|
Tritone Paradox
__NOTOC__ The tritone paradox is an auditory illusion in which a sequentially played pair of Shepard tones separated by an interval of a tritone, or half octave, is heard as ascending by some people and as descending by others. Different populations tend to favor one of a limited set of different spots around the chromatic circle as central to the set of "higher" tones. Roger Shepard in 1963 had argued that such tone pairs would be heard ambiguously as either ascending or descending. However, psychology of music researcher Diana Deutsch in 1986 discovered that when the judgments of individual listeners were considered separately, their judgments depended on the positions of the tones along the chromatic circle. For example, one listener would hear the tone pair C–F as ascending and the tone pair G–C as descending. Yet another listener would hear the tone pair C–F as descending and the tone pair G–C as ascending. Furthermore, the way these tone pairs were perceived va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritone Paradox Example
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval spanning three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F above i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone (linguistics)
Tone is the use of pitch (music), pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflection, inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation (linguistics), intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with ''phoneme''. Tonal languages are common in East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas, and the Pacific islands, Pacific. Tonal languages are different from pitch-accent languages in that tonal languages can have each syllable with an independent tone whilst pitch-accent languages may have one syllable in a word or morpheme that is more prominent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxes
A paradox is a logically self-contradictory statement or a statement that runs contrary to one's expectation. It is a statement that, despite apparently valid reasoning from true or apparently true premises, leads to a seemingly self-contradictory or a logically unacceptable conclusion. A paradox usually involves contradictory-yet-interrelated elements that exist simultaneously and persist over time. They result in "persistent contradiction between interdependent elements" leading to a lasting "unity of opposites". In logic, many paradoxes exist that are known to be invalid arguments, yet are nevertheless valuable in promoting critical thinking, while other paradoxes have revealed errors in definitions that were assumed to be rigorous, and have caused axioms of mathematics and logic to be re-examined. One example is Russell's paradox, which questions whether a "list of all lists that do not contain themselves" would include itself and showed that attempts to found set theory on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Illusions
Auditory illusions are illusions of real sound or outside stimulus. These false perceptions are the equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or sounds that should not be possible given the circumstance on how they were created. Humans are fairly susceptible to illusions, despite an innate ability to process complex stimuli. Confirmation bias is believed to be largely responsible for the inaccurate judgments that people make when evaluating information, given that humans typically interpret and recall information that appeals to their own biases. Amongst these misinterpretations, known as illusions, falls the category of auditory illusions. The brain uses multiple senses simultaneously to process information, spatial information is processed with greater detail and accuracy in vision than in hearing. Auditory illusions highlight areas where the human ear and brain, as organic survival tools, differentiate from per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Au File Format
