|
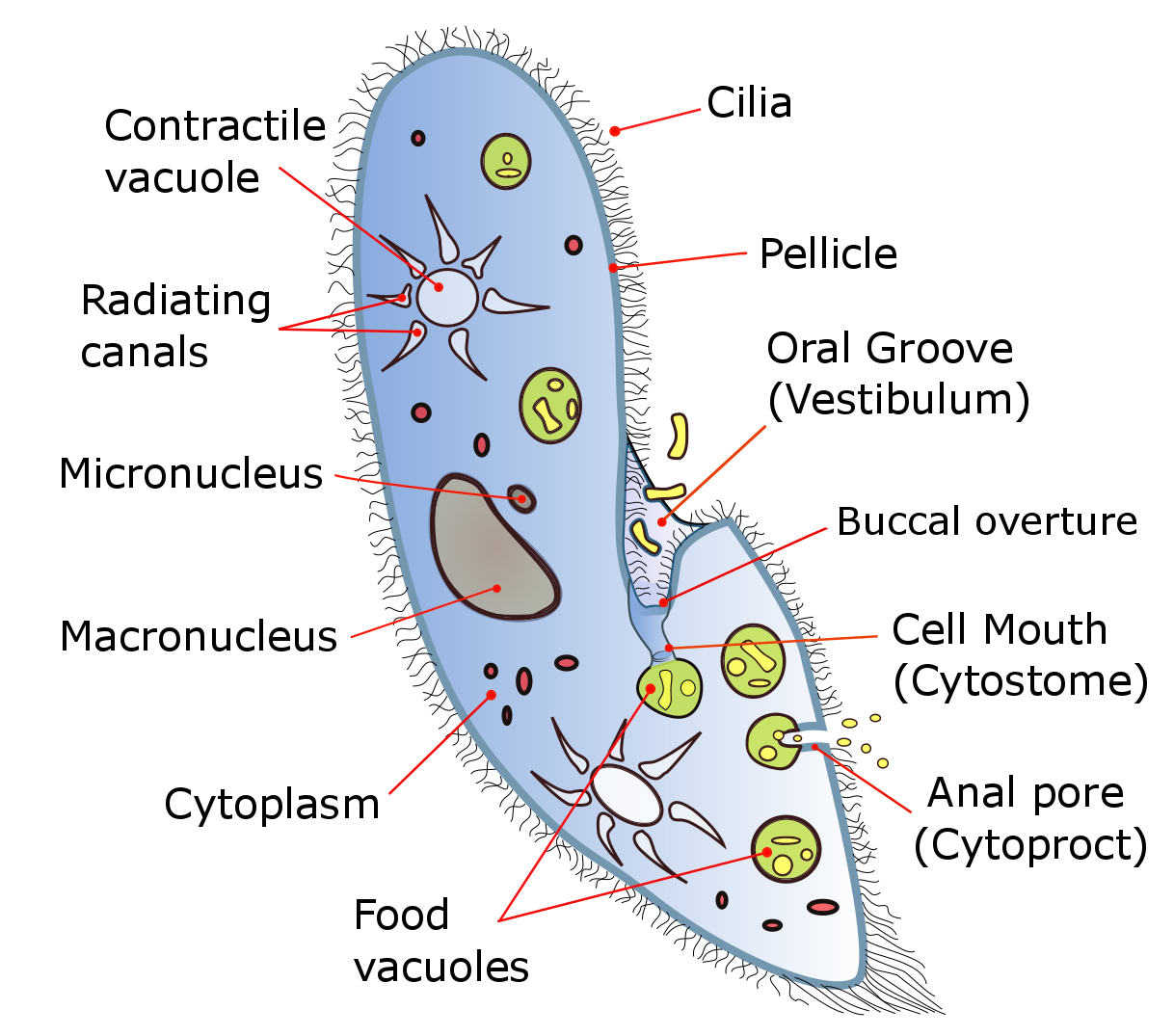
Trichodinidae
Trichodinidae is a family of ciliates of the order Mobilida, class Oligohymenophorea. Members of the family are ectoparasites (or, alternatively, ectocommensals) of a wide variety of aquatic organisms, including fish, amphibians, hydrozoans, molluscs and crustaceans. Suggestion from an anonymous editor: Trichodina actually infect Hydra too, so someone needs to add that in, along with a citation. Genera The family consists of four genera. * '' Dipartiella'' Stein, 1961 * '' Paratrichodina'' Lom, 1963 * ''Trichodina Trichodina is a genus of ciliate alveolates that is ectocommensal or parasitic on aquatic animals, particularly fish. They are characterised by the presence of a ring of interlocking cytoskeletal denticles, which provide support for the cell an ...'' Ehrenberg, 1830 * '' Trichodinella'' Srámek-Husek, 1953 References * Oligohymenophorea Parasitic alveolates Ciliate families {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobilida
Mobilida is a group of parasitic or symbiotic peritrich ciliates, comprising more than 280 species. Mobilids live on or within a wide variety of aquatic organisms, including fish, amphibians, molluscs, cnidarians, flatworms and other ciliates, attaching to their host organism by means of an aboral adhesive disk. Some mobilid species are pathogens of wild or farmed fish, causing severe and economically damaging diseases such as trichodinosis. Morphology and Feeding As the name suggests, mobilida cells are mobile, capable of moving about on the body of a host organism, and of swimming between hosts. This sets them apart from the predominantly sessile peritrichs of the order Sessilida, such as Vorticella and Epistylis, which, during the feeding, or vegetative, phase of the life cycle remain attached to submerged surfaces, often by means of a stalk. Like all peritrichs, the mobilids possess a spiral wreathe of cilia running counterclockwise around the oral region (peristome), at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipartiella
''Dipartiella'' is a genus of marine Eukaryotes from the family Trichodinidae Trichodinidae is a family of ciliates of the order Mobilida, class Oligohymenophorea. Members of the family are ectoparasites (or, alternatively, ectocommensals) of a wide variety of aquatic organisms, including fish, amphibians, hydrozoans, mol .... There are two species, '' Dipartiella Simplex'' and '' Dipartiella Stein'', both of which can be found in edible fish.Kazubski, S.L.Redescription of trichodinid Dipartiella simplex (Raabe, 1959) (Ciliophora: Peritrichida) and remarks on the genus Dipartiella Stein, 19611/ref> References {{Taxonbar, from=Q25362124 Oligohymenophorea Ciliate genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodina
Trichodina is a genus of ciliate alveolates that is ectocommensal or parasitic on aquatic animals, particularly fish. They are characterised by the presence of a ring of interlocking cytoskeletal denticles, which provide support for the cell and allow for adhesion to surfaces including fish tissue. Taxonomy Trichodinids are members of the peritrichous ciliates, a paraphyletic group within the Oligohymenophorea. Specifically, they are mobiline peritrichs because they are capable of locomotion, as opposed to sessiline peritrichs such as ''Vorticella'' and ''Epistylis'', which adhere to the substrate via a stalk or lorica. There are over 150 species in the genus ''Trichodina''. '' Trichodinella'', '' Tripartiella'', '' Hemitrichodina'', '' Paratrichodina'' and '' Vauchomia'' are similar genera. Morphology Trichodinids are round ciliates that may be disc-shaped or hemispherical. The cytostome (cell mouth) is on the surface that faces away from the host; this is termed the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramacronucleata
Intramacronucleata is a subphylum of ciliates. The group is characterized by the manner in which division of the macronucleus is accomplished during binary fission of the cell. In ciliates of this subphylum, division of the macronucleus is achieved by the action of microtubules which are assembled ''inside'' the macronucleus itself. This is in contrast to heterotrich The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are ... ciliates of the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora, in which division of the macronucleus relies on microtubules formed ''outside'' the macronuclear envelope. References * * External links * Ciliate taxonomy Bikont subphyla {{Ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligohymenophorea
The Oligohymenophorea are a large class of ciliates. There is typically a ventral groove containing the mouth and distinct oral cilia, separate from those of the body. These include a paroral membrane to the right of the mouth and membranelles, usually three in number, to its left. The cytopharynx is inconspicuous and never forms the complex cyrtos found in similar classes. Body cilia generally arise from monokinetids, with dikinetids occurring in limited distribution over part of the body. In most groups the body cilia are uniform and often dense, while the oral cilia are inconspicuous and sometimes reduced, but among the peritrichs almost the opposite is the case. Members are widely distributed, and include many free-living (typically fresh-water, but many marine) and symbiotic forms. Most are microphagous, grazing on smaller organisms swept into the mouth by the cilia, but various other feeding habits occur. In one group, the astomes, the mouth and associated structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits, and parasitoidism, which is similar to parasitism but the parasitoid has a free-living state and instead of just harming its host, it eventually ends up killing it. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fishes. Remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |