|
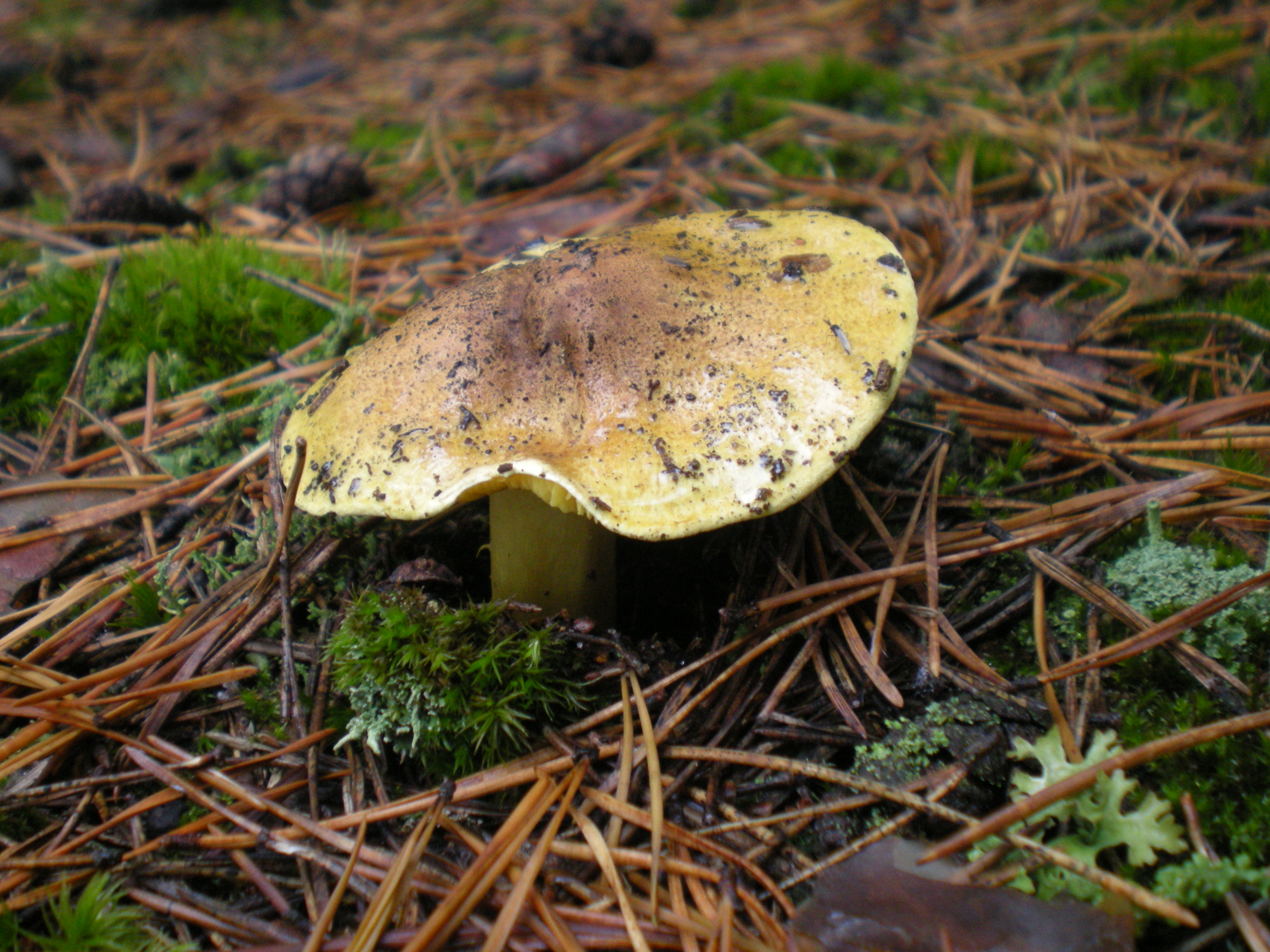
Tricholoma Aurantium
''Tricholoma aurantium'', commonly known as the golden orange tricholoma, is a mushroom of the agaric genus ''Tricholoma''. Originally described by Jacob Christian Schäffer in 1774, it was transferred to the genus ''Tricholoma'' by Adalbert Ricken in 1915. Description The cap is broadly convex to more or less flat, measuring wide with an margin that is initially rolled inward. Fresh specimens are sticky or slimy. The cap color is orange to dull reddish-orange. Parts that have been handled bruise dark red. The surface texture ranges from smooth to covered with scattered appressed fibrils and scales. The closely spaced gills are whitish, but develop brownish to reddish-brown stains in maturity. They are narrowly attached to the stipe, sometimes by a notch. The often hollow stipe measures long by thick, and is either roughly the same width throughout, or tapers slightly to the base. Its surface is covered with dense orangish scales that terminate in a line near the top of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Wallichiana
''Pinus wallichiana'' is a coniferous evergreen tree native to the Himalaya, Karakoram and Hindu Kush mountains, from eastern Afghanistan east across northern Pakistan and north west India to Yunnan in southwest China. It grows in mountain valleys at altitudes of 1800–4300 m (rarely as low as 1200 m), reaching in height. It favours a temperate climate with dry winters and wet summers. In Pashto, it is known as ''Nishtar''. This tree is often known as Bhutan pine, (not to be confused with the recently described Bhutan white pine, '' Pinus bhutanica'', a closely related species). Other names include blue pine, Himalayan pine and Himalayan white pine. Description The leaves ("needles") are in fascicles (bundles) of five and are 12–18 cm long. They are noted for being flexible along their length, and often droop gracefully. The cones are long and slender, 16–32 cm, yellow-buff when mature, with thin scales; the seeds are 5–6 mm long with a 20–30&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of North America
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of Europe
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of Asia
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1774
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MycoBank
MycoBank is an online database, documenting new mycological names and combinations, eventually combined with descriptions and illustrations. It is run by the Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute in Utrecht. Each novelty, after being screened by nomenclatural experts and found in accordance with the ICN ( International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants), is allocated a unique MycoBank number before the new name has been validly published. This number then can be cited by the naming author in the publication where the new name is being introduced. Only then, this unique number becomes public in the database. By doing so, this system can help solve the problem of knowing which names have been validly published and in which year. MycoBank is linked to other important mycological databases such as ''Index Fungorum'', Life Science Identifiers, Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and other databases. MycoBank is one of three nomenclatural repositories r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tricholoma Species
This is a list of species in the agaric genus ''Tricholoma''. , Index Fungorum lists 379 species in the genus. __NOTOC__ A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V U W X Y Z A *'' Tricholoma abietinum'' Velen. 1920 – Europe *''Tricholoma acerbum'' (Bull.) Quél. 1872 *'' Tricholoma acicularum'' Velen. 1947 *'' Tricholoma acutistramineum'' Corner 1994 – Singapore *'' Tricholoma aeruginascens'' Corner 1994 *'' Tricholoma aestivum'' Velen. 1920 – Europe *''Tricholoma aestuans'' (Fr.) Gillet 1874 *'' Tricholoma albatum'' Velen. 1920 – Europe *'' Tricholoma albidulum'' N.Ayala, G.Moreno & Esteve-Rav. 1997 *''Tricholoma albidum'' Bon 1984 *''Tricholoma albobrunneum'' (Pers.) P.Kumm. 1871 *'' Tricholoma alboconicum'' (J.E.Lange) Clémençon 1983 *'' Tricholoma alboluteum'' Velen. 1920 – Europe *''Tricholoma albosquamulatum'' Beeli 1927 * ''Tricholoma album'' (Schaeff.) P.Kumm. 1871 *'' Tricholoma altaicum'' Singer 1943 *''Tricholoma amplum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of North American Tricholoma
This is a list of ''Tricholoma'' species found in North America. *'' Tricholoma acre'' *''Tricholoma aestuans'' *''Tricholoma albidum'' *''Tricholoma apium'' - scented knight *''Tricholoma argenteum'' *''Tricholoma arvernense'' *''Tricholoma atrodiscum'' *''Tricholoma atrosquamosum'' - dark scaled knight *'' Tricholoma atroviolaceum'' *'' Tricholoma aurantio-olivaceum'' *''Tricholoma aurantium'' - orange knight *''Tricholoma caligatum'' *'' Tricholoma cingulatum'' - girdled knight *'' Tricholoma colossus'' - giant knight *'' Tricholoma davisiae'' *'' Tricholoma dryophilum'' *''Tricholoma equestre'' - yellow knight *'' Tricholoma farinaceum'' *''Tricholoma floridanum'' *'' Tricholoma focale'' - booted knight *''Tricholoma fracticum'' *''Tricholoma fulvimarginatum'' *''Tricholoma fulvum'' - birch knight *''Tricholoma fumosoluteum'' *''Tricholoma griseoviolaceum'' *''Tricholoma hordum'' *''Tricholoma huronense'' *''Tricholoma imbricatum'' - matt knight *''Tricholoma inamoenum'' *''Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
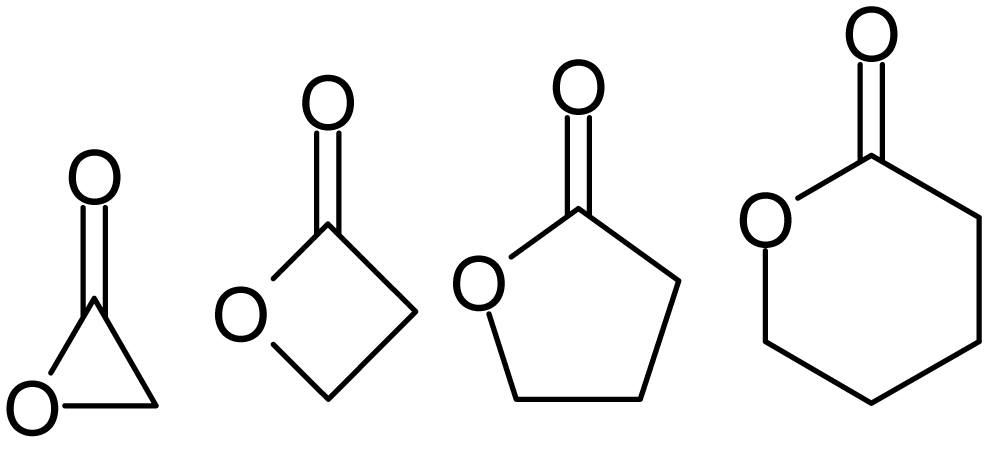
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diterpene
Diterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and antiinflammatory. Structures As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. Biosynthesis Diterpenes are derived from the addition of one IPP unit to FPP to form geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate (GGPP). From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P450. Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geranylger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |