|
Trictrac Lenain
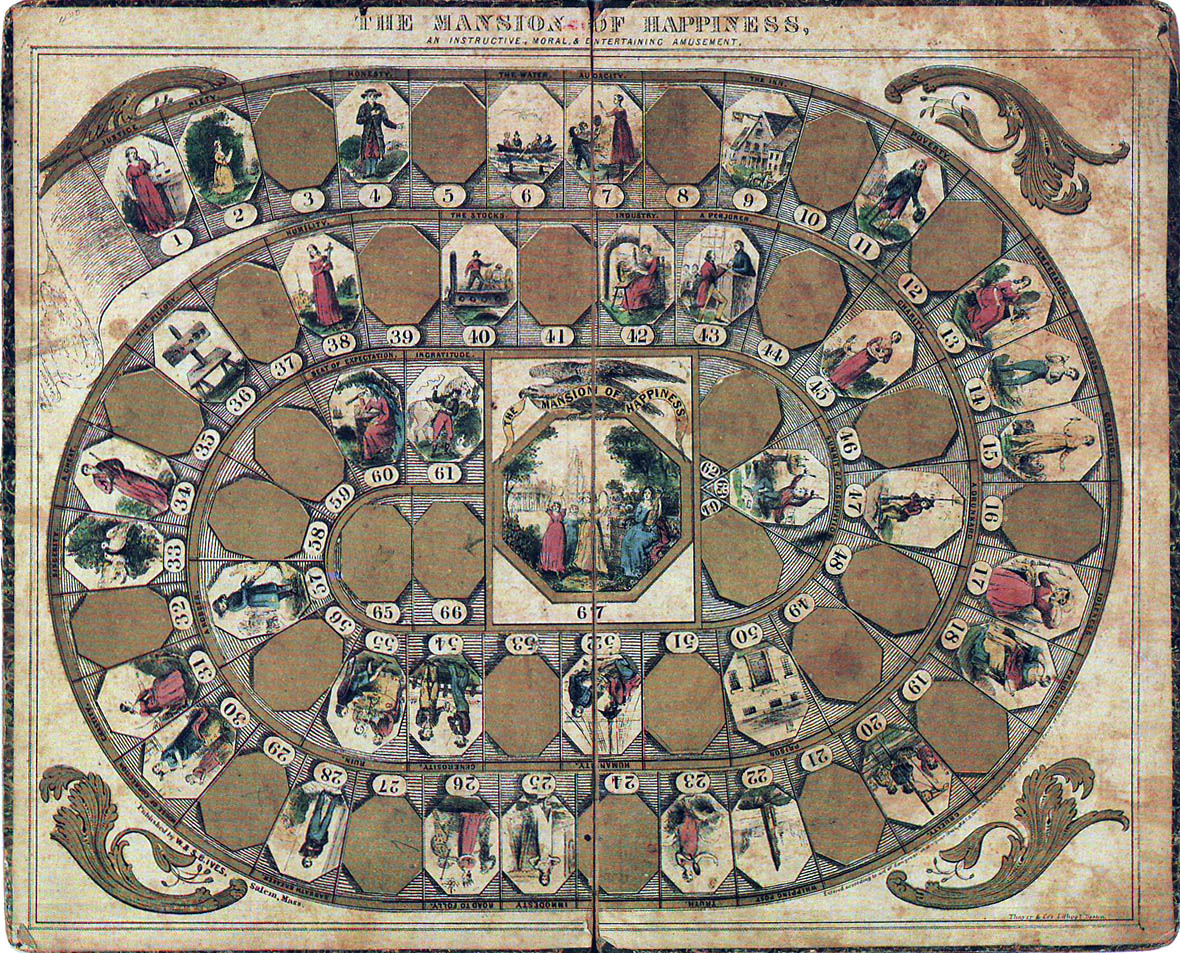
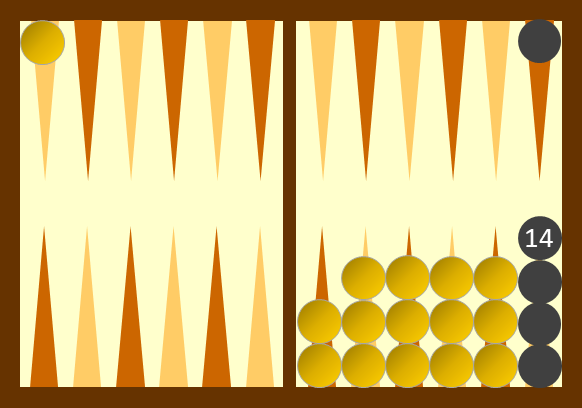
Trictrac is a French board game of skill and chance for two players that is played with dice on a game board similar, but not identical, to that of backgammon. It was "the classic tables game" of France in the way that backgammon is in the English-speaking world.Parlett (1999), p. 86. Trictrac's gaming interest lies in its multiple combinations, the importance of decision-making and its comprehensive rules which have been well documented and remained stable since the early 17th century. It requires constant attention from the players whether or not it is their turn. Its vocabulary, which is very rich, frequently occurs in French literature. The object of the game is not to get out the men as quickly as possible as in jacquet or backgammon, but to score as many points as possible. The game usually ends before all the men have been borne off. The name is sometimes spelt tric trac or tric-trac. History Trictrac was very popular in France at the royal court and in aristocratic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. '' Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as ''Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in ''Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, and distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laquet
Laquet is an historical Castilian tables game that was described as a new game in the 13th century. It may be the ancestor of Jacquet. Unlike Backgammon and most other tables games, it has an asymmetrical starting position; only three of the four quadrants are used and the pieces may not be 'hit'.''Laquet'' at the ''Salon des Jeux''. Retrieved 12 November 2021. History Laquet is described in the '''', a game book written for King Alfonso of Castile between 1251 and 1283. It was described as being a "new game". It shares with the much later French game of Jacquet the |
Trictrac Lenain
Trictrac is a French board game of skill and chance for two players that is played with dice on a game board similar, but not identical, to that of backgammon. It was "the classic tables game" of France in the way that backgammon is in the English-speaking world.Parlett (1999), p. 86. Trictrac's gaming interest lies in its multiple combinations, the importance of decision-making and its comprehensive rules which have been well documented and remained stable since the early 17th century. It requires constant attention from the players whether or not it is their turn. Its vocabulary, which is very rich, frequently occurs in French literature. The object of the game is not to get out the men as quickly as possible as in jacquet or backgammon, but to score as many points as possible. The game usually ends before all the men have been borne off. The name is sometimes spelt tric trac or tric-trac. History Trictrac was very popular in France at the royal court and in aristocratic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Willughby
Francis Willughby (sometimes spelt Willoughby, la, Franciscus Willughbeius) FRS (22 November 1635 – 3 July 1672) was an English ornithologist and ichthyologist, and an early student of linguistics and games. He was born and raised at Middleton Hall, Warwickshire, the only son of an affluent country family. He was a student at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he was tutored by the mathematician and naturalist John Ray, who became a lifetime friend and colleague, and lived with Willughby after 1662 when Ray lost his livelihood through his refusal to sign the Act of Uniformity. Willughby was elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1661, then aged 27. Willughby, Ray, and others such as John Wilkins were advocates of a new way of studying science, relying on observation and classification, rather than the received authority of Aristotle and the Bible. To this end, Willughby, Ray and their friends undertook a number of journeys to gather information and specimens, ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Cotton
Charles Cotton (28 April 1630 – 16 February 1687) was an English poet and writer, best known for translating the work of Michel de Montaigne from the French, for his contributions to ''The Compleat Angler'', and for the influential ''The Compleat Gamester'' attributed to him. Early life He was born in Alstonefield, Staffordshire, at Beresford Hall, near the Derbyshire Peak District. His father, Charles Cotton the Elder, was a friend of Ben Jonson, John Selden, Sir Henry Wotton and Izaak Walton. The son was apparently not sent to university, but was tutored by Ralph Rawson, one of the fellows ejected from Brasenose College, Oxford, in 1648. Cotton travelled in France and perhaps in Italy, and at the age of twenty-eight he succeeded to an estate greatly encumbered by lawsuits during his father's lifetime. Like many Royalist gentlemen after the English Civil War the rest of his life was spent chiefly in quiet country pursuits, in Cotton's case in the Peak District and North Staf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Centre For Textual And Lexical Resources
The (CNRTL) ( en, National Center of Textual and Lexical Resources) is a French organisation which publishes linguistic data and information online. History and description The CNRTL was created by the management of the department ''Homme et Société'' and the management of the scientific information of the CNRS, based on the UMR of the (ATILF) of the Nancy 2 University, which developed the (TLFi). This project is incorporated into the European project CLARIN. The database In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases sp ... is expanded with the help of voluntary sources who wish to make viable and release linguistic content and who accept the charter produced by the CNRTL. If necessary, the CNRTL can contribute to the formatting of the information available online. The contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bocage
Bocage (, ) is a terrain of mixed woodland and pasture characteristic of parts of Northern France, Southern England, Ireland, the Netherlands and Northern Germany, in regions where pastoral farming is the dominant land use. ''Bocage'' may also refer to a small forest, a decorative element of leaves, or a type of rubble-work, comparable with the English use of "rustic" in relation to garden ornamentation. In the decorative arts, especially porcelain, it refers to a leafy screen spreading above and behind figures. Though found on continental figures, it is something of an English speciality, beginning in the mid-18th century, especially in Chelsea porcelain, and later spreading to more downmarket Staffordshire pottery figures. In English, ''bocage'' refers to a terrain of mixed woodland and pasture, with fields and winding country lanes sunken between narrow low ridges and banks surmounted by tall thick hedgerows that break the wind but also limit visibility. It is the sort o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of Middle Ages, medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area (french: functional area (France), aire d'attraction) is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coquimbert
Reversis, or more rarely, Réversi, is a very old trick-taking card game of the Hearts group whose origin is supposed to be Italian, transformed into Spain and then in France. It is considered one of the two probable ancestors of Hearts, Black Lady and Black Maria, the other being ''Coquimbert'' or ''Coquinbert''. It was very popular with the French aristocracy in the 17th and 18th centuries, and much played elsewhere, except in Britain. Initially quite simple, the game eventually developed into an elaborate affair involving vast quantities of counters and a complex system of pools and side-payments. Its name may have possibly come from the reverse order and construction of the game itself, or even from its exceptional slam which, like "shooting the moon" in Black Lady, reverses the entire aim of the game. History The game of Reversis was first mentioned in France in 1601, under the name Reversin, played with a 52-card pack and is the subject of a poem written around 1611 by Anto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table De Tric-trac (Paris Vers 1785) - Musée Des Arts Décoratifs (Paris) 20210629 153520
Table may refer to: * Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs * Table (landform), a flat area of land * Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns * Table (database), how the table data arrangement is used within databases * Calligra Tables, a spreadsheet application * Mathematical table * Table (parliamentary procedure) * Tables (board game) * Table, surface of the sound board (music) of a string instrument * ''Al-Ma'ida'', the fifth ''surah'' of the Qur'an, usually translated as “The Table” * Water table See also * Spreadsheet, a computer application * Table cut, a type of diamond cut * The Table (other) * Table Mountain (other) * Table Rock (other) * Tabler (other) * Tablet (other) Tablet may refer to: Medicine * Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill" Computing * Tablet computer, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliothèque Nationale De France
The Bibliothèque nationale de France (, "National Library of France"; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris. It is the national repository of all that is published in France and also holds extensive historical collections. History The National Library of France traces its origin to the royal library founded at the Louvre Palace by Charles V in 1368. Charles had received a collection of manuscripts from his predecessor, John II, and transferred them to the Louvre from the Palais de la Cité. The first librarian of record was Claude Mallet, the king's valet de chambre, who made a sort of catalogue, ''Inventoire des Livres du Roy nostre Seigneur estans au Chastel du Louvre''. Jean Blanchet made another list in 1380 and Jean de Bégue one in 1411 and another in 1424. Charles V was a patron of learning and encouraged the making and collection of books. It is known that he employed Nicholas Oresme, Raoul de Presle and others to transcribe ancient texts. At the dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliothèque Nationale De France
The Bibliothèque nationale de France (, 'National Library of France'; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris on two main sites known respectively as ''Richelieu'' and ''François-Mitterrand''. It is the national repository of all that is published in France. Some of its extensive collections, including books and manuscripts but also precious objects and artworks, are on display at the BnF Museum (formerly known as the ) on the Richelieu site. The National Library of France is a public establishment under the supervision of the Ministry of Culture. Its mission is to constitute collections, especially the copies of works published in France that must, by law, be deposited there, conserve them, and make them available to the public. It produces a reference catalogue, cooperates with other national and international establishments, and participates in research programs. History The National Library of France traces its origin to the royal library founded at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_MET_DP-12374-056_(cropped).jpg)