The Au file format is a simple audio file format introduced by Sun Microsystems. The format was common on NeXT systems and on early Web pages. Originally it was headerless, being 8-bit μ-law algorithm, μ-law-encoded data at an 8000 Hz sample rate. Hardware from other vendors often used sample rates as high as 8192 Hz, often integer multiples of video clock signal frequencies. Newer files have a header that consists of six Signedness, unsigned 32-bit computing, 32-bit words, an optional information chunk which is always of non-zero size, and then the data (in Endianness, big-endian format). Although the format now supports many digital audio, audio encoding formats, it remains associated with the μ-law logarithmic encoding. This encoding was native to the SPARCstation 1 hardware, where SunOS exposed the encoding to application programs through the /dev/audio device file interface. This encoding and interface became a de facto standard for Unix sound. New format All fields a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society. The editor-in-chief is Richard Dixon (UNT). Overview Each issue covers a specific area of the biological sciences. Each issue aims to create an original and authoritative synthesis, often bridging traditional disciplines, which showcases current developments and provides a foundation for future research, applications and policy decisions. Each issue is edited by one or more expert guest editors. The themes fall into one of four general categories: * Cell and Development * Health and Disease * Environment and Evolution * Neuroscience and Cognition All articles become freely accessible one year after their publication date. History ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' was established in 1665 by the Royal Society and is the oldest scientific journal in the English-speaking world. Henry Oldenburg was appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
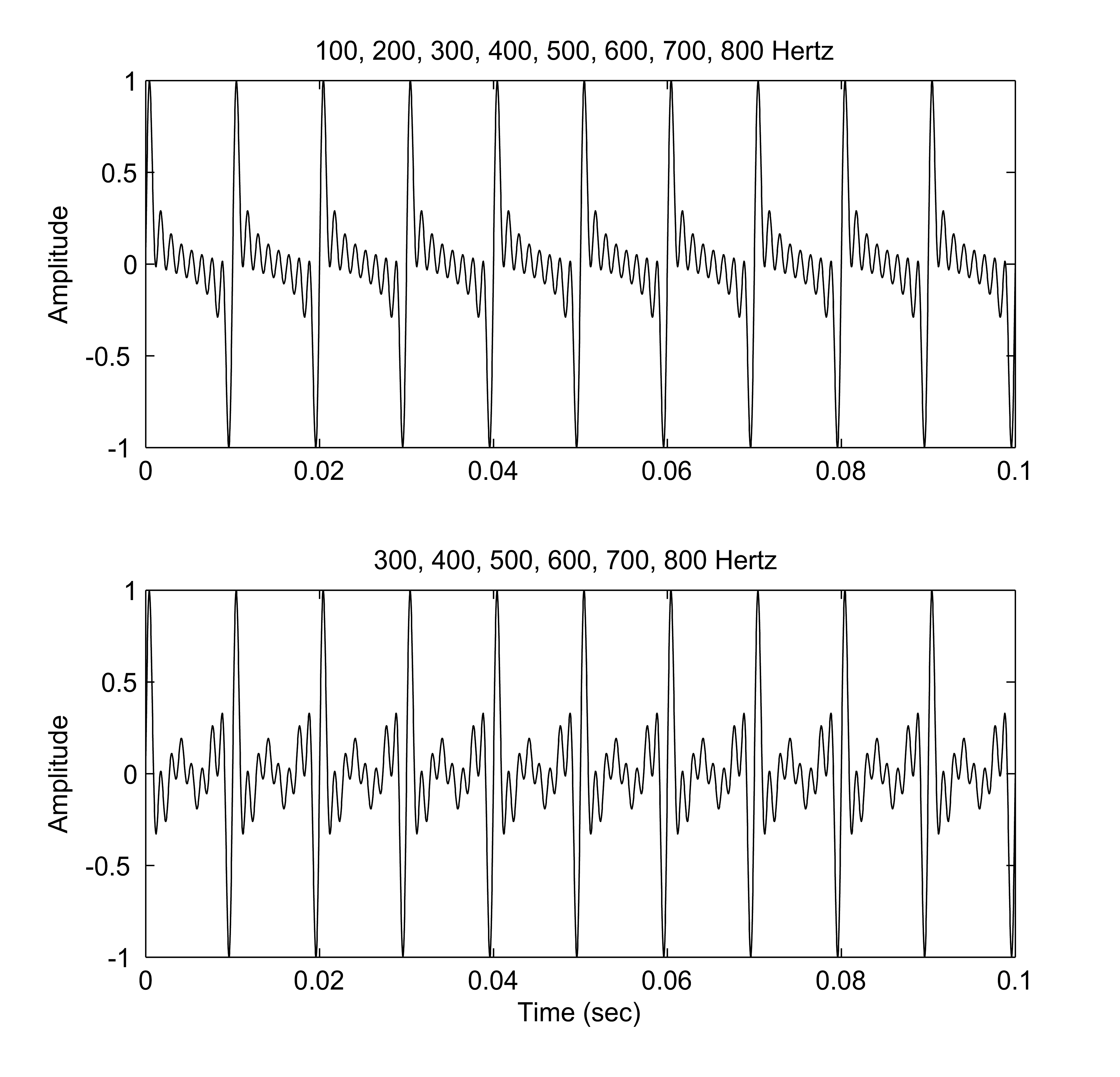
Missing Fundamental
The pitch being perceived with the first harmonic being absent in the waveform is called the missing fundamental phenomenon. It is established in psychoacoustics that the auditory system, with its natural tendency to distinguish a tone from another, will persistently assign a pitch to a complex tone given that a sufficient set of harmonics are present in the spectrum. For example, when a note (that is not a pure tone) has a pitch (music), pitch of 100 hertz, Hz, it will consist of frequency components that are integer multiples of that value (e.g. 100, 200, 300, 400, 500.... Hz). However, smaller loudspeakers may not produce low frequencies, so in our example, the 100 Hz component may be missing. Nevertheless, a pitch corresponding to the fundamental may still be heard. Explanation A low pitch (psychophysics), pitch (also known as the pitch of the missing fundamental or virtual pitch) can sometimes be heard when there is no apparent source or component of that frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanging
Flanging is an audio signal processing, audio effect produced by mixing two identical audio signal, signals together, one signal delayed by a small and (usually) gradually changing period, usually smaller than 20 milliseconds. This produces a swept comb filter effect: peaks and notches are produced in the resulting frequency spectrum, related to each other in a linear harmonic series (music), harmonic series. Varying the time delay causes these to sweep up and down the frequency spectrum. A flanger is an effects unit that creates this effect. Part of the output signal is usually fed back to the input (a re-circulating Delay (audio effect), delay line), producing a resonance effect that further enhances the intensity of the peaks and troughs. The phase of the fed-back signal is sometimes inverted, producing another variation on the flanger sound. Origin As an audio effect, a listener hears a ''drainpipe'' or ''swoosh'' or ''jet plane'' sweeping effect as shifting sum-and-differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barberpole Illusion
The barberpole illusion is a visual illusion that reveals biases in the processing of visual motion in the human brain. This visual illusion occurs when a diagonally striped pole is rotated around its vertical axis (horizontally), it appears as though the stripes are moving in the direction of its vertical axis (downwards in the case of the animation to the right) rather than around it. History In 1929, psychologist J.P. Guilford informally noted a paradox in the perceived motion of stripes on a rotating barber pole. The barber pole turns in place on its vertical axis, but the stripes appear to move upwards rather than turning with the pole. Guilford tentatively attributed the phenomenon to eye movements, but acknowledged the absence of data on the question. In 1935, Hans Wallach published a comprehensive series of experiments related to this topic, but since the article was in German it was not immediately known to English-speaking researchers. An English summary of the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Language
Vietnamese () is an Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic language Speech, spoken primarily in Vietnam where it is the official language. It belongs to the Vietic languages, Vietic subgroup of the Austroasiatic language family. Vietnamese is spoken natively by around 86 million people, and as a second language by 11 million people, several times as many as the rest of the Austroasiatic family combined. It is the native language of Vietnamese people, ethnic Vietnamese (Kinh), as well as the second language, second or First language, first language for List of ethnic groups in Vietnam, other ethnicities of Vietnam, and used by Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese diaspora in the world. Like many languages in Southeast Asia and East Asia, Vietnamese is highly analytic language, analytic and is tone (linguistics), tonal. It has head-initial directionality, with subject–verb–object order and modifiers following the words they modify. It also uses noun classifier (linguistics), classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Illusion
Auditory illusions are Illusion, illusions of real sound or outside stimulus. These false perceptions are the equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the Stimulus (physiology), stimulus, or sounds that should not be possible given the circumstance on how they were created. Humans are fairly susceptible to illusions, despite an innate ability to process complex stimuli. Confirmation bias is believed to be largely responsible for the inaccurate judgments that people make when evaluating information, given that humans typically interpret and recall information that appeals to their own biases. Amongst these misinterpretations, known as illusions, falls the category of auditory illusions. The brain uses multiple senses simultaneously to process information, spatial information is processed with greater detail and accuracy in vision than in hearing. Auditory illusions highlight areas where the human ear and human brain, brain, as or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |