|
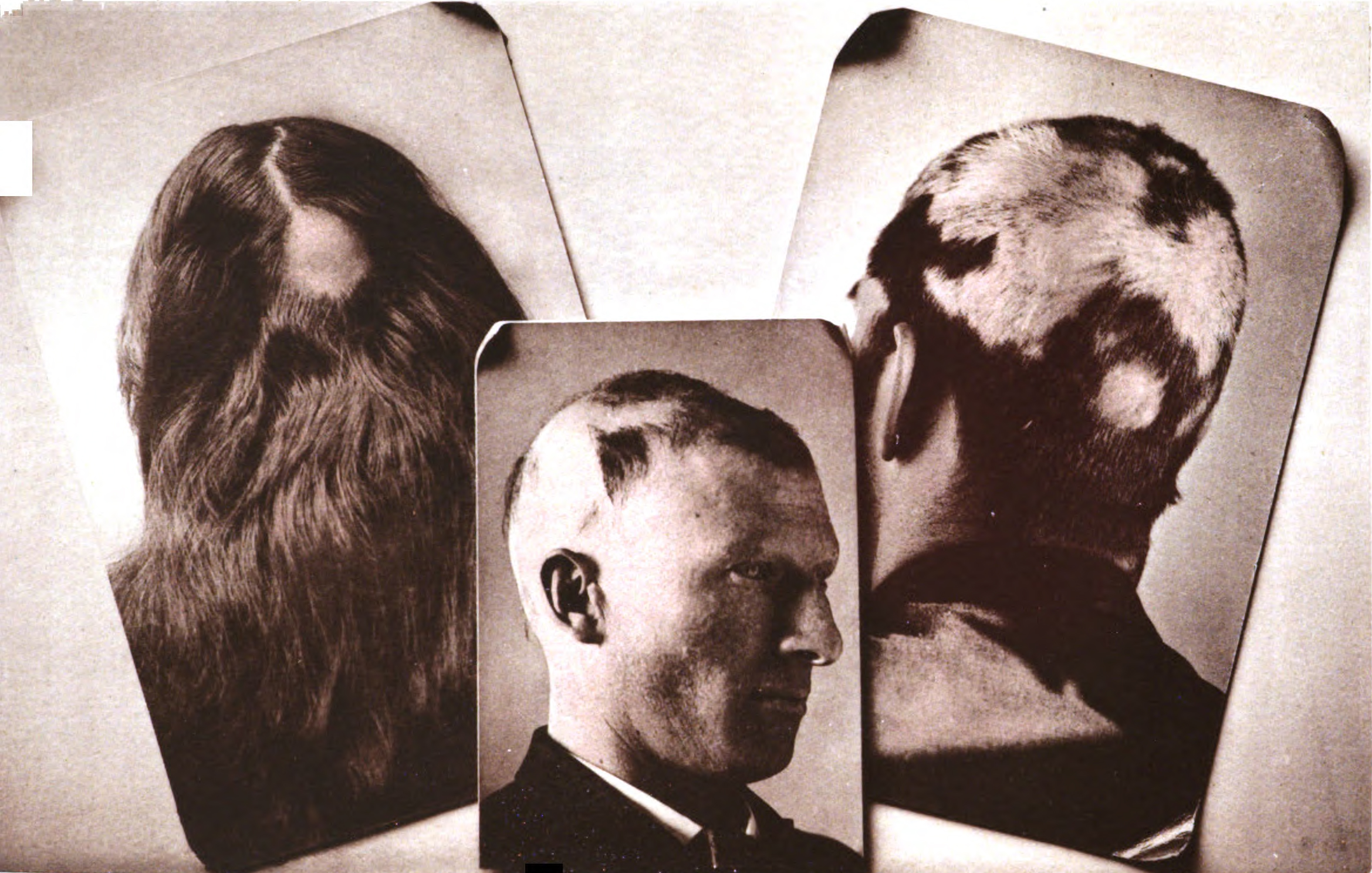
Triangular Alopecia
Triangular alopecia is hair loss that may be congenital but usually appears in childhood as a focal patch of loss that may be complete or leaving fine vellus hairs behind.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Affected individuals are typically entirely healthy. Hair restoration surgery using follicular unit transplantation has been a successful treatment modality for TTA Presentation Association with Other Conditions TTA has been associated with several disorders, such as Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis. And a rare syndrome Setleis syndrome. It is inherited by the autosomal dominant trait and is characterized by cutis aplasia or atrophic skin at the temples, which is said to resemble forceps marks. There may also be a coarse facial appearance, anomalies of the eyelashes and eyebrows, and periorbital puffiness. Frequency The suggested frequency for this condition in the general population is around 0.11%. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vellus Hair
Vellus hair is short, thin, light-colored, and barely noticeable hair that develops on most of a human’s body during childhood. Exceptions include the lips, the back of the ear, the palm of the hand, the sole of the foot, some external genital areas, the navel, and scar tissue. The density of hair – the number of hair follicles per area of skin – varies from person to person. Each strand of vellus hair is usually less than 2 mm (1/13 inch) long and the follicle is not connected to a sebaceous gland. Vellus hair is most easily observed on children and adult women, who generally have less terminal hair to obscure it. Vellus hair is not lanugo hair. Lanugo hair is a much thicker type of hair that normally grows only on fetuses. Vellus hair is differentiated from the more visible terminal or androgenic hair, which develops only during and after puberty, usually to a greater extent on men than it does on women. The Latin language uses the word ''vellus'' to designate "a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Alopecia
Triangular alopecia is hair loss that may be congenital but usually appears in childhood as a focal patch of loss that may be complete or leaving fine vellus hairs behind.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Affected individuals are typically entirely healthy. Hair restoration surgery using follicular unit transplantation has been a successful treatment modality for TTA Presentation Association with Other Conditions TTA has been associated with several disorders, such as Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis. And a rare syndrome Setleis syndrome. It is inherited by the autosomal dominant trait and is characterized by cutis aplasia or atrophic skin at the temples, which is said to resemble forceps marks. There may also be a coarse facial appearance, anomalies of the eyelashes and eyebrows, and periorbital puffiness. Frequency The suggested frequency for this condition in the general population is around 0.11%. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis
Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis is a rare neurocutanous condition where there is coexistence of a capillary malformation ( port-wine stain) with various melanocytic lesions, including dermal melanocytosis ( Mongolian spots), nevus spilus, and nevus of Ota. Types Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis is subdivided into five types:Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). Page 1012. McGraw-Hill. . * Type 1 PWS + epidermal nevus * Type 2 (most common): PWS + dermal melanocytosis +/- nevus anemicus * Type 3: PWS + nevus spilus +/- nevus anemicus * Type 4: PWS + nevus spilus + dermal melanocytosis +/- nevus anemicus * Type 5: CMTC (Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita) + dermal melanocytosis They all can contain capillary malformation. Type 2 is the most common and can be associated with granular cell tumor. Some further subdivide each type into categories A & B; with A representing oculocutaneous involvement and subtype B representing ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setleis Syndrome
Setleis syndrome is a very rare genetic condition characterized by facial skin abnormalities and double upper eyelashes and missing lower eyelashes. It belongs to a group of diseases known as ectodermal dysplasias. Ectodermal dysplasias typically affect the hair, teeth, nails, and/or skin. Setleis syndrome is characterized by distinctive abnormalities of the facial area that may be apparent at birth (congenital). Most affected infants have multiple, scar-like, circular depressions on both temples (bitemporal). These marks closely resemble those made when forceps are used to assist delivery. The range and severity of symptoms may vary from case to case. Most cases of Setleis syndrome are thought to be inherited as an autosomal recessive genetic trait due to mutations in the TWIST2 gene. The differential diagnosis of Setleis syndrome includes X-linked focal dermal hypoplasia, or Goltz syndrome; a syndrome of focal dermal hypoplasia, morning glory anomaly, and polymicrogyria; in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutis Aplasia
Cutis may refer to several unrelated biological structures: * Cutis (anatomy), the outermost layers of skin * Cutis (mycology), a type of pileipellis in a fungus Other * ''Cutis'' (journal), an academic journal of dermatology published by Frontline Medical Communications Front line refers to the forward-most forces on a battlefield. Front line, front lines or variants may also refer to: Books and publications * ''Front Lines'' (novel), young adult historical novel by American author Michael Grant * ''Frontlines ... * Cutiş, a village in Almașu Commune, Sălaj County, Romania {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost ('' alopecia totalis''), or all body hair is lost ('' alopecia universalis''). Hair loss can be permanent, or temporary. It is distinct from pattern hair loss, which is common among males. Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recogniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring is not usually present. Hair loss in some people causes psychological distress. Common types include male- or female-pattern hair loss, alopecia areata, and a thinning of hair known as telogen effluvium. The cause of male-pattern hair loss is a combination of genetics and male hormones; the cause of female pattern hair loss is unclear; the cause of alopecia areata is autoimmune; and the cause of telogen effluvium is typically a physically or psychologically stressful event. Telogen effluvium is very common following pregnancy. Less common causes of hair loss without inflammation or scarring include the pulling out of hair, certain medications including chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, hypothyroidism, and malnutrition including i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Lesion
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
