|
Tris(2-methyl-1-aziridinyl)phosphine Oxide
Metepa is a chemosterilant, with the capability to restrict ovarian development. Metepa can also result in carcinogenesis, in particular the formation of teratomas. It is sometimes used as a Rocket propellant Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propuls .... References Flame retardants Pesticides Phosphoramides Aziridines {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Index
''The Merck Index'' is an encyclopedia of chemical substance, chemicals, pharmaceutical drug, drugs and biomolecule, biologicals with over 10,000 monographs, monograph on single substances or groups of related chemical compound, compounds published online by the Royal Society of Chemistry. History The first edition of the Merck's Index was published in 1889 by the German chemical company Merck Group, Emanuel Merck and was primarily used as a sales catalog for Merck's growing list of chemicals it sold. The American subsidiary was established two years later and continued to publish it. During World War I the US government seized Merck's US operations and made it a separate American "Merck" company that continued to publish the Merck Index. In 2012 the Merck Index was licensed to the Royal Society of Chemistry. An online version of The Merck Index, including historic records and new updates not in the print edition, is commonly available through research libraries. It also include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemosterilant
A chemosterilant is a chemical compound that causes reproductive sterility in an organism. Chemosterilants are particularly useful in controlling the population of species that are known to cause disease, such as insects, or species that are, in general, economically damaging. The sterility induced by chemosterilants can have temporary or permanent effects. Chemosterilants can be used to target one or both sexes, and it prevents the organism from advancing to be sexually functional. They may be used to control pest populations by sterilizing males. The need for chemosterilants is a direct consequence of the limitations of insecticides. Insecticides are most effective in regions in which there is high vector density in conjunction with endemic transmission, and this may not always be the case. Additionally, the insects themselves will develop a resistance to the insecticide either on the target protein level or through avoidance of the insecticide in what is called a behavioral res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to cancer w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratomas
A teratoma is a tumor made up of several different types of tissue, such as hair, muscle, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the ovary, testicle, or coccyx. Symptoms Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular teratoma may present as a painless lump. Complications may include ovarian torsion, testicular torsion, or hydrops fetalis. They are a type of germ cell tumor (a tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or eggs). They are divided into two types: mature and immature. Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous. Most ovarian teratomas are mature. In adults, testicular teratomas are generally cancerous. Definitive diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Treatment of coccyx, testicular, and ovarian teratomas is generally by surgery. Testicular and immature ovarian teratomas are also frequently treated with chemotherapy. Teratomas occur in the coccyx in about one in 30,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
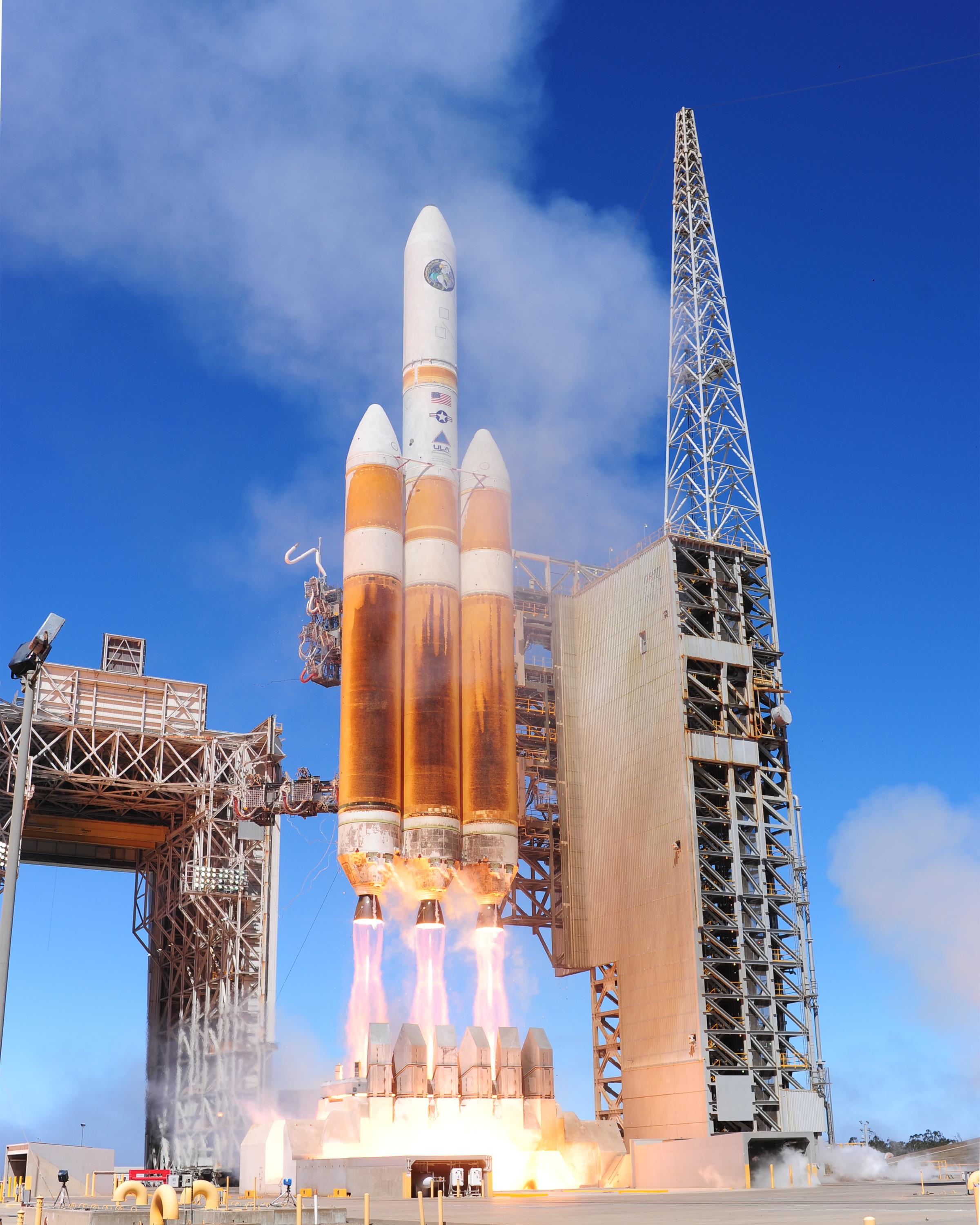
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, in accordanc ... to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and Rocket engine nozzle, nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Retardants
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and are intended to prevent or slow the further development of ignition by a variety of different physical and chemical methods. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or (particularly for textiles) applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive. Classes Both Reactive and Additive Flame retardants types, can be further separated into four distinct classes: * Minerals such as aluminium hydroxide (ATH), magnesium hydroxide (MDH), huntite and hydromagnesite, various hydrates, red phosphorus, and boron compounds, mostly borates. * Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
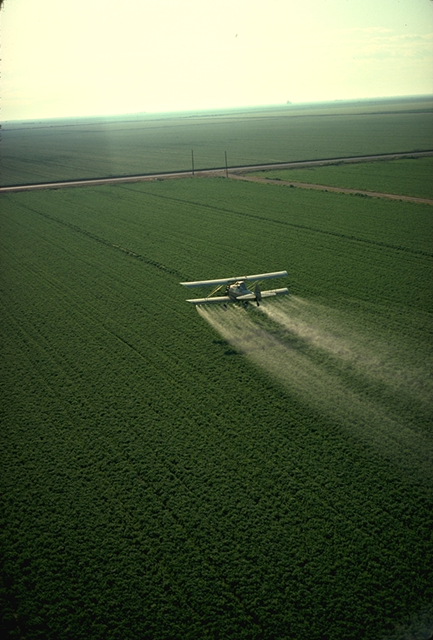
Pesticides
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus ''Alternaria solani'' is used to combat the aquatic weed ''Salvinia''. In general, a pesticide is a chemical (such as carbamate) or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoramides
Phosphoramides are a class of phosphorus compounds with the formula O=P(NR2)3-n(OH)n. They can be considered derivatives of phosphoric acid where OH groups have been replaced with an amino or R-substituted amino group. In practise the term is commonly confined to the phosphoric triamides (P(=O)(NR2)3), essentially phosphoramide and derivatives thereof. Derivatives with the general structures P(=O)(OH)(NR2)2 or P(=O)(OH)2(NR2) are usually referred to as phosphoramidic acids. Examples *Phenyl phosphorodiamidate, a phosphoramide but also a phosphate ester, is used in agriculture to enhance the effectiveness of urea-based fertilizers. *Hexamethylphosphoramide Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the formula This colorless liquid is a useful reagent in organic synthesis. Structure and reactivity HMPA is the oxide of the highly basic t ... (HMPA) is a polar solvent. References {{Organophosphorus Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
