|
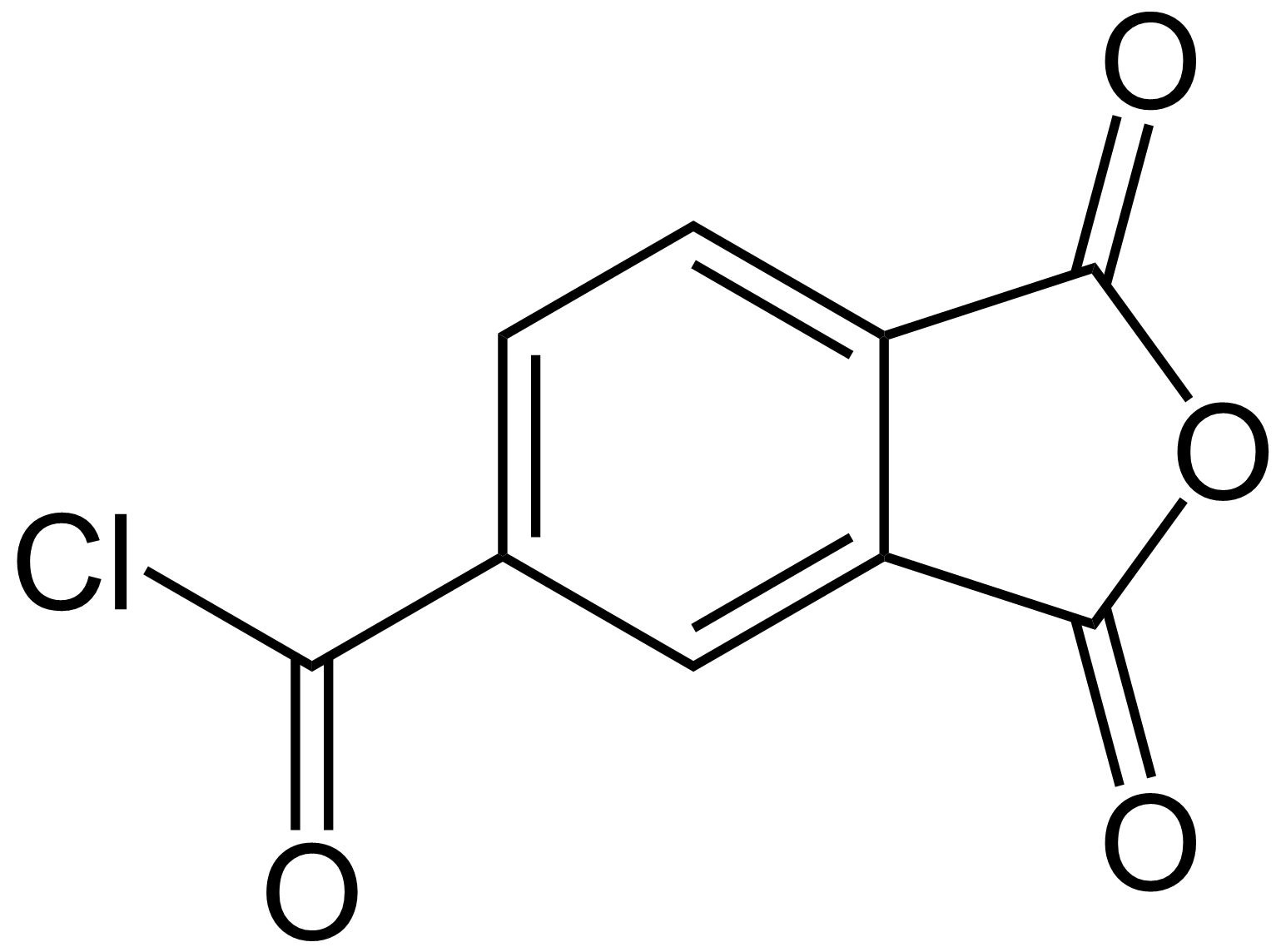
Trimellitic Acid Chloride
Trimellitic anhydride chloride is a chemical compound used to produce polyamide-imide Polyamide-imides are either thermosetting or thermoplastic, amorphous polymers that have exceptional mechanical, thermal and chemical resistant properties. Polyamide-imides are used extensively as wire coatings in making magnet wire. They are pre ... plastic. See also * Mellitic acid * Trimellitic anhydride References Acyl chlorides Phthalic anhydrides Organochlorides {{Organohalide-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyamide-imide
Polyamide-imides are either thermosetting or thermoplastic, amorphous polymers that have exceptional mechanical, thermal and chemical resistant properties. Polyamide-imides are used extensively as wire coatings in making magnet wire. They are prepared from isocyanates and TMA (trimellic acid-anhydride) in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). A prominent distributor of polyamide-imides is Solvay Specialty Polymers, which uses the trademark Torlon. Polyamide-imides display a combination of properties from both polyamides and polyimides, such as high strength, melt processibility, exceptional high heat capability, and broad chemical resistance. Polyamide-imide polymers can be processed into a wide variety of forms, from injection or compression molded parts and ingots, to coatings, films, fibers and adhesives. Generally these articles reach their maximum properties with a subsequent thermal cure process. Other high-performance polymers in this same realm are polyetheretherketones and pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mcgraw-Hill
McGraw Hill is an American educational publishing company and one of the "big three" educational publishers that publishes educational content, software, and services for pre-K through postgraduate education. The company also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. McGraw Hill operates in 28 countries, has about 4,000 employees globally, and offers products and services to about 140 countries in about 60 languages. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. Corporate History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888 when James H. McGraw, co-founder of the company, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway Appliances''. He continued to add further publications, eventually establishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellitic Acid
Mellitic acid, also called graphitic acid or benzenehexacarboxylic acid, is an acid first discovered in 1799 by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in the mineral mellite (honeystone), which is the aluminium salt of the acid. It crystallizes in fine silky needles and is soluble in water and alcohol. Preparation Mellitic acid may be prepared by warming mellite with ammonium carbonate, boiling off the excess of the ammonium salt, and adding ammonia to the solution. The precipitated alumina is filtered off, the filtrate evaporated, and the ammonium salt of the acid purified by recrystallization. The ammonium salt is then converted into the lead salt by precipitation with lead acetate, and the lead salt is then decomposed by hydrogen sulfide. The acid may also be prepared by the oxidation of pure carbon, graphite or hexamethylbenzene, by alkaline potassium permanganate in the cold, or by hot concentrated nitric acid. Reactions It is a very stable compound; chlorine, concentrated nitric a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimellitic Anhydride
Trimellitic anhydride is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ... with the formula HO2CC6H3(C2O3). It is the cyclic anhydride of trimellitic acid. Several thousand tons of this colorless solid are produced annually as a precursor to plasticizers for polyvinyl chloride. It is produced by air-oxidation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene.{{Ullmann , doi=10.1002/14356007.a05_249, title=Carboxylic Acids, Aromatic, year=2000, last1=Röhrscheid, first1=Freimund References Tricarboxylic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Chlorides
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, . Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides. Nomenclature Where the acyl chloride moiety takes priority, acyl chlorides are named by taking the name of the parent carboxylic acid, and substituting ''-yl chloride'' for ''-ic acid''. Thus: : : When other functional groups take priority, acyl chlorides are considered prefixes — ''chlorocarbonyl-'': : Properties Lacking the ability to form hydrogen bonds, acyl chlorides have lower boiling and melting points than similar carboxylic acids. For example, acetic acid boils at 118 °C, whereas acetyl chloride boils at 51 °C. Like most carbonyl compounds, infrared spectroscopy reveals a band near 1750 cm−1. The simplest s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthalic Anhydrides
Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year. Synthesis and production Phthalic anhydride was first reported in 1836 by Auguste Laurent. Early procedures involved liquid-phase mercury-catalyzed oxidation of naphthalene. The modern industrial variant process instead uses vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) as the catalyst in a gas-phase reaction with naphthalene using molecular oxygen. The overall process involves oxidative cleavage of one of the rings and loss of two of the carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. An alternative process involves oxidation of the two methy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |