|
Tritan Copolyester
Tritan is a copolymer offered by Eastman Chemical Company since 2007 to replace polycarbonate, because of health concerns about Bisphenol A (BPA). Tritan is a copolymer made from three monomers: dimethyl terephthalate (DMT), cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM), and 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol (CBDO). Tritan is made without using any BPA. In April 2008, Nalgene announced it would phase out production of its outdoor line of polycarbonate containers containing the chemical bisphenol A. Nalgene then used Tritan, because it did not contain BPA. Health controversy In 2011, a neurobiologist at the University of Texas, George Bittner, published an article claiming most polymers, including Tritan, contained trace amounts of Bisphenol A. Eastman Chemical Company sued, and after a jury ruled in Eastman's favor, the Court barred Bittner from making claims about Tritan’s oestrogen Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 and nylon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastman Chemical Company
Eastman Chemical Company is an American company primarily involved in the chemical industry. Once a subsidiary of Kodak, today it is an independent global specialty materials company that produces a broad range of advanced materials, chemicals and fibers for everyday purposes. Founded in 1920 and based in Kingsport, Tennessee, the company now has more than 50 manufacturing sites worldwide and employs approximately 14,000 people. Eastman was spun off from parent Eastman Kodak in 1994. In 2021 it had sales revenue of approximately $10.5 billion. Business segments Eastman manufactures and markets chemicals, fibers, and plastics. It provides coatings, adhesives and specialty plastics products, is a major supplier of cellulose acetate fibers, and produces copolyesters for packaging. The company's products and operations are managed and reported in four operating segments: Additives & Functional Products, Advanced Materials, Chemical Intermediates, and Fibers. ;Additives & Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA). Structure Carbonate esters have planar OC(OC)2 cores, which confers rigidity. The unique O=C bond is short (1.173 Å in the depicted example), while the C-O bonds are more ether-like (the bond distances of 1.326 Å for the example depicted). Polycarbonates received their name because they are polymers containing carbonate groups (−O−(C=O)−O−). A balance of useful features, including temperature resistance, impact resistance and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial scale by the condensation of phenol and acetone, and has a global production scale which is expected to reach 10 million tonnes in 2022. BPA's largest single application is as a co-monomer in the production of polycarbonates, which accounts for 65–70% of all BPA production. The manufacturing of epoxy resins and vinyl ester resins account for 25–30% of BPA use. The remaining 5% is used as a major component of several high-performance plastics, and as a minor additive in PVC, polyurethane, thermal paper, and several other materials. It is not a plasticizer, although it is often wrongly labelled as such. The health effects of BPA have been the subject of prolonged public and scientific debate. BPA is a xenoestrogen, exhibiting hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomers
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Monomers can be classified in many ways. They can be subdivided into two broad classes, depending on the kind of the polymer that they form. Monomers that participate in condensation polymerization have a different stoichiometry than monomers that participate in addition polymerization: : Other classifications include: *natural vs synthetic monomers, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively *polar vs nonpolar monomers, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively *cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two different monomers. In the case of condensation polymerizations, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Terephthalate
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COOCH3)2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.Richard J. Sheehan "Terephthalic Acid, Dimethyl Terephthalate, and Isophthalic Acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. Production Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally, and still of commercial value, is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-esterification steps from p-xylene via methyl ''p''-toluate (PT). Dimethyl terephthalate by the Witten process The method for the production of DMT from ''p''-xylene (PX) and methanol consists of a multistep process involving both oxidation and esterification. A mixture of p-xylene (PX) and methyl ''p''-toluate is oxidized with air in the presence of cobalt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanedimethanol
Cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM) is a mixture of isomeric organic compounds with formula C6H10(CH2OH)2. It is a colorless low-melting solid used in the production of polyester resins. Commercial samples consist of a mixture of cis and trans isomers. It is a di-substituted derivative of cyclohexane and is classified as a diol, meaning that it has two OH functional groups. Commercial CHDM typically has a cis/trans ratio of 30:70. Applications Via the process called polycondensation, CHDM is a precursor to polyesters. It is one of the most important comonomers for production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or polyethylene terephthalic ester (PETE), from which plastic bottles are made. Thermoplastic polyesters containing CHDM exhibit enhanced strength, clarity, and solvent resistance. The properties of the polyesters vary from the high melting crystalline poly(1,4-cyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate), PCT, to the non-crystalline copolyesters derived from both ethylene glycol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
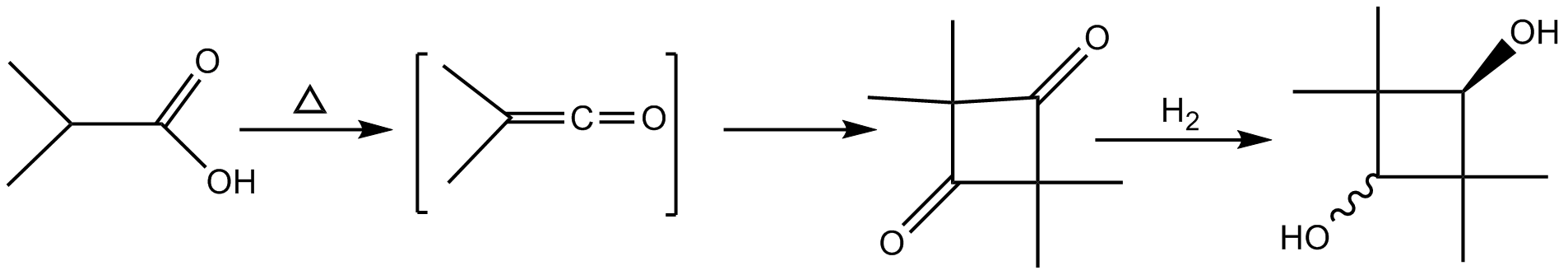
2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol
2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol (CBDO) is an aliphatic diol. This diol is produced as a mixture of ''cis''- and ''trans''-isomers, depending on the relative stereochemistry of the hydroxyl groups. It is used as a monomer for the synthesis of polymeric materials. CBDO is currently being researched as an alternative to bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is a precursor used in the production of a wide range of polymers including polycarbonates, polyesters, polysulfones, and polyester ketones. Replacement for BPA The controversies associated with BPA in large quantities are ultimately related to its endocrine disrupting abilities. Like BPA, CBDO is a diol with a structure suitable for making polyesters. CBDO’s C4 ring is sufficiently rigid to prevent the two OH groups from forming cyclic structures. Unlike BPA, there is no current evidence of carcinogenic or toxic effects from CBDO-based consumer products. There are, however, few studies on the toxicology of CBDO for both long ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalgene
Nalgene is a brand of plastic products developed originally for laboratory use, including such items as jars, bottles, test tubes, and Petri dishes, that were shatterproof and lighter than glass. The properties of plastic products make them suitable for work with many substances in various temperature ranges. Nalgene products are manufactured by Nalge Nunc International, which in 2004 became a subsidiary of Fisher Scientific, now Thermo Fisher Scientific. The name ''Nalgene'' is a registered trademark. Nalgene Outdoor In the 1970s, conservationists began discouraging the disposal of cans and glass bottles by burning and burial in wilderness and recreation areas, and some places began forbidding such materials by regulation. Nalgene products became popular replacements among backpackers for storing consumables; the light, wide-mouthed high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonate bottles were more secure than plastic bags and were used for both liquids and solid foods. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Their presence in both vertebrates and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient evolutionary history. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ER ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycarbonates
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA). Structure Carbonate esters have planar OC(OC)2 cores, which confers rigidity. The unique O=C bond is short (1.173 Å in the depicted example), while the C-O bonds are more ether-like (the bond distances of 1.326 Å for the example depicted). Polycarbonates received their name because they are polymers containing carbonate groups (−O−(C=O)−O−). A balance of useful features, including temperature resistance, impact resistance and op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity Chemicals
Commodity chemicals (or bulk commodities or bulk chemicals) are a group of chemicals that are made on a very large scale to satisfy global markets. The average prices of commodity chemicals are regularly published in the chemical trade magazines and web sites such aChemical WeekanICIS There have been several studies of the scale and complexity of this market for example in the USA. Commodity chemicals are a sub-sector of the chemical industry (other sub sectors are fine chemicals, specialty chemicals, inorganic chemicals, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, renewable energy (e.g. biofuels) and materials (e.g. biopolymers)) Commodity chemicals are differentiated primarily by the bulk of their manufacture. Types Chemical compounds are often classified into two classes, inorganic and organic. Inorganic chemicals * aluminium sulfate * ammonia * ammonium nitrate * ammonium sulfate * carbon black * chlorine * diammonium phosphate * monoammonium phosphate * hydrochloric acid * hydrogen fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |