|
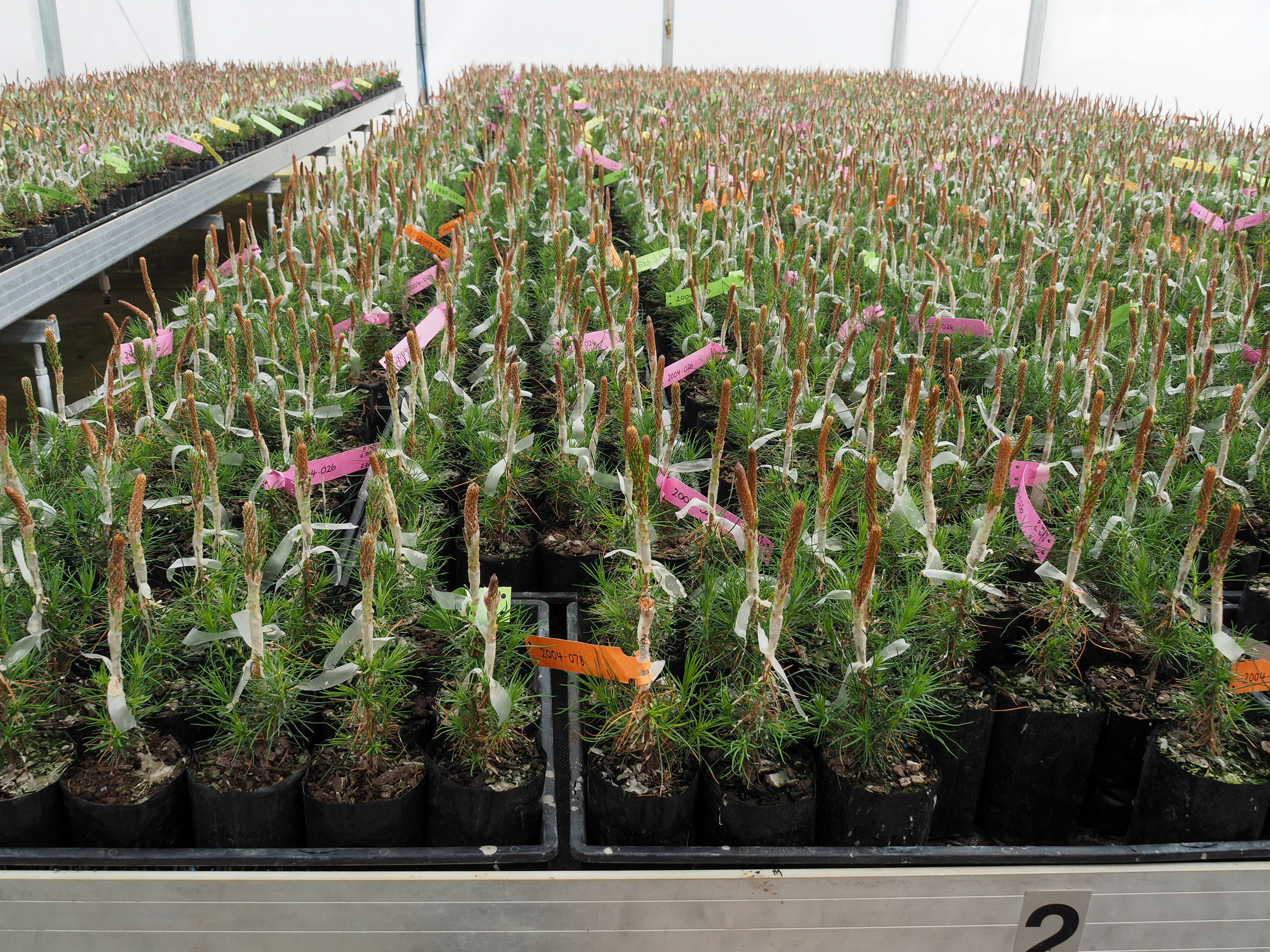
Tree Breeding
Tree breeding is the application of genetic, reproductive biology and economics principles to the genetic improvement and management of forest trees. In contrast to the selective breeding of livestock, arable crops, and horticultural flowers over the last few centuries, the breeding of trees, with the exception of fruit trees, is a relatively recent occurrence. A typical forest tree breeding program starts with selection of superior phenotypes (plus trees) in a natural or planted forest, often based on growth rate, tree form and site adaptation traits. This application of mass selection improves the mean performance of the forest. Offspring is obtained from selected trees and grown in test plantations that act as genetic trials. Based on such tests the best genotypes among the parents can be selected. Selected trees are typically multiplied by either seeds or grafting and seed orchards are established when the preferred output is improved seed. Alternatively, the best genotypes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
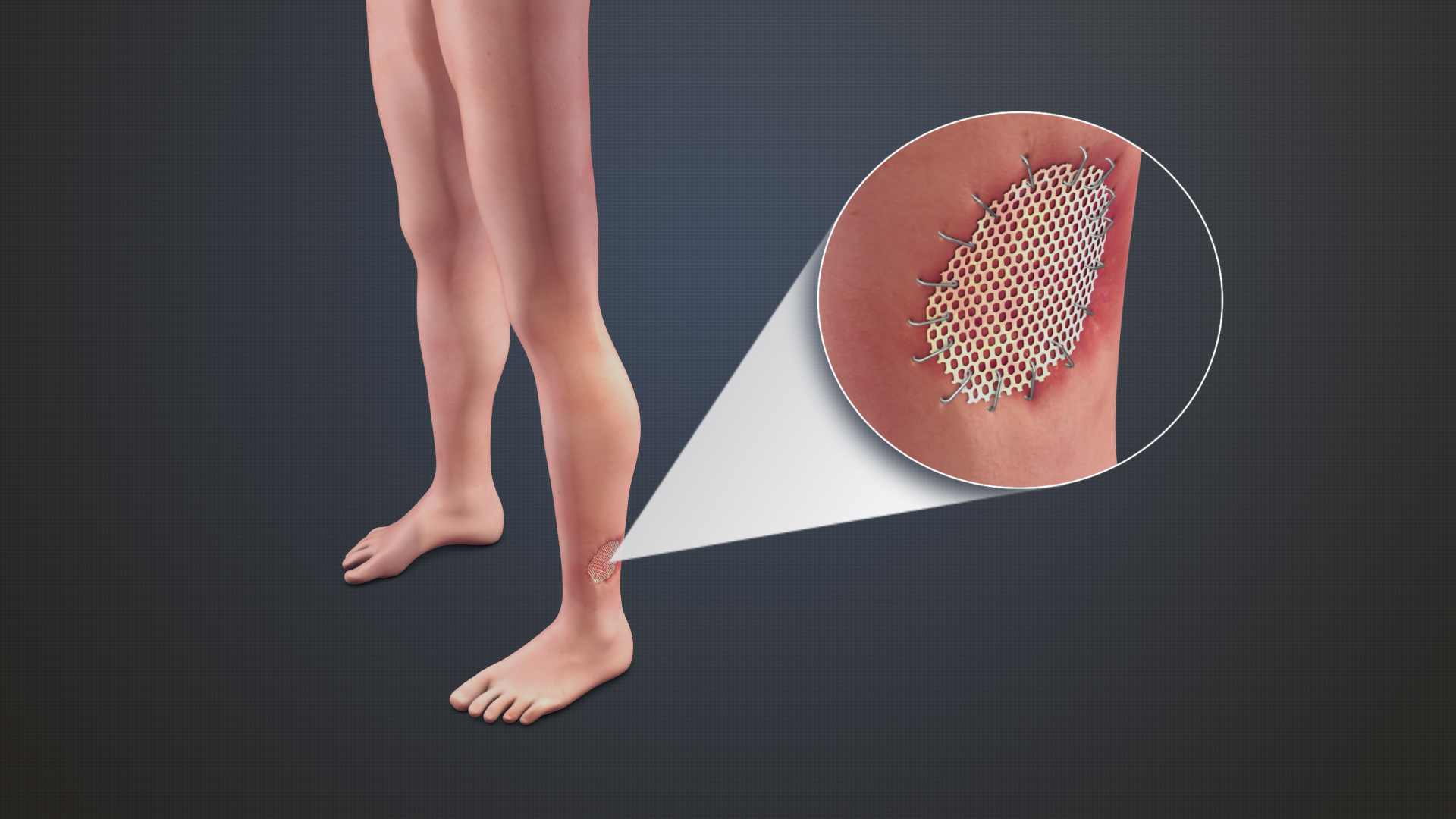
Grafts
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis. Classification Autografts and isografts are usually not considered as foreign and, therefore, do not elicit rejection. Allografts and xenografts may be recognized as foreign by the recipient and rejected. * Autograft: graft taken from one part of the body of an individual and transplanted onto another site in the same individual, e.g., skin graft. * Isograft: graft taken from one individual and placed on another individual of the same genetic constitution, e.g., grafts between i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolation Bags
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual. Isolation or isolated may also refer to: Sociology and psychology *Isolation (health care), various measures taken to prevent contagious diseases from being spread **Isolation ward, a separate ward used to isolate patients with infectious diseases * Isolation (psychology), a defense mechanism in psychoanalytic theory *Emotional isolation, a feeling of isolation despite a functioning social network *Isolation effect, a psychological effect of distinctive items more easily remembered Mathematics * Real-root isolation * Isolation lemma, a technique used to reduce the number of solutions to a computational problem. Natural sciences *Electrical or galvanic isolation, isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flowing between them *An isolated system, a system without any external exchange *Isolating language, a type of language with a low morpheme-per-word ratio *Isolation (datab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection Methods In Plant Breeding Based On Mode Of Reproduction
Plant breeders use different methods depending on the mode of reproduction of crops, which include: * Self-fertilization, where pollen from a plant will fertilise reproductive cells or ovules of the same plant * Cross-pollination, where pollen from one plant can only fertilize a different plant * Asexual propagation (e.g. runners from strawberry plants) where the new plant is genetically identical to its parent * Apomixis (self-cloning), where seeds are produced asexually and the new plant is genetically identical to its parent The mode of reproduction of a crop determines its genetic composition, which, in turn, is the deciding factor to develop suitable breeding and selection methods. Knowledge of mode of reproduction is also essential for its artificial manipulation to breed improved types. Only those breeding and selection methods are suitable for a crop which does not interfere with its natural state or ensure the maintenance of such a state. It is due to such reasons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grafting
Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion () while the lower part is called the rootstock. The success of this joining requires that the vascular tissues grow together and such joining is called inosculation. The technique is most commonly used in asexual propagation of commercially grown plants for the horticultural and agricultural trades. In most cases, one plant is selected for its roots and this is called the stock or rootstock. The other plant is selected for its stems, leaves, flowers, or fruits and is called the scion or cion. The scion contains the desired genes to be duplicated in future production by the stock/scion plant. In stem grafting, a common grafting method, a shoot of a selected, desired plant cultivar is grafted onto the stock of another type. In another common form called bud grafting, a dormant side bud is gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Orchard
A seed orchard is an intensively-managed plantation of specifically arranged trees for the mass production of genetically improved seeds to create plants, or seeds for the establishment of new forests. General Seed orchards are a common method of mass-multiplication for transferring genetically improved material from breeding populations to production populations (forests) and in this sense are often referred to as "multiplication" populations. A seed orchard is often composed of grafts (vegetative copies) of selected genotypes, but seedling seed orchards also occur mainly to combine orchard with progeny testing. Seed orchards are the strong link between breeding programs and plantation establishment. They are designed and managed to produce seeds of superior genetic quality compared to those obtained from seed production areas, seed stands, or unimproved stands. Material and connection with breeding population In first generation seed orchards, the parents usually are phenotypical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. ''Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization. Mating may also lead to external fertilization, as seen in amphibians, fishes and plants. For most species, mating is between two individuals of opposite sexes. However, for some hermaphroditic species, copulation is not required because the parent organism is capable of self-fertilization (autogamy); for example, banana slugs. The term ''mating'' is also applied to related processes in bacteria, archaea and viruses. Mating in these cases involves the pairing of individuals, accompanied by the pairing of their homologous chromosomes and then exchange of genomic information leading to formation of recombinant progeny (see mating systems). Animals For animals, mating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Spruce '', native to the central and southern Rocky Mountains of the United States
{{plant common name ...
White spruce is a common name for several species of spruce (''Picea'') and may refer to: * ''Picea glauca'', native to most of Canada and Alaska with limited populations in the northeastern United States * ''Picea engelmannii'', native to the Rocky Mountains and Cascade Mountains of the United States and Canada * ''Picea pungens The blue spruce (''Picea pungens''), also commonly known as green spruce, Colorado spruce, or Colorado blue spruce, is a species of spruce tree. It is native to North America, and is found in USDA growing zones 1 through 7. It is found naturally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinophyta
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Tree
A genetically modified tree (GMt, GM tree, genetically engineered tree, GE tree or transgenic tree) is a tree whose DNA has been modified using genetic engineering techniques. In most cases the aim is to introduce a novel trait to the plant which does not occur naturally within the species. Examples include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, and herbicide tolerance, or the alteration of lignin levels in order to reduce pulping costs. Genetically modified forest trees are not yet approved ("deregulated") for commercial use with the exception of insect-resistant poplar trees in China and one case of GM Eucalyptus in Brazil. Several genetically modified forest tree species are undergoing field trials for deregulation, and much of the research is being carried out by the pulp and paper industry, primarily with the intention of increasing the productivity of existing tree stock. Certain genetically modified orchard tree species have been dere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection (biology)
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend to survive and reproduce more than individuals with o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Management
Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall administrative, legal, economic, and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects, such as silviculture, protection, and forest regulation. This includes management for timber, aesthetics, recreation, urban values, water, wildlife, inland and nearshore fisheries, wood products, plant genetic resources, and other forest resource values. Management objectives can be for conservation, utilisation, or a mixture of the two. Techniques include timber extraction, planting and replanting of different species, building and maintenance of roads and pathways through forests, and preventing fire. Definition The forest is a natural system that can supply different products and services. Forests supply water, mitigate climate change, provide habitats for wildlife including many pollinators which are essential for sustainable food production, provide timber and fuelwood, serve as a source of non-wood forest products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |