|
Relative Strength Index
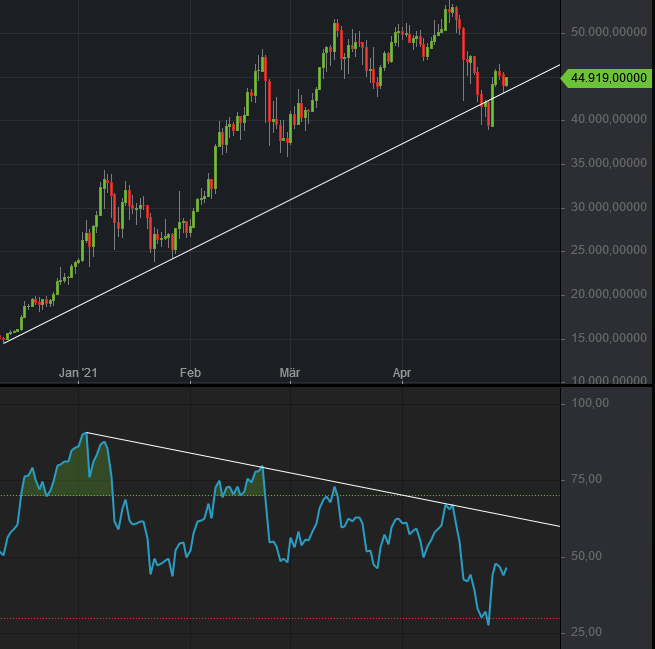
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength. The RSI is classified as a momentum oscillator, measuring the velocity and magnitude of price movements. Momentum is the rate of the rise or fall in price. The relative strength RS is given as the ratio of higher closes to lower closes, with closes here meaning averages of absolute values of price changes. The RSI computes momentum as the ratio of higher closes to overall closes: stocks which have had more or stronger positive changes have a higher RSI than stocks which have had more or stronger negative changes. The RSI is most typically used on a 14-day timeframe, measured on a scale from 0 to 100, with high and low levels marked at 70 and 30, respectively. Short or longe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillator (technical Analysis)
An oscillator is a technical analysis indicator that varies over time within a band (above and below a center line, or between set levels). Oscillators are used to discover short-term overbought or oversold conditions. Common oscillators are MACD, ROC, RSI, CCI. See also * Technical analysis ReferencesInvestopedia - Oscillator {{technical analysis Technical analysis Technical indicators [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Indicator
In technical analysis in finance, a technical indicator is a mathematical calculation based on historic price, volume, or (in the case of futures contracts) open interest information that aims to forecast financial market direction. Technical indicators are a fundamental part of technical analysis In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the sa ... and are typically plotted as a chart pattern to try to predict the market trend. Indicators generally overlay on price chart data to indicate where the price is going, or whether the price is in an "overbought" condition or an "oversold" condition. Many technical indicators have been developed and new variants continue to be developed by traders with the aim of getting better results. New Indicators are often backtested on historic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Smoothing
Exponential smoothing is a rule of thumb technique for smoothing time series data using the exponential window function. Whereas in the simple moving average the past observations are weighted equally, exponential functions are used to assign exponentially decreasing weights over time. It is an easily learned and easily applied procedure for making some determination based on prior assumptions by the user, such as seasonality. Exponential smoothing is often used for analysis of time-series data. Exponential smoothing is one of many window functions commonly applied to smooth data in signal processing, acting as low-pass filters to remove high-frequency noise. This method is preceded by Poisson's use of recursive exponential window functions in convolutions from the 19th century, as well as Kolmogorov and Zurbenko's use of recursive moving averages from their studies of turbulence in the 1940s. The raw data sequence is often represented by \ beginning at time t = 0, and the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
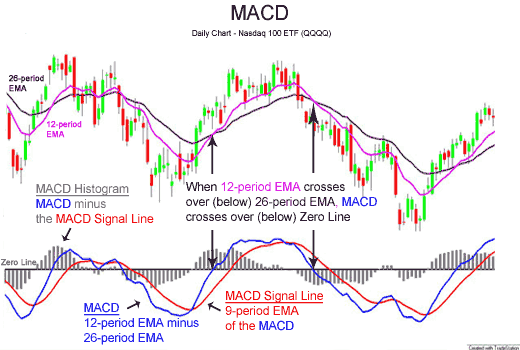
MACD
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price. The MACD indicator (or "oscillator") is a collection of three time series calculated from historical price data, most often the closing price. These three series are: the MACD series proper, the "signal" or "average" series, and the "divergence" series which is the difference between the two. The MACD series is the difference between a "fast" (short period) exponential moving average (EMA), and a "slow" (longer period) EMA of the price series. The average series is an EMA of the MACD series itself. The MACD indicator thus depends on three time parameters, namely the time constants of the three EMAs. The notation "MACD(''a'',''b'',''c'')" usually denotes the indicator where the MACD series is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Oscillator
In technical analysis of securities trading, the stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that uses support and resistance levels. George Lane developed this indicator in the late 1950s. The term ''stochastic'' refers to the point of a current price in relation to its price range over a period of time. This method attempts to predict price turning points by comparing the closing price of a security to its price range. The 5-period stochastic oscillator in a daily timeframe is defined as follows: :\%K = 100\times\frac \%D_N = \frac where \mathrm_5 and \mathrm_5 are the highest and lowest prices in the last 5 days respectively, while %''D'' is the ''N''-day moving average of %''K'' (the last ''N'' values of %''K''). Usually this is a simple moving average, but can be an exponential moving average for a less standardized weighting for more recent values. There is only one valid signal in working with %''D'' alone — a divergence between %''D'' and the analyzed secur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Average (finance)
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. It is also called a moving mean (MM) or rolling mean and is a type of finite impulse response filter. Variations include: simple, cumulative, or weighted forms (described below). Given a series of numbers and a fixed subset size, the first element of the moving average is obtained by taking the average of the initial fixed subset of the number series. Then the subset is modified by "shifting forward"; that is, excluding the first number of the series and including the next value in the subset. A moving average is commonly used with time series data to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles. The threshold between short-term and long-term depends on the application, and the parameters of the moving average will be set accordingly. It is also used in economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Smoothing
Exponential smoothing is a rule of thumb technique for smoothing time series data using the exponential window function. Whereas in the simple moving average the past observations are weighted equally, exponential functions are used to assign exponentially decreasing weights over time. It is an easily learned and easily applied procedure for making some determination based on prior assumptions by the user, such as seasonality. Exponential smoothing is often used for analysis of time-series data. Exponential smoothing is one of many window functions commonly applied to smooth data in signal processing, acting as low-pass filters to remove high-frequency noise. This method is preceded by Poisson's use of recursive exponential window functions in convolutions from the 19th century, as well as Kolmogorov and Zurbenko's use of recursive moving averages from their studies of turbulence in the 1940s. The raw data sequence is often represented by \ beginning at time t = 0, and the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitcoin RSI14 Divergence
Bitcoin ( abbreviation: BTC; sign: ₿) is a decentralized digital currency that can be transferred on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network. Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. The cryptocurrency was invented in 2008 by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The currency began use in 2009, when its implementation was released as open-source software. The word "''bitcoin''" was defined in a white paper published on October 31, 2008. It is a compound of the words ''bit'' and ''coin''. The legality of bitcoin varies by region. Nine countries have fully banned bitcoin use, while a further fifteen have implicitly banned it. A few governments have used bitcoin in some capacity. El Salvador has adopted Bitcoin as legal tender, although use by merchants remains low. Ukraine has accepted cryptocurrency donations to fund the resistance to the 2022 Russian i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buy And Hold
Buy and hold, also called position trading, is an investment strategy whereby an investor buys financial assets or non-financial assets such as real estate, to hold them long term, with the goal of realizing price appreciation, despite volatility. This approach implies confidence that the value of the investments will be higher in the future. Investors must not be affected by recency bias, emotions, and must understand their propensity to risk aversion. Investors must buy financial instruments that they expect to appreciate in the long term. Buy and hold investors do not sell after a decline in value. They do not engage in market timing (i.e. selling a security with the goal of buying it again at a lower price) and do not believe in calendar effects such as Sell in May. Buy and hold is an example of passive management. It has been recommended by Warren Buffett, Jack Bogle, Burton Malkiel, John Templeton, Peter Lynch, and Benjamin Graham since, in the long run, there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Average
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. It is also called a moving mean (MM) or rolling mean and is a type of finite impulse response filter. Variations include: simple, cumulative, or weighted forms (described below). Given a series of numbers and a fixed subset size, the first element of the moving average is obtained by taking the average of the initial fixed subset of the number series. Then the subset is modified by "shifting forward"; that is, excluding the first number of the series and including the next value in the subset. A moving average is commonly used with time series data to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles. The threshold between short-term and long-term depends on the application, and the parameters of the moving average will be set accordingly. It is also used in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |