|
Setleis Syndrome
Setleis syndrome is a very rare genetic condition characterized by facial skin abnormalities and double upper eyelashes and missing lower eyelashes. It belongs to a group of diseases known as ectodermal dysplasias. Ectodermal dysplasias typically affect the hair, teeth, nails, and/or skin. Setleis syndrome is characterized by distinctive abnormalities of the facial area that may be apparent at birth (congenital). Most affected infants have multiple, scar-like, circular depressions on both temples (bitemporal). These marks closely resemble those made when forceps are used to assist delivery. The range and severity of symptoms may vary from case to case. Most cases of Setleis syndrome are thought to be inherited as an autosomal recessive genetic trait due to mutations in the TWIST2 gene. The differential diagnosis of Setleis syndrome includes X-linked focal dermal hypoplasia, or Goltz syndrome; a syndrome of focal dermal hypoplasia, morning glory anomaly, and polymicrogyria; in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectodermal Dysplasias
Ectodermal dysplasia (ED) is a group of genetic syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . More than 150 different syndromes have been identified. Despite some of the syndromes having different genetic causes, the symptoms are sometimes very similar. Diagnosis is usually by clinical observation, often with the assistance of family medical histories so that it can be determined whether transmission is autosomal dominant or recessive. Ectodermal dysplasias are described as "heritable conditions in which there are abnormalities of two or more ectodermal structures such as the hair, teeth, nails, sweat glands, salivary glands, cranial-facial structure, digits and other parts of the body." Presentation Hair Individuals affected by an ED syndrome frequently have abnormalities of the hair follicles. Scalp and body hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
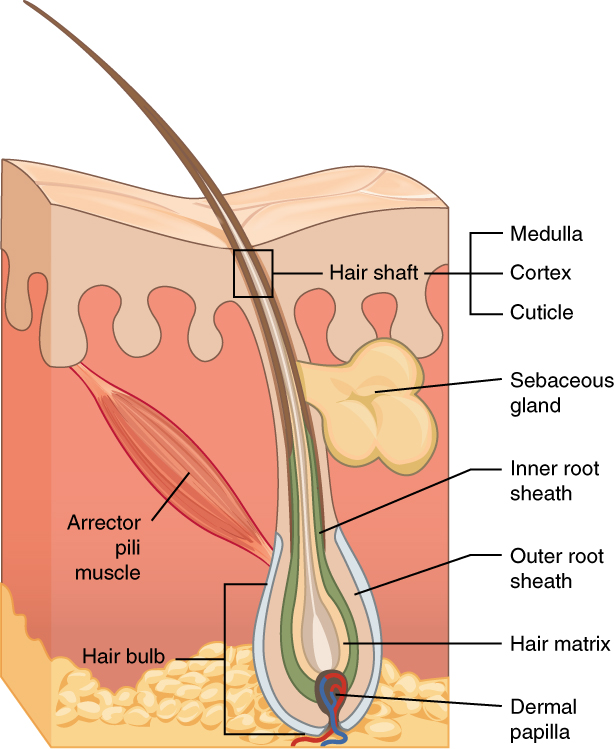
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects needed to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively in the fields of biology and medicine. Outside biology and medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps. Mechanically, forceps employ the principle of the lever to grasp and apply pressure. Depending on their function, basic surgical forceps can be categorized into the following groups: # Non-disposable forceps. They should withstand various kinds of physical and chemical effects of body fluids, secretions, cleaning agents, and sterilization methods. # Disposable forceps. They are usually made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TWIST2
Twist-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TWIST2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor and shares similarity with another bHLH transcription factor, TWIST1. bHLH transcription factors have been implicated in cell lineage determination and differentiation. It is thought that during osteoblast development, this protein may inhibit osteoblast maturation and maintain cells in a preosteoblast phenotype. Interactions TWIST2 has been shown to interact with SREBF1. Clinical significance Mutations in the ''TWIST2'' gene that alter DNA-binding activity through both dominant-negative and gain-of-function effects are associated with ablepharon macrostomia syndrome and Barber–Say syndrome Barber-Say syndrome (BSS) is a very rare congenital disorder associated with excessive hair growth ( hypertrichosis), fragile ( atrophic) skin, eyelid deformities ( ectropion), and an overly broad mouth (macrostomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Dermal Hypoplasia
Focal dermal hypoplasia is a form of ectodermal dysplasia. It is a multisystem disorder characterized primarily by skin manifestations to the atrophic and hypoplastic areas of skin which are present at birth. These defects manifest as yellow-pink bumps on the skin and pigmentation changes. The disorder is also associated with shortness of stature and some evidence suggests that it can cause epilepsy. Genetics Focal dermal hypoplasia has been associated with PORCN gene mutations on the X chromosome. 90% of the individuals who are affected with the syndrome are female: the commonly accepted, though unconfirmed, explanation for this is that the non-mosaic hemizygous males are not viable. The differential diagnosis of focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz) syndrome includes autosomal recessive Setleis syndrome due to TWIST2 gene mutations. It associated with morning glory anomaly, polymicrogyria, incontinentia pigmenti, oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome and micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goltz Syndrome
Goltz is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Bogumil Goltz (1801–1870), German humorist and satirist *Boris Goltz (1913–1942), Soviet composer *Christel Goltz (1912–2008), German operatic soprano *Dave Goltz (born 1949), American baseball player *Franziska Goltz (born 1985), German sports sailor *Friedrich Goltz (1834–1902), German physiologist *Hans Goltz (1873–1927), German art dealer *Hendrick Goltz (1558–1617), German-born Dutch printmaker and artist *Hubert Goltz (1526–1583), Dutch printmaker and artist *Justin Goltz (born 1987), American football player *Paolo Goltz (born 1985), Argentine football player *Rick Goltz (born 1955), Canadian football player *Thomas Goltz (born 1954), American author and journalist * Ursula Goltz, German computer scientist See also *von der Goltz Von der Goltz is the name of an old and influential German noble family whose members occupied many important positions in the Kingdom of Prussia and later in the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incontinentia Pigmenti
Incontinentia pigmenti (IP) is a rare X-linked dominant genetic disorder that affects the skin, hair, teeth, nails and central nervous system. It is named from its appearance under a microscope. The disease is characterized by skin abnormalities that begin in childhood, usually a blistering rash which heals, followed by the development of harder skin growths. The skin may develop grey or brown patches which fade with time. Other symptoms can include hair loss, dental abnormalities, eye abnormalities that can lead to vision loss and lined or pitted fingernails and toenails. Associated problems can include delayed development, intellectual disability, seizures and other neurological problems. Most males with the disease do not survive to childbirth. Incontinentia pigmenti is caused by a mutation in the '' IKBKG'' gene, which encodes the NEMO protein, which serves to protect cells against TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. A lack of IKBKG therefore makes cells more prone to apoptosis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculocerebrocutaneous Syndrome
Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome is a condition characterized by orbital cysts, microphthalmia, porencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and facial skin tags. Presentation These include * Skin lesions ** Hypoplastic or aplastic skin defects ** Pedunculated, hamartomatous or nodular skin appendages * Eye lesions **Cystic microphthalmia * Brain lesions ** Forebrain anomalies *** Agenesis of the corpus callosum *** Enlarged lateral ventricles *** Interhemispheric cysts *** Hydrocephalus *** Polymicrogyria *** Periventricular nodular heterotopia ** Mid-hindbrain malformation *** Giant dysplastic tectum *** Absent cerebellar vermis *** Small cerebellar hemispheres *** Large posterior fossa fluid collections Genetics This is not understood but it is suspected that the gene(s) responsible may lie on the X chromosome. Diagnosis Differential diagnosis * Aicardi syndrome * Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis * Focal dermal hypoplasia * Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum Epidemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome
Rothmund–Thomson syndrome (RTS) is a rare autosomal recessive skin condition. There have been several reported cases associated with osteosarcoma. A hereditary basis, mutations in the DNA helicase '' RECQL4'' gene, causing problems during initiation of DNA replication has been implicated in the syndrome. Signs and symptoms * Sun-sensitive rash with prominent poikiloderma and telangiectasias * Juvenile cataracts * Saddle nose * Congenital bone defects, including short stature and radial ray anomalies such as absent thumbs * Hair growth problems (absent eyelashes, eyebrows and/or hair) * Hypogonadism has not been well documented * Hypodontia * Calcium problems (not documented in journals) * Ear problems (not documented in journals but identified by patients in support groups) * Produces osteosarcoma The skin is normal at birth. Between 3 and 6 months of age, the affected carrier develops poikiloderma on the cheeks. This characteristic "rash" that all RTS carriers have can devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HCCS (gene)
Cytochrome c-type heme lyase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HCCS'' gene on chromosome X. Structure The ''HCCS'' gene is located on the Xp22 region of chromosome X and encodes a protein that is ~30 kDa in size. The HCCS protein is localized to the inner mitochondrial membrane and is expressed in multiple tissue including prominently in the cardiovascular system and the central nervous system. Function The HCCS protein functions as a lyase to covalently attach the heme group to the apoprotein of cytochrome c on the inner mitochondrial membrane of the mitochondrion. The heme group is required for cytochrome c to transport electrons from complex III to complex IV of the electron transport chain during respiration. Heme attachment to cytochrome c takes place in the intermembrane space and requires conserved heme-interacting residues on HCCS on one of the two heme-binding domains on HCCS, including His154. The HCCS protein may function to regulate mitochondrial l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |