpet-like members of the family (cornet, flugelhorn, saxhorn, etc.). Other brass instruments use rotary valves, notably the orchestral horns and many tuba models, but also a number of rotary-valved variants of those brass instruments which more commonly employ piston valves. The first piston-valved musical instruments were developed just after the start of the 19th century. The Stölzel valve (invented by Heinrich Stölzel in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and a bloody civil war. The Russian Revolution can also be seen as the precursor for the other European revolutions that occurred during or in the aftermath of WWI, such as the German Revolution of 1918–1919, German Revolution of 1918. The Russian Revolution was inaugurated with the February Revolution in 1917. This first revolt focused in and around the then-capital Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg). After major military losses during the war, the Russian Army had begun to mutiny. Army leaders and high ranking officials were convinced that if Nicholas II of Russia, Tsar Nicholas II abdicated, the domestic unrest would subside. Nicholas agreed and stepped down, usher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate. It relates to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid (or a solid). A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as '' volatile''. The pressure exhibited by vapor present above a liquid surface is known as vapor pressure. As the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules also increases. As the kinetic energy of the molecules increases, the number of molecules transitioning into a vapor also increases, thereby increasing the vapor pressure. The vapor pressure of any substance increases non-linearly with temperature according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR Class 99
Class 99 is the classification of German narrow gauge locomotives used by the Deutsche Reichsbahn or her successor administrations. It is therefore divided into numerous sub-classes that are listed in this table. Bibliography * Weisbrod, Manfred, Hans Müller and Wolfgang Petznik (1995). ''Dampflokomotiven deutscher Eisenbahnen. Band 4: Baureihe 99''. Berlin: Transpress. See also {{Commons category, DRG Class 99 * Deutsche Reichsbahn * Deutsche Bundesbahn * Deutsche Reichsbahn (GDR) * List of DRG locomotives and railcars * Einheitsdampflokomotive Narrow gauge locomotives Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft locomotives, 99 Deutsche Bundesbahn locomotives, 99 Deutsche Reichsbahn (East Germany) locomotives, 99 Steam locomotives of Germany, 99 German railway-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works
The Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works (german: Dampflokwerk Meiningen) is a railway repair shop in Meiningen, Germany. It is owned by Deutsche Bahn and has specialised in the maintenance of museum steam locomotives since 1990, having extensive experience in maintaining steam engines. Today, customers of the factory include railway museums and museum railways from all over Europe. The factory is responsible for the safety inspections of all operational German steam locomotives. Dampflokwerk Meiningen is the only facility in Europe capable of constructing new locomotive boilers up to modern standards of construction, performance, and safety. The newly built British steam locomotive 60163 ''Tornado'' that was delivered in 2008 had her all-steel, high-performance boiler made at Meiningen; the only part that could not be made in Britain. History In 1863 the Werra Railway (''Werrabahn'') built a locomotive repair shop opposite Meiningen station, which became a main workshop for the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine Technology
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |