|
Triplex Locomotive
A Triplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using three pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame. Inevitably any such locomotive will be articulated. All the examples that have been produced have been of the Mallet type but with one extra set of driving wheels under the tender. Triplex classes Baldwin Locomotive Works built three Triplex locomotives for the Erie Railroad between 1914 and 1916. The first was named ''Matt H. Shay'', after a beloved employee of that road. These Triplexes were given the classification of "P1" and they could reportedly pull 650 freight cars. The Triplexes were primarily used as pushers on grades requiring helper locomotives. Slow moving, the Triplexes were not considered highly successful, and no more were built for Erie. The Erie Railroad scrapped their Triplexes from 1929, 1931, and 1933.. Another very similar designed Triplex was built by Baldwin as a 2-8-8-8-4 for the Virgini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERIE 28882
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 at the 2020 census. The estimated population in 2021 had decreased to 93,928. The Erie metropolitan area, equivalent to all of Erie County, consists of 266,096 residents. The Erie-Meadville combined statistical area had a population of 369,331 at the 2010 census. Erie is roughly equidistant from Buffalo and Cleveland, each being about 100 miles (160 kilometers) away. Erie's manufacturing sector remains prominent in the local economy, though insurance, healthcare, higher education, technology, service industries, and tourism are emerging as significant economic drivers. As with the other Great Lakes port cities, Erie is accessible to the oceans via the Lake Ontario and St. Lawrence River network in Canada. The local climate is humid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
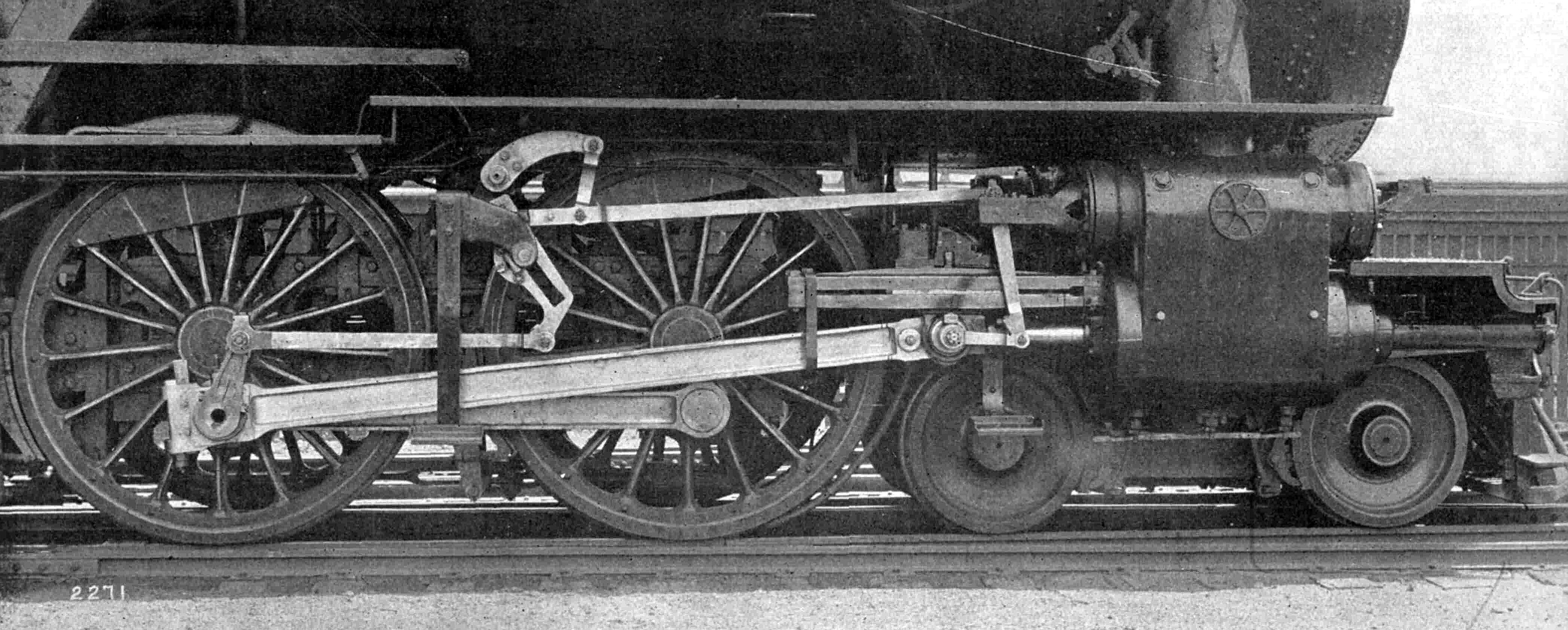
Driving Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunting locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets which are linked together within the set. Diameter Driving wheels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
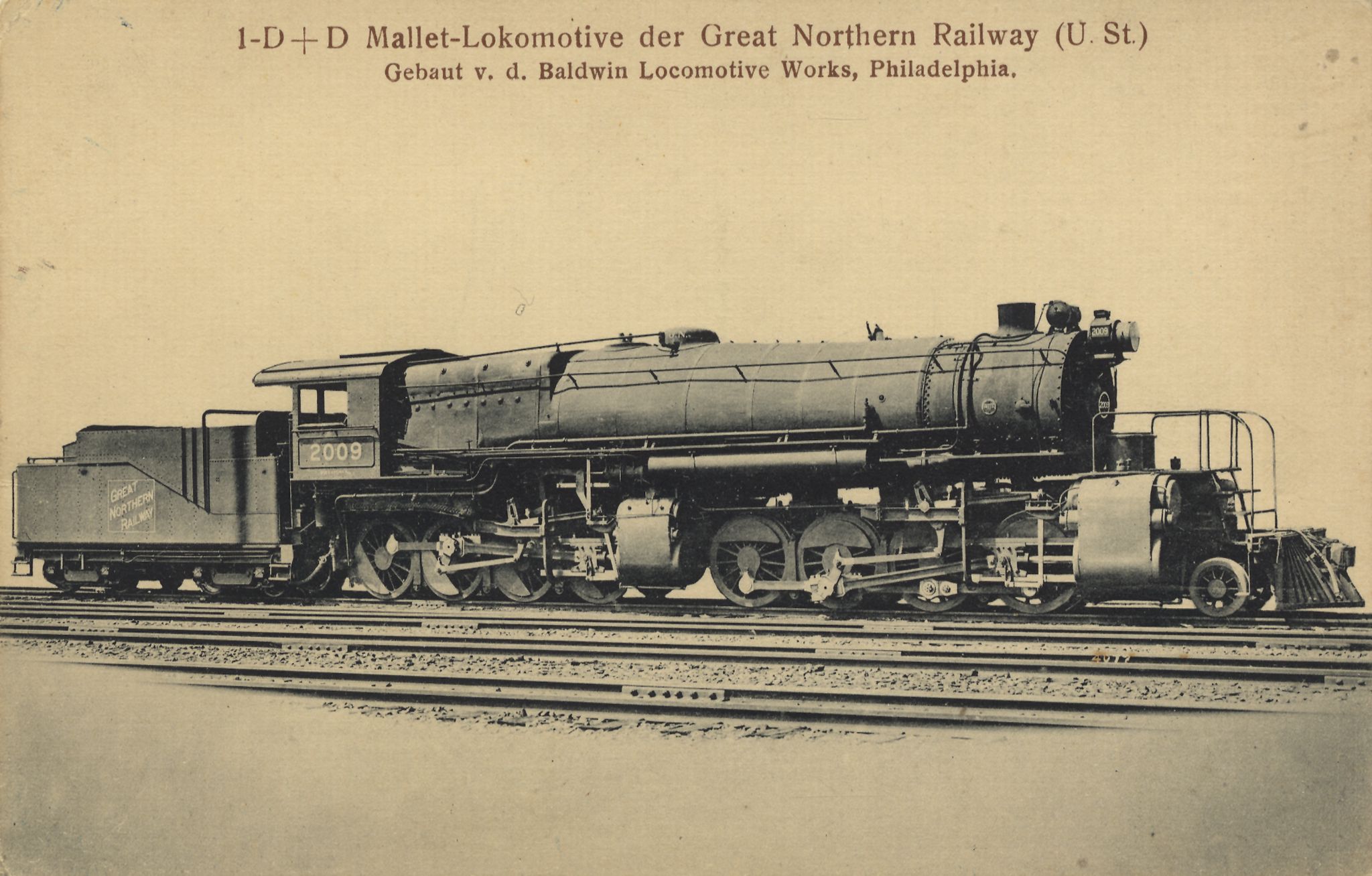
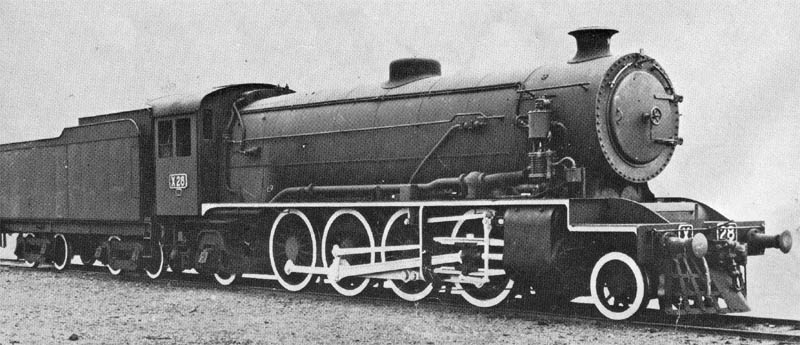
Articulated Locomotive
An articulated locomotive is a steam locomotive (rarely, an electric locomotive) with one or more engine units that can move independent of the main frame. Articulation allows the operation of locomotives that would otherwise be too large to negotiate a railroad's curves, whether mainlines or special lines with extreme curvature such as logging, industrial, or mountain railways. Articulated locomotives saw service in many nations, but were very popular on narrow-gauge railways in Europe. The largest examples were developed in the United States, where the Union Pacific Big Boy 4-8-8-4s and the Allegheny H-8 2-6-6-6s were some of the largest steam locomotives ever built. Many schemes for articulation were developed over the years. Of these, the Mallet locomotive and its simple-expansion derivative were the most popular, followed by the Garratt type (mostly built in the United Kingdom, popular throughout Europe, Africa and European colonies), and the various geared steam locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trains (magazine)
''Trains'' is a monthly magazine about trains and railroads Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ... aimed at railfan, railroad enthusiasts and railroad industry employees. The magazine primarily covers railroad happenings in the United States and Canada, but has some articles on railroading elsewhere. It is among the 11 magazines published by Kalmbach Media, based in Waukesha, Wisconsin. It was founded as ''Trains'' in 1940 by publisher Al C. Kalmbach and editorial director Linn Westcott. From October 1951 to March 1954, the magazine was named ''Trains and Travel''. Jim Wrinn, a former reporter and editor at the ''Charlotte Observer'', served as editor from 2004 until his death in 2022. Carl A. Swanson succeeded him. Editors * Al C. Kalmbach, 1940–1948 * Willard V. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
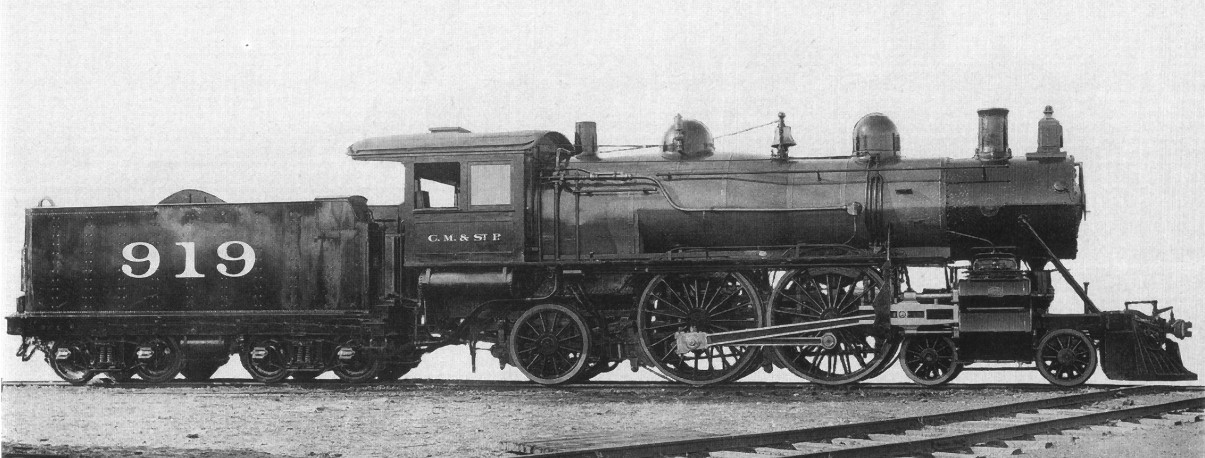
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atchison, Topeka, And Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison and Topeka, Kansas, and Santa Fe, New Mexico. The railroad reached the Kansas–Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farmland from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress. Despite being chartered to serve the city, the railroad chose to bypass Santa Fe, due to the engineering challenges of the mountainous terrain. Eventually a branch line from Lamy, New Mexico, brought the Santa Fe railroad to its namesake city. The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at various times, it operated an airline, the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway, and the fleet of Santa Fe Railroad Tugboats. Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Locomotive Company
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades the world's largest producer of steam locomotives, but struggled to compete as demand switched to diesel locomotives. Baldwin produced the last of its 70,000-plus locomotives in 1951, before merging with the Lima-Hamilton Corporation on September 11, 1951, to form the Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton Corporation. The company has no relation to the E.M. Baldwin and Sons of New South Wales, Australia, a builder of small diesel locomotives for sugar cane railroads. History: 19th century Beginning The Baldwin Locomotive Works had a humble beginning. Matthias W. Baldwin, the founder, was a jeweler and whitesmith, who, in 1825, formed a partnership with machinist David H. Mason, and engaged in the manufacture of bookbinders' tools and cylinders for cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-8-2
A 2-8-8-2, in the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangements, is an articulated locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. The equivalent UIC classification is, refined to Mallet locomotives, (1'D)D1'. These locomotives usually employ the Mallet principles of articulation—with the rear engine rigidly attached to the boiler and the front engine free to rotate—and compounding. The 2-8-8-2 was a design largely limited to American locomotive builders. The last 2-8-8-2 was retired in 1962 from the N&W's roster, two years past the ending of steam though steam was still used on steel mill lines and other railroads until 1983. Other equivalent classifications are: UIC classification: 1DD1 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) French classification: 140+041 Turkish classification: 45+45 Swiss classification: 4/5+4/5 The first 2-8-8-2 was built in 1909 by Baldwin, who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-8-0
In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-8-8-0 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and no trailing truck. These were nicknamed "Bull Mooses". Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: 1DD (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 140+040 *Turkish classification: 45+44 *Swiss classification: 4/5+4/4 The UIC classification is refined to (1'D)D for Mallet locomotives. Examples The Great Northern Railway used the 2-8-8-0s as their N-1's which were built by Baldwin in 1912. They were rebuilt by GN in 1932 as a N-2, and later re-rebuilt in 1940 as an N-3, The locomotives, after their third rebuild into a N-3, had a larger boiler and bigger tender. The N-3's served on the GN for a collective 45 years (including previous service lives as N-1 and N-2 classes), in use until retired in 1957. The Union Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. At times it was also referred to on some railroads in the United States of America as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tank Engine
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locomotive a tender holds some or all of the fuel, and may hold some water also. There are several different types of tank locomotive, distinguished by the position and style of the water tanks and fuel bunkers. The most common type has tanks mounted either side of the boiler. This type originated about 1840 and quickly became popular for industrial tasks, and later for shunting and shorter-distance main line duties. Tank locomotives have advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional locomotives that required a separate tender to carry needed water and fuel. History Origins The first tank locomotive was the ''Novelty'' that ran at the Rainhill Trials in 1829. It was an example of a ''Well Tank''. However, the more common form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |