|
Triphenylmethyl Hexafluorophosphate
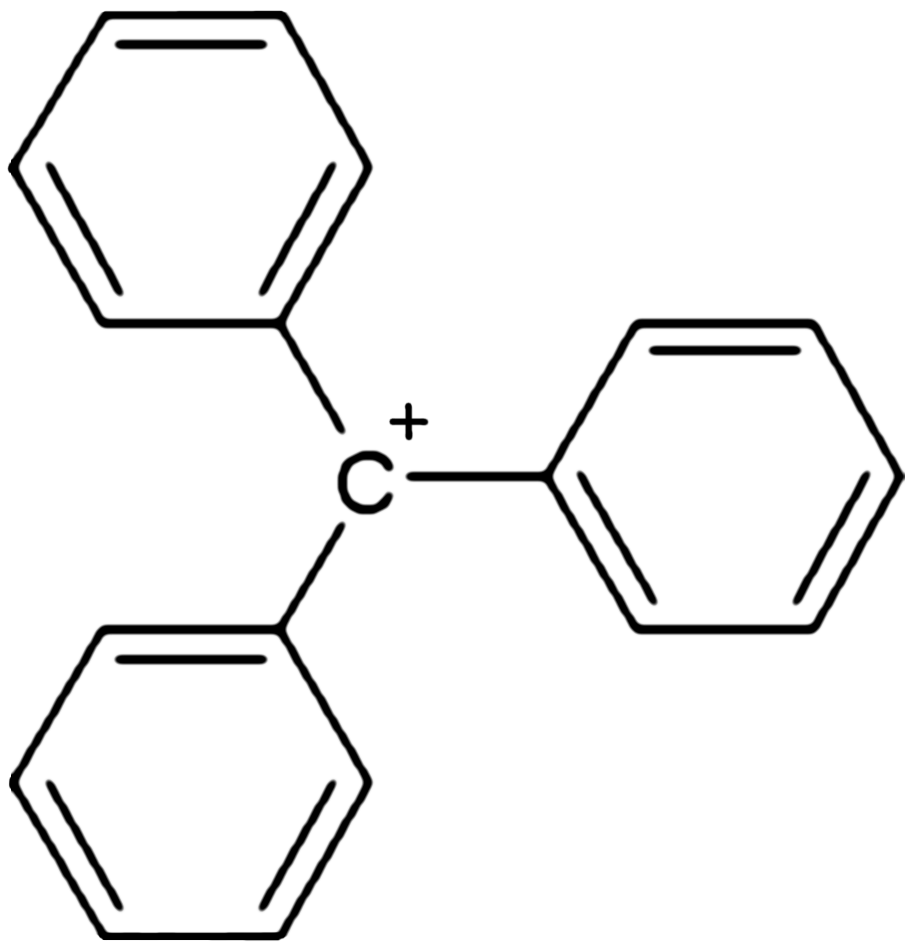
Triphenylmethyl (also triphenylcarbenium, trityl, or tritylium) hexafluorophosphate is an organic salt with the formula or , consisting of the triphenylmethyl cation and the hexafluorophosphate anion . Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is a brown powder that hydrolyzes readily to triphenylmethanol. It is used as a catalyst and reagent in organic syntheses. Preparation Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate can be prepared by combining silver hexafluorophosphate with triphenylmethyl chloride: :AgPF6 + (C6H5)3CCl → (C6H5)3CPF6 + AgCl A second method involves protonolysis of trityl hydroxide: :HPF6 + (C6H5)3COH → (C6H5)3CPF6 + H2O Structure and reactions Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate readily hydrolyzes, in a reaction that is the reverse of one of its syntheses: :(C6H5)3CPF6 + H2O → (C6H5)3COH + HPF6 Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate has been used for abstracting hydride () from organic compounds. Treatment of metal-alkene and diene complexes one can generate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Complex
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures. Examples The allyl ligand is commonly found in organometallic chemistry. Most commonly, allyl ligands bind to metals via all three carbon atoms, the η3-binding mode. The η3-allyl group is classified as an LX-type ligand in the Green LXZ ligand classification scheme, serving as a 3e– donor using neutral electron counting and 4e– donor using ionic electron counting. More common are complexes with allyl and other ligands. Examples include (η3-allyl)Mn(CO)4 and CpPd(allyl). Homoleptic complexes * bis(allyl)nickel * bis(allyl)palladium * bis(allyl)platinum *tris(allyl)chromium * tris(allyl)rhodium * tris(allyl)iridium Synthetic methods Allyl complexes are often generated by ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocations
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountered (e.g., ethylene dication ). Until the early 1970s, all carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. This nomenclature was proposed by G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called 'non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on smell, before their general chemical properties are understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation with their smell. Heteroarenes are closely related, since at least one carbon atom of CH group is replaced by one of the heteroatoms oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples of non-benzene compounds with aromatic properties are furan, a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring that includes a single oxygen atom, and pyridine, a heterocyclic compound with a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom. Hydrocarbons without an aromatic ring are called aliphatic. Benzene ring model Benzene, C6H6, is the least complex aromatic hydrocarbon, and it was the first one named as suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethyl Chloride
Triphenylmethyl chloride or trityl chloride (TrCl) is a white solid with the chemical formula C19H15Cl. It is an alkyl halide, sometimes used to introduce the trityl protecting group. Preparation Triphenylmethyl chloride is commercially available. It may be prepared by the reaction of triphenylmethanol with acetyl chloride, or by the Friedel–Crafts alkylation of benzene with carbon tetrachloride to give the trityl chloride-aluminium chloride adduct, which is then hydrolyzed. Reactions Triphenylmethylsodium can be prepared from trityl chloride dissolved in an aprotic solvent and sodium: :(C6H5)3CCl + 2 Na → (C6H5)3CNa + NaCl Reaction with silver hexafluorophosphate gives triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate. Trityl chloride reacts with zinc in nonpolar solvents (e.g. benzene) to form Gomberg's dimer.{{cite journal , last1=Gomberg , first1=M. , title=An Instance of Trivalent Carbon: Triphenylmethyl , journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society , date=1900 , volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethanol
Triphenylmethanol (also known as triphenylcarbinol, TrOH) is an organic compound. It is a white crystalline solid that is insoluble in water and petroleum ether, but well soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene. In strongly acidic solutions, it produces an intensely yellow color, due to the formation of a stable "trityl" carbocation. Many derivatives of triphenylmethanol are important dyes. History After the German chemist August Kekulé and his Belgian student Antoine Paul Nicolas Franchimont (1844–1919) first synthesized triphenylmethane in 1872, the Russian doctoral student Walerius Hemilian (1851–1914) first synthesized triphenylmethanol in 1874 by reacting triphenylmethyl bromide with water as well as by oxidizing triphenylmethane. Structure and properties Triphenylmethanol features three phenyl (Ph) rings and an alcohol group bound to a central tetrahedral carbon atom. All three C–Ph bonds are typical of ''sp''3-''sp''2 carbon-carbon bonds with lengths of appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethane
Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display fluorescence. A trityl group in organic chemistry is a triphenylmethyl group Ph3C, e.g. triphenylmethyl chloride (trityl chloride) and the triphenylmethyl radical (trityl radical). Preparation Triphenylmethane was first synthesized in 1872 by the German chemist August Kekulé and his Belgian student Antoine Paul Nicolas Franchimont (1844–1919) by heating diphenylmercury (Hg(C6H5)2, ''Quecksilberdiphenyl'') with benzal chloride (C6H5CHCl2, ''Benzylenchlorid''). Triphenylmethane can be synthesized by Friedel–Crafts reaction from benzene and chloroform with aluminium chloride catalyst: :3 C6H6 + CHCl3 → Ph3CH + 3 HCl Alternatively, benzene may react with carbon tetrachloride us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethyl Radical
The triphenylmethyl radical (often shorted to trityl radical) is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)3C. It is a persistent radical. It was the first radical ever to be described in organic chemistry. Because of its accessibility, the trityl radical has been heavily exploited. Preparation and properties It can be prepared by homolysis of triphenylmethyl chloride 1 by a metal like silver or zinc in benzene or diethyl ether. The radical 2 forms a chemical equilibrium with the quinoid-type dimer 3 (Gomberg's dimer). In benzene the concentration of the radical is 2%. Solutions containing the radical are yellow; when the temperature of the solution is raised, the yellow color becomes more intense as the equilibrium is shifted in favor of the radical (in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle). When exposed to air, the radical rapidly oxidizes to the peroxide, and the color of the solution changes from yellow to colorless. Likewise, the radical reacts with iodine to tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethyl Perchlorate
The triphenylmethyl radical (often shorted to trityl radical) is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)3C. It is a persistent radical. It was the first radical ever to be described in organic chemistry. Because of its accessibility, the trityl radical has been heavily exploited. Preparation and properties It can be prepared by homolysis of triphenylmethyl chloride 1 by a metal like silver or zinc in benzene or diethyl ether. The radical 2 forms a chemical equilibrium with the quinoid-type dimer 3 (Gomberg's dimer). In benzene the concentration of the radical is 2%. Solutions containing the radical are yellow; when the temperature of the solution is raised, the yellow color becomes more intense as the equilibrium is shifted in favor of the radical (in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle). When exposed to air, the radical rapidly oxidizes to the peroxide, and the color of the solution changes from yellow to colorless. Likewise, the radical reacts with iodine to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentadienyl Complex
In organic chemistry, pentadienyl refers to the organic radical, anion, or cation with the formula , where ''z'' = 0, −1, +1, respectively. Organometallic chemistry In organometallic chemistry, the pentadienyl anion is a ligand, the acyclic analogue of the more-common cyclopentadienyl anion. The pentadienyl anion is generated by deprotonation of pentadiene. A number of complexes are known, including bis(pentadienyl) iron, , the "open" analog of ferrocene. Only few pentadienyl complexes feature simple ligands. More common is the dimethyl derivative 2,4-. Additionally, many pentadienyl ligands are cyclic, being derived from the addition of hydride to ''η''6-arene complexes or hydride abstraction from cyclohexadiene complexes. The first pentadienyl complex to be reported was derived from protonolysis of a complex of pentadienol: :Fe(C5H7OH)(CO)3 + H+ -> e(C5H7)(CO)3 + H2O Treatment of this cation with sodium borohydride gives the pentadiene complex: : e(C5H7)(CO)3 + H- -> Fe( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Alkene Complex
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal alkene complex is a coordination compound containing one or more alkene ligands. Such compounds are intermediates in many catalytic reactions that convert alkenes to other organic products.Elschenbroich, C. ”Organometallics” (2006) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. Mono- and dialkenes are often used as ligands in stable complexes. Monoalkenes The simplest monoalkene is ethene. Many complexes of ethene are known, including Zeise's salt (see figure), Rh2Cl2(C2H4)4, Cp*2Ti(C2H4), and the homoleptic Ni(C2H4)3. Substituted monoalkene include the cyclic cyclooctene, as found in chlorobis(cyclooctene)rhodium dimer. Alkenes with electron-withdrawing groups commonly bind strongly to low-valent metals. Examples of such ligands are TCNE, tetrafluoroethylene, maleic anhydride, and esters of fumaric acid. These acceptors form adducts with many zero-valent metals. Dienes, trienes, polyenes, keto-alkenes, and other complicated alkene ligands Butadiene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylcarbenium
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an ion with formula or , consisting of a carbon atom with a positive charge connected to three phenyl groups. It is a charged version of the triphenylmethyl radical •. The name is often abbreviated to triphenylmethyl or trityl in salts, although these names also denote the chemical group in compounds like triphenylmethyl chloride that do not contain the cation. Triphenylcarbenium is a relatively stable carbenium ion, because the positive charge is partially distributed among 10 of the carbon atoms (the 3 carbon atoms in the ''ortho'' and ''para'' positions of each of the three phenyl groups, plus the central carbon atom). Derivatives The cation exists in important chemical reagents and catalysts such as triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate . Related salts are known with diverse anions including (), hexachloroantimonate (), and perchlorate (). This and other similar cations can be ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |