|
Treponema Pallidum Particle Agglutination Assay
The ''Treponema pallidum'' particle agglutination assay (also called TPPA test) is an indirect agglutination assay used for detection and titration of antibodies against the causative agent of syphilis, ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. It also detects other treponematoses. In the test, gelatin particles are sensitized with ''T. pallidum'' antigen. Patient serum is mixed with the reagent containing the sensitized gelatin particles. The particles aggregate to form clumps when the patient serum is positive for syphilis. In other words, the patient's serum contains antibodies to ''T. pallidum''. A negative test shows no clumping of gelatin particles. This is a type of specific treponemal test for syphilis. A similar specific treponemal test for syphilis is the ''Treponema pallidum'' hemagglutination assay or TPHA. TPHA is an indirect hemagglutination assay used for the detection and titration of antibodies against the causative agent of syphilis, ''Treponema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
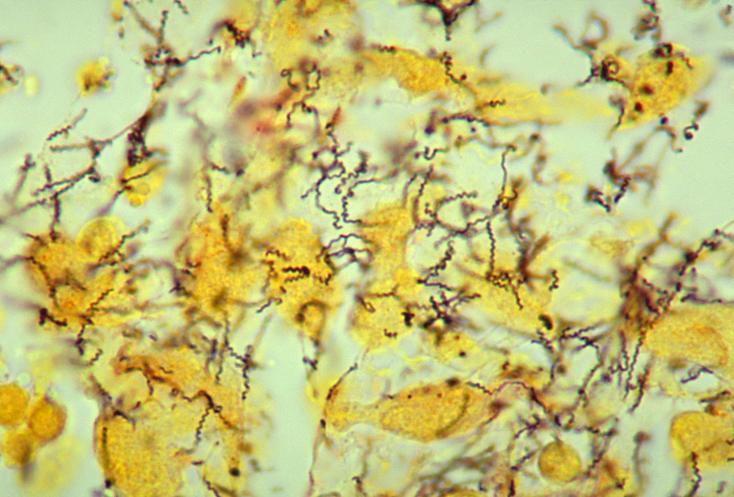
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. ''Treponema pallidum'' consists of three subspecies, ''T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum,'' and ''T. p. pertenue,'' each of which has a distinct associated disease. Subspecies Three subspecies of ''T. pallidum'' are known: * ''Treponema pallidum pallidum'', which causes syphilis * ''T. p. endemicum'', which causes bejel or endemic syphilis * ''T. p. pertenue'', which causes yaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treponematoses
Treponematosis is a term used to individually describe any of the diseases caused by four members of the bacterial genus ''Treponema''. The four diseases are collectively referred to as treponematoses: * Syphilis (''Treponema pallidum pallidum'') * Yaws (''Treponema pallidum pertenue'') * Bejel (''Treponema pallidum endemicum'') * Pinta (''Treponema carateum'') Traditional laboratory tests cannot distinguish the treponematoses. However, sequence differences among the ''T. pallidum'' subspecies have been identified. Molecular approaches involving PCR PCR or pcr may refer to: Science * Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule * Principal component regression, a statistical technique Medicine * Polymerase chain reaction ** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain r ... to identify these sequences are being developed. References External links Spirochaetes Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions {{infectious-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Diseases And Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of passing the infection on to others. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital herpes, HIV/AIDS, and genital warts. Parasitic STIs include trichomoniasis. STI diagnostic tests are usually easily available in the developed world, but they are often unavailable in the developing world. Some vaccinations may also decrease the risk of certain infections including hepatitis B and some types of HPV. Safe sex practices, such as use of condoms, having a smaller num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |