|
Trilophosaurus NT Small
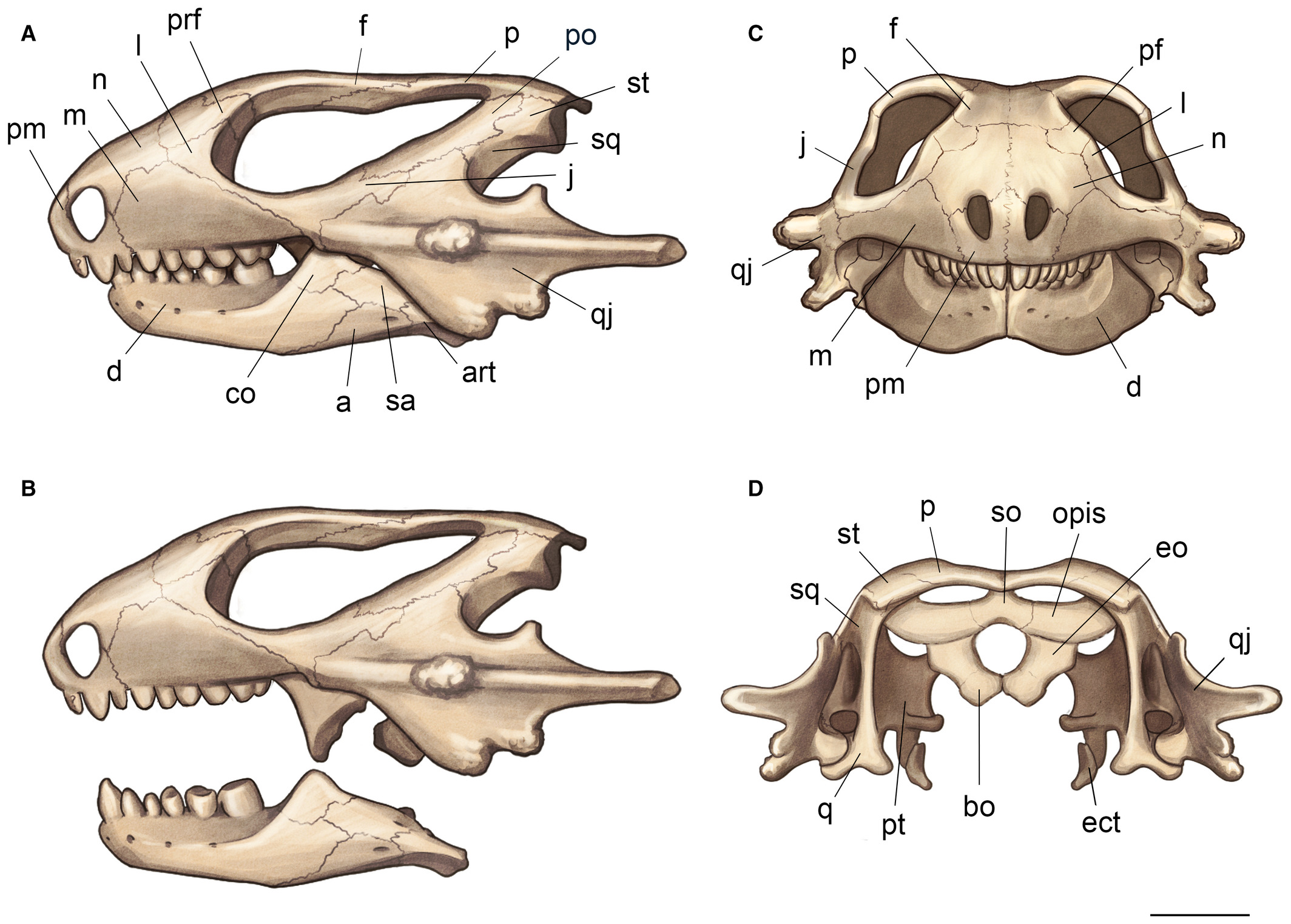
''Trilophosaurus'' (Greek for "lizard with three ridges") is a lizard-like trilophosaurid allokotosaur known from the Late Triassic of North America. It was a herbivore up to 2.5 m long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak. The skull is also unusual in that the lower temporal opening is missing, giving the appearance of a euryapsid skull. Because of this, the trilophosaurs were once classified with placodonts within Sauropterygia. Carroll (1988) suggested that the lower opening may have been lost to strengthen the skull. ''Trilophosaurus'' is traditionally thought to include two valid species: the typical ''T. buettneri'' and the more robust ''T. jacobsi''. In 1993, paleontologists Hans-Dieter Sues and Paul E. Olsen reassigned ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilophosaurus Buettneri (1)
''Trilophosaurus'' (Greek for "lizard with three ridges") is a lizard-like trilophosaurid allokotosaur known from the Late Triassic of North America. It was a herbivore up to 2.5 m long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak. The skull is also unusual in that the lower temporal opening is missing, giving the appearance of a euryapsid skull. Because of this, the trilophosaurs were once classified with placodonts within Sauropterygia. Carroll (1988) suggested that the lower opening may have been lost to strengthen the skull. ''Trilophosaurus'' is traditionally thought to include two valid species: the typical ''T. buettneri'' and the more robust ''T. jacobsi''. In 1993, paleontologists Hans-Dieter Sues and Paul E. Olsen reassigned '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allokotosauria
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivorous archosauromorphs was recovered by Sterling J. Nesbitt, John J. Flynn, Adam C. Pritchard, J. Michael Parrish, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and André R. Wyss in 2015. The name Allokotosauria is derived from Greek meaning "strange reptiles" in reference to unexpected grouping of early archosauromorph with a high disparity of features typically associated with herbivory. History Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2015) defined the group as a stem-based taxon containing ''Azendohsaurus madagaskarensis'' and '' Trilophosaurus buettneri'' and all taxa more closely related to them than to ''Tanystropheus longobardicus'', ''Proterosuchus fergusi'', ''Protorosaurus speneri'' or ''Rhynchosaurus articeps''. Therefore, Allokotosauria includes the families Azendoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analysis
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonidae
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variodens
''Variodens'' is an extinct genus of trilophosaur. Fossils have been found from the Emborough Quarries in the Mendip Hills of Somerset, England. These fossils have been uncovered from a Late Triassic fissure fill within Carboniferous-age limestone. The type and only known species is ''V. inopinatus'', named in 1957. Description ''Variodens'' is unusual among most reptiles in that it has a heterodont dentition consisting of different types of teeth. The five anteriormost teeth at the front of the jaw are simple and conical in shape. The cheek teeth toward the back of the jaw are wide and have several cusps. They are either tricuspid or multicuspid. The anterior tricuspid teeth of ''Variodens'' are narrower medially (toward the inside of the mouth) than they are laterally (toward the outside of the mouth). ''Variodens'' also has distinctive bulbous-shaped penultimate teeth. The teeth of ''Variodens'' are very similar to the postcanine teeth of the cynodont ''Cricodon'' from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricuspisaurus
''Tricuspisaurus'' is an extinct genus of reptile originally described as a trilophosaurid; it was later considered likely to be a procolophonid, but recent analyses have affirmed the original classification. Fossils are known from the Ruthin Quarry in Glamorgan, Wales, one of several Late Triassic to Early Jurassic British fissure deposits. Like some trilophosaurs, it has an edentulous, or toothless beak. ''Tricuspisaurus'' gets its name from its heterodont dentition, which includes ''tricuspid'' teeth, or teeth with three cusps. The type species, ''T. thomasi'', was named in 1957 along with the possible trilophosaur '' Variodens inopinatus'' from Somerset, England. Although originally classified as a trilophosaur, ''Tricuspisaurus'' was reclassified as a procolophonid in 1993 by paleontologists Hans-Dieter Sues and Paul E. Olsen Paul E. Olsen (born August 4, 1953) is an American paleontologist and author and co-author of a large number of technical papers. Growing up as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilophosaurus NT Small
''Trilophosaurus'' (Greek for "lizard with three ridges") is a lizard-like trilophosaurid allokotosaur known from the Late Triassic of North America. It was a herbivore up to 2.5 m long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak. The skull is also unusual in that the lower temporal opening is missing, giving the appearance of a euryapsid skull. Because of this, the trilophosaurs were once classified with placodonts within Sauropterygia. Carroll (1988) suggested that the lower opening may have been lost to strengthen the skull. ''Trilophosaurus'' is traditionally thought to include two valid species: the typical ''T. buettneri'' and the more robust ''T. jacobsi''. In 1993, paleontologists Hans-Dieter Sues and Paul E. Olsen reassigned ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert L
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)