|
Tripod (foundation)
The tripod is a type of foundation for offshore wind turbines. The tripod is generally more expensive than other types of foundation. However, for large turbines and higher water depth, the cost disadvantage might be compensated when durability is also taken into account. History Start of the offshore wind industry The exploration of offshore wind energy started with the introduction of monopile foundations for wind turbines in a range from 1 up to 3MW in water depth of about 10 to 20m during the 1990s. Germany has been facing water depths up to 40m, when it joined this new field of renewable energy. At the same time the 5MW turbine class appeared. One representative of this new turbine generation was the Multibrid M5000 with a rotor diameter of 116m, later 135m under the labels Areva and Adwen. The first prototype of this machine was erected in Bremerhaven in 2004 onshore. Already in this stage Bremerhaven had supported the development on behalf of BIS Bremerhavener Gesellsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripod Wind Energy Brhv
A tripod is a portable three-legged frame or stand, used as a platform for supporting the weight and maintaining the stability of some other object. The three-legged (triangular stance) design provides good stability against gravitational loads as well as horizontal shear forces, and better leverage for resisting tipping over due to lateral forces can be achieved by spreading the legs away from the vertical centre. Variations with one, two, and four legs are termed ''monopod'', ''bipod'', and ''quadripod'' (similar to a Table (furniture), table). Etymology First attested in English in the early 17th century, the word ''tripod'' comes via Latin ''tripodis'' (genitive, GEN of ''tripus''), which is the romanization of Greek language, Greek (''tripous''), "three-footed" (GEN , ''tripodos''), ultimately from (''tri-''), "three times" (from , ''tria'', "three") + (''pous''), "foot". The earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek , ''ti-ri-po'', written in Linear B s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Ministry For The Environment, Nature Conservation, Building And Nuclear Safety
The Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection (german: Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz, nukleare Sicherheit und Verbraucherschutz, ), abbreviated BMUV, is a cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany. It has branches in Bonn and Berlin. The ministry was established on 6 June 1986 in response to the Chernobyl disaster. The then Federal Government wanted to combine environmental authority under a new minister in order to face new environmental challenges more effectively. Furthermore The Greens had been formed a few years prior in part as an anti-nuclear environmentalist party and had achieved federal representation in 1983 and Joschka Fischer had been appointed minister of the environment for Hesse the previous year, marking the first state level red-green coalition in Germany. Thus the CDU/CSU intended to project a message of taking the environment seriously in an era in which the Greens were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell (structure)
A shell is a type of structural element which is characterized by its geometry, being a three-dimensional solid whose thickness is very small when compared with other dimensions, and in structural terms, by the stress resultants calculated in the middle plane displaying components which are both coplanar and normal to the surface. Essentially, a shell can be derived from a plate (structure), plate by two means: by initially forming the middle surface as a singly or doubly curved surface, and by applying loads which are coplanar to a plate's plane (geometry), plane which generate significant stresses. Thin-shell structures (also called plate and shell structures) are lightweight constructions using List of structural elements, shell elements. These elements, typically curved, are assembled to make large structures. Typical applications include aircraft fuselages, boat hulls, and the roofs of large buildings. Definition A thin shell is defined as a shell with a thickness which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Rolled
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature, the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold working processes... Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams, angle stock, channel stock), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mills ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending Moment
In solid mechanics, a bending moment is the reaction induced in a structural element when an external force or moment is applied to the element, causing the element to bend. The most common or simplest structural element subjected to bending moments is the beam. The diagram shows a beam which is simply supported (free to rotate and therefore lacking bending moments) at both ends; the ends can only react to the shear loads. Other beams can have both ends fixed (known as encastre beam); therefore each end support has both bending moments and shear reaction loads. Beams can also have one end fixed and one end simply supported. The simplest type of beam is the cantilever, which is fixed at one end and is free at the other end (neither simple or fixed). In reality, beam supports are usually neither absolutely fixed nor absolutely rotating freely. The internal reaction loads in a cross-section of the structural element can be resolved into a resultant force and a resultant couple. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deflection (engineering)
In structural engineering, deflection is the degree to which a part of a structural element is displaced under a load (because it deforms). It may refer to an angle or a distance. The deflection distance of a member under a load can be calculated by integrating the function that mathematically describes the slope of the deflected shape of the member under that load. Standard formulas exist for the deflection of common beam configurations and load cases at discrete locations. Otherwise methods such as virtual work, direct integration, Castigliano's method, Macaulay's method or the direct stiffness method are used. The deflection of beam elements is usually calculated on the basis of the Euler–Bernoulli beam equation while that of a plate or shell element is calculated using plate or shell theory. An example of the use of deflection in this context is in building construction. Architects and engineers select materials for various applications. [Baidu] |
Tidal Scour
Tidal scour is “sea-floor erosion caused by strong tidal currents resulting in the removal of inshore sediments and formation of deep holes and channels”. Examples of this hydrological process can be found globally. Two locations in the United States where tidal scour is the predominant shaping force is the San Francisco Bay and the Elkhorn Slough.Silberstein 1989 M, Campbell E. 1989. Elkhorn Slough. Monterey, CA: Monterey Bay Aquarium. 64 p. Tidal force can also contribute to bridge scour. Historical Perspective and Relevance Research on tidal scour is largely centered at Elkhorn Slough in California. The slough was directly exposed to tidal flux beginning in 1947 with the creation of the Moss Landing Harbor. Multiple studies have been done on the slough since tidal exposure to catalog the morphological change and determine how long it will take for the system to reach equilibrium. Formation Tidal Scours are formed in tide-dominated deltas and estuaries with the changing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
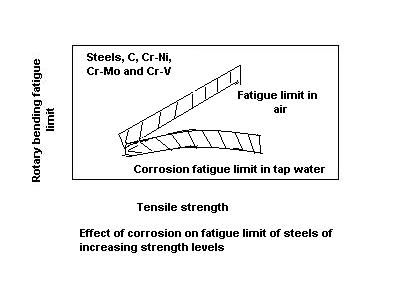
Corrosion Fatigue
Corrosion fatigue is fatigue in a corrosive environment. It is the mechanical degradation of a material under the joint action of corrosion and cyclic loading. Nearly all engineering structures experience some form of alternating stress, and are exposed to harmful environments during their service life. The environment plays a significant role in the fatigue of high-strength structural materials like steel, aluminum alloys and titanium alloys. Materials with high specific strength are being developed to meet the requirements of advancing technology. However, their usefulness depends to a large extent on the degree to which they resist corrosion fatigue. The effects of corrosive environments on the fatigue behavior of metals were studied as early as 1930. The phenomenon should not be confused with stress corrosion cracking, where corrosion (such as pitting) leads to the development of brittle cracks, growth and failure. The only requirement for corrosion fatigue is that the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splash Zone
In offshore construction, the splash zone is the transition from air to water when lowering heavy burdens into the sea. The overall efforts applied on the crane change dramatically when the load starts touching water, up to the point where it is completely submerged. Its buoyancy Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the p ... reduces the static mass that the crane has to support, but contact with the waves creates widely fluctuating dynamic forces. Simulation of these changing efforts are necessary to correctly dimension cranes and lifting equipment. See for examplDNV-RP-H103(Det Norske Veritas recommended practices) for a mention of the piston effect created in the splash zone between two walls. Offshore engineering {{Engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripod 6b
A tripod is a portable three-legged frame or stand, used as a platform for supporting the weight and maintaining the stability of some other object. The three-legged (triangular stance) design provides good stability against gravitational loads as well as horizontal shear forces, and better leverage for resisting tipping over due to lateral forces can be achieved by spreading the legs away from the vertical centre. Variations with one, two, and four legs are termed '' monopod'', '' bipod'', and ''quadripod'' (similar to a table). Etymology First attested in English in the early 17th century, the word ''tripod'' comes via Latin ''tripodis'' ( GEN of ''tripus''), which is the romanization of Greek (''tripous''), "three-footed" (GEN , ''tripodos''), ultimately from (''tri-''), "three times" (from , ''tria'', "three") + (''pous''), "foot". The earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek , ''ti-ri-po'', written in Linear B syllabic script. Cultural use Many cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripod 4b
A tripod is a portable three-legged frame or stand, used as a platform for supporting the weight and maintaining the stability of some other object. The three-legged (triangular stance) design provides good stability against gravitational loads as well as horizontal shear forces, and better leverage for resisting tipping over due to lateral forces can be achieved by spreading the legs away from the vertical centre. Variations with one, two, and four legs are termed '' monopod'', '' bipod'', and ''quadripod'' (similar to a table). Etymology First attested in English in the early 17th century, the word ''tripod'' comes via Latin ''tripodis'' ( GEN of ''tripus''), which is the romanization of Greek (''tripous''), "three-footed" (GEN , ''tripodos''), ultimately from (''tri-''), "three times" (from , ''tria'', "three") + (''pous''), "foot". The earliest attested form of the word is the Mycenaean Greek , ''ti-ri-po'', written in Linear B syllabic script. Cultural use Many cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borkum West II
Trianel Windpark Borkum (formerly Borkum West II) is an offshore wind farm near Borkum. Its first phase of 40 turbines rated at a total capacity of 200 MW is operational, with a planned, additional 200 MW in a second phase. The project was approved for construction in 2008 and will cost over €1 billion to construct once fully operational (€900m for phase I alone). Originally known as Borkum West II the name was changed to Trianel Windpark Borkum in early 2013. Phase 1 of the installation was completed in the 4th quarter of 2014 and consist of 40 Areva M5000-116 turbines (5 MW turbines) on Tripod foundations. It was connected to the grid in August 2015. In the six months before March 2016 the wind farm produced 452.33 GWh, i.e. a capacity factor of 51.6%. In September 2016 Senvion Senvion S.A. (called REpower Systems SE until 2014) was a German wind turbine manufacturer founded in 2001 in Germany, majority owned by a private equity firm. Senvion a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)