|
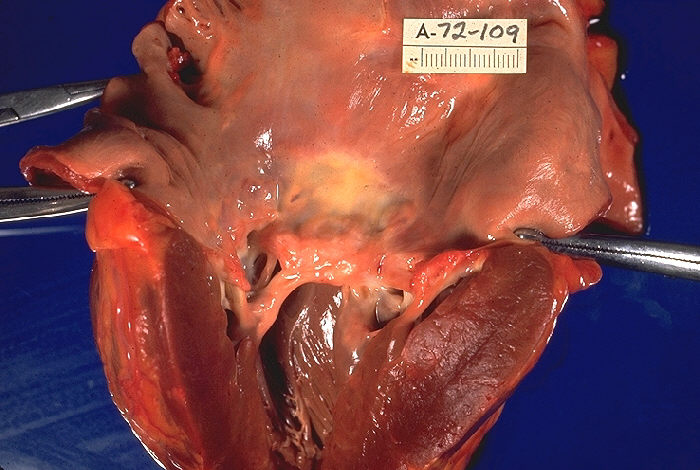
Trilogy Of Fallot
The Trilogy of Fallot also called Fallot's trilogy is a rare congenital heart disease consisting of the following defects: pulmonary valve stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy and atrial septal defect. It occurs in 1.2% of all congenital heart defects. A 1960 case report of 22 patients who underwent surgery showed an excess of females with a ratio of 3:2, with the youngest person being 7 months old and the oldest being 50 years old. Symptoms and signs Mechanism Trilogy of Fallot is a combination of three congenital heart defects: pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an atrial septal defect. The first two of these are also found in the more common tetralogy of Fallot. However, the tetralogy has a ventricular septal defect instead of an atrial one, and it also involves an overriding aorta The Three Malformations Diagnosis Diagnosis is done via echocardiography or angiography. Treatment It is treated using surgery to repair the atrial septal defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasternal Heave
A parasternal heave, lift, or thrust is a precordial impulse that may be felt (palpated) in patients with cardiac or respiratory disease. Precordial impulses are visible or palpable pulsations of the chest wall, which originate on the heart or the great vessels. __TOC__ Technique A parasternal impulse may be felt when the heel of the hand is rested just to the left of the sternum with the fingers lifted slightly off the chest. Normally no impulse or a slight inward impulse is felt. The heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. Palpation with the fingers over the pulmonary area may reveal the palpable tap of pulmonary valve closure (palpable P2) in cases of pulmonary hypertension. Interpretation Parasternal heave occurs during right ventricular hypertrophy (i.e. enlargement) or very rarely severe left atrial enlargement. This is due to the position of the heart within the chest: the right ventricle is most anterior (closest to the chest wall). Hypertrophy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Heart Valve
An artificial heart valve is a one-way valve implanted into a person's heart to replace a heart valve that is not functioning properly (valvular heart disease). Artificial heart valves can be separated into three broad classes: mechanical heart valves, bioprosthetic tissue valves and engineered tissue valves. The human heart contains four valves: tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve and aortic valve. Their main purpose is to keep blood flowing in the proper direction through the heart, and from the heart into the major blood vessels connected to it (the pulmonary artery and the aorta). Heart valves can malfunction for a variety of reasons, which can impede the flow of blood through the valve ( stenosis) and/or let blood flow backwards through the valve ( regurgitation). Both processes put strain on the heart and may lead to serious problems, including heart failure. While some dysfunctional valves can be treated with drugs or repaired, others need to be replaced wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Surgery
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to correct congenital heart disease; or to treat valvular heart disease from various causes, including endocarditis, Rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation. History 19th century The earliest operations on the pericardium (the sac that surrounds the heart) took place in the 19th century and were performed by Francisco Romero (surgeon), Francisco Romero (1801) in the city of Almería (Spain), Dominique Jean Larrey (1810), Henry Dalton (1891), and Daniel Hale Williams (1893). The first surgery on the heart itself was performed by Axel Cappelen on 4 September 1895 at Rikshospitalet in Kristiania, now Oslo. Cappelen ligature (medicine), ligated a bleeding coronary circulation, coronary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Insufficiency
Pulmonary (or pulmonic) insufficiency (or incompetence, or regurgitation) is a condition in which the pulmonary valve is incompetent and allows backflow from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle of the heart during diastole. While a small amount of backflow may occur ordinarily, it is usually only shown on an echocardiogram and is harmless. More pronounced regurgitation that is noticed through a routine physical examination is a medical sign of disease and warrants further investigation. If it is secondary to pulmonary hypertension it is referred to as a Graham Steell murmur. Signs and symptoms Because pulmonic regurgitation is the result of other factors in the body, any noticeable symptoms are ultimately caused by an underlying medical condition rather than the regurgitation itself. However, more severe regurgitation may contribute to right ventricular enlargement by dilation, and in later stages, right heart failure. A diastolic decrescendo murmur can sometimes be ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Valve Repair
Heart valve repair is a cardiac surgery procedure, carried out to repair one or more faulty heart valves. In some valvular heart diseases repair where possible is preferable to valve replacement. A mechanical heart valve is a replacement valve that is not itself subject to repair. General Valvuloplasty is the widening of a stenotic valve using a balloon catheter. Types include: * Aortic valvuloplasty in repair of a stenotic aortic valve * Mitral valvuloplasty in the correction of an uncomplicated mitral Valvulotomy Commissurotomy of heart valves is called a valvulotomy. By valve Mitral valve repair ''Mitral valve repair'' is mainly used to treat stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage) of the mitral valve. Aortic valve repair Aortic valve repair is a surgical procedure used to correct some aortic valve disorders as an alternative to aortic valve replacement. Aortic valve repair is performed less often and is more technically difficult than mitral valve repair. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. The word itself comes from the Greek words ἀγγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular imaging techniques such as CO2 angiography, CT angiography and MR angiography. The term ''isotope a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interatrial Septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart. Structure The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at angle of 65 degrees from right posterior to left anterior because right atrium is located at the right side of the body while left atrium is located at the left side of the body. Development The interatrial septum forms during the first and second months of fetal development. Formation of the septum occurs in several stages. The first is the development of the septum primum, a crescent-shaped piece of tissue forming the initial divider between the right and left atria. Because of its crescent shape, the septum primum does not fully occlude the space between the left and right atria; the opening that remains is called the ostium primum. During fetal development, this opening allows blood to be shunted from the right atrium to the left. As the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the lower-end of the heart and it receives blood from the right atrium and pumps blood into the lungs. Since RVH is an enlargement of muscle it arises when the muscle is required to work harder. Therefore, the main causes of RVH are pathologies of systems related to the right ventricle such as the pulmonary artery, the tricuspid valve or the airways. RVH can be benign and have little impact on day-to-day life or it can lead to conditions such as heart failure, which has a poor prognosis. Signs and symptoms Symptoms Although presentations vary, individuals with right ventricular hypertrophy can experience symptoms that are associated with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and/or a reduced cardiac output. These include: * Difficulty breathing on exertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too narrow, leading to a reduction of flow of blood to the lungs. While the most common cause of pulmonary valve stenosis is congenital heart disease, it may also be due to a malignant carcinoid tumor. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are forms of pulmonic stenosis (nonvalvular and valvular, respectively) but pulmonary valve stenosis accounts for 80% of pulmonic stenosis. PVS was the key finding that led Jacqueline Noonan to identify the syndrome now called Noonan syndrome. Symptoms and signs Among some of the symptoms consistent with pulmonary valve stenosis are the following: * Heart murmur * Cyanosis * Dyspnea * Dizziness * Upper thorax pain * Developmental disorders Cause In regards to the cause of pul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overriding Aorta
An overriding aorta is a congenital heart defect where the aorta is positioned directly over a ventricular septal defect (VSD), instead of over the left ventricle. The result is that the aorta receives some blood from the right ventricle, causing mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, and thereby reducing the amount of oxygen delivered to the tissues. It is one of the four findings in the classic tetralogy of Fallot Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are: *pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the ri .... The other three findings are right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) obstruction (most often subpulmonary stenosis), right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), and ventricular septal defect (VSD). References External links Congenital heart defects {{circulatory-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |