|
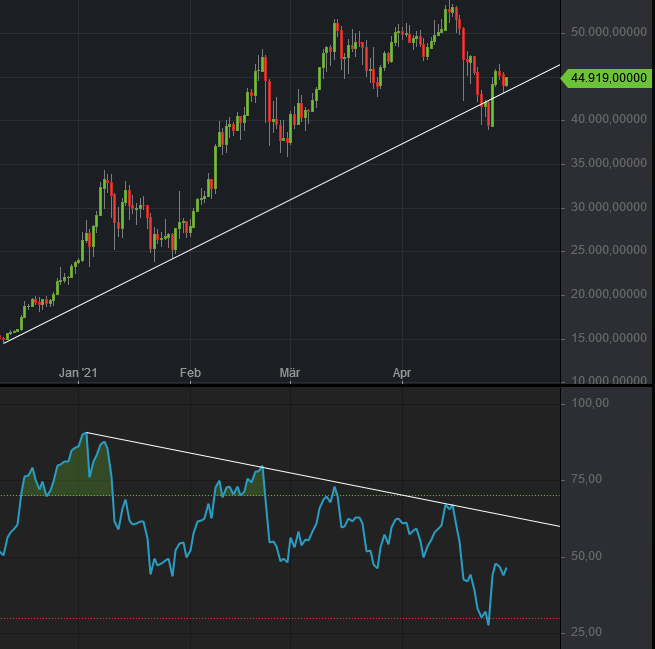
Trend Line (technical Analysis)
In finance, a trend line is a bounding line for the price movement of a security. It is formed when a diagonal line can be drawn between a minimum of three or more price pivot points. A line can be drawn between any two points, but it does not qualify as a trend line until tested. Hence the need for the third point, the test. Trend lines are commonly used to decide entry and exit timing when trading securities. They can also be referred to as a Dutch line, as the concept was first used in Holland. A support trend line is formed when a securities price decreases and then rebounds at a pivot point that aligns with at least two previous support pivot points. Similarly a resistance trend line is formed when a securities price increases and then rebounds at a pivot point that aligns with at least two previous resistance pivot points. Stock often begin or end trending because of a stock catalyst such as a product launch or change in management. Trend lines are a simple and widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security (finance)
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any form of financial instrument, even though the underlying legal and regulatory regime may not have such a broad definition. In some jurisdictions the term specifically excludes financial instruments other than Stock, equities and Fixed income instruments. In some jurisdictions it includes some instruments that are close to equities and fixed income, e.g., Warrant (finance), equity warrants. Securities may be represented by a certificate or, more typically, they may be "non-certificated", that is in electronic (Dematerialization (securities), dematerialized) or "book entry only" form. Certificates may be ''bearer'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights under the security merely by holding the security, or ''registered'', meaning they enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Analysis
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the same tools of technical analysis, which, being an aspect of active management, stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of both technical and fundamental analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. History The principles of technical analysis are derived from hundreds of years of financial market data. Some aspects of technical analysis began to appear in Amsterdam-based merchant Joseph de la Vega's accounts of the Dutch financial markets in the 17th century. In Asia, technical analysis is said to be a method developed by Homma Munehis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S&P 500
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices. As of December 31, 2020, more than $5.4 trillion was invested in assets tied to the performance of the index. The S&P 500 index is a free-float weighted/ capitalization-weighted index. As of August 31, 2022, the nine largest companies on the list of S&P 500 companies accounted for 27.8% of the market capitalization of the index and were, in order of highest to lowest weighting: Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet (including both class A & C shares), Amazon.com, Tesla, Berkshire Hathaway, UnitedHealth Group, Johnson & Johnson and ExxonMobil. The components that have increased their dividends in 25 consecutive years are known as the S&P 500 Dividend Aristocrats. The index is one of the factors in computation of the Conference Board Leading Econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Scale
A logarithmic scale (or log scale) is a way of displaying numerical data over a very wide range of values in a compact way—typically the largest numbers in the data are hundreds or even thousands of times larger than the smallest numbers. Such a scale is nonlinear: the numbers 10 and 20, and 60 and 70, are not the same distance apart on a log scale. Rather, the numbers 10 and 100, and 60 and 600 are equally spaced. Thus moving a unit of distance along the scale means the number has been ''multiplied'' by 10 (or some other fixed factor). Often exponential growth curves are displayed on a log scale, otherwise they would increase too quickly to fit within a small graph. Another way to think about it is that the ''number of digits'' of the data grows at a constant rate. For example, the numbers 10, 100, 1000, and 10000 are equally spaced on a log scale, because their numbers of digits is going up by 1 each time: 2, 3, 4, and 5 digits. In this way, adding two digits ''multiplies'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
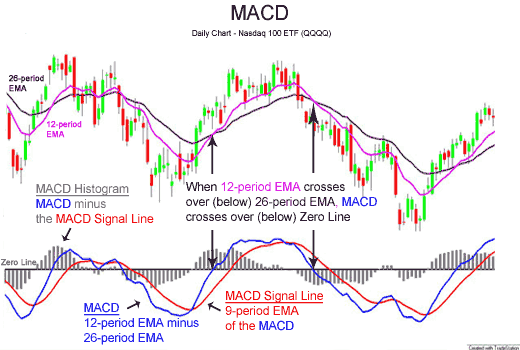
MACD
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price. The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price. These three series are: the MACD series proper, the "signal" or "average" series, and the "divergence" series which is the difference between the two. The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series. The average series is an EMA of the MACD series itself. The MACD indicator thus depends on three time parameters, namely the time constants of the three EMAs. The notation "MACD(''a'',''b'',''c'')" usually denotes the indicator where the MACD series is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Strength Index
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength. The RSI is classified as a momentum oscillator, measuring the velocity and magnitude of price movements. Momentum is the rate of the rise or fall in price. The relative strength RS is given as the ratio of higher closes to lower closes, with closes here meaning averages of absolute values of price changes. The RSI computes momentum as the ratio of higher closes to overall closes: stocks which have had more or stronger positive changes have a higher RSI than stocks which have had more or stronger negative changes. The RSI is most typically used on a 14-day timeframe, measured on a scale from 0 to 100, with high and low levels marked at 70 and 30, respectively. Short or longe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support And Resistance
In stock market technical analysis, support and resistance are certain predetermined levels of the price of a security at which it is thought that the price will tend to stop and reverse. These levels are denoted by multiple touches of price without a breakthrough of the level. Support versus resistance A support level is a level where the price tends to find support as it falls due to an increase in demand for the asset. This means that the price is more likely to "bounce" off this level rather than break through it. However, once the price has breached this level, by an amount exceeding some noise, it is likely to continue falling until meeting another support level. A resistance level is the opposite of a support level. It is where the price tends to find resistance as it rises due to an increase in selling interest. Again, this means that the price is more likely to "bounce" off this level rather than break through it. However, once the price has breached this level, by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)