|
Tree Volume Measurement
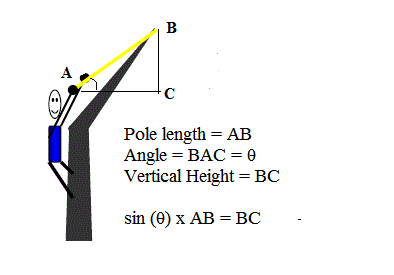
Tree volume is one of many parameters that are measured to document the size of individual trees. Tree volume measurements serve a variety of purposes, some economic, some scientific, and some for sporting competitions. Measurements may include just the volume of the trunk, or the volume of the trunk and the branches depending on the detail needed and the sophistication of the measurement methodology. Other commonly used parameters, outlined in Tree measurement: Tree height measurement, Tree girth measurement, and Tree crown measurement. Volume measurements can be achieved via tree climbers making direct measurements or through remote methods.Blozan, Will. 2004, 2008. The Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society. http://www.nativetreesociety.org/measure/Tree_Measuring_Guidelines-revised1.pdf Accessed March 4, 2013.Blozan, Will F. and Riddle, Jess D. 2006. Tsuga Search progress report October 2006. http://www.nativetreesociety.org/tsuga/oct2006/tsuga_search_oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Measurement
Trees have a wide variety of sizes and shapes and growth habits. Specimens may grow as individual trunks, multitrunk masses, coppices, clonal colonies, or even more exotic tree complexes. Most champion tree programs focus finding and measuring the largest single-trunk example of each species. There are three basic parameters commonly measured to characterize the size of a single trunk tree: tree height measurement, tree girth measurement, and tree crown measurement. Foresters also perform tree volume measurements. A detailed guideline to these basic measurements is provided in ''The Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society'' by Will Blozan.Blozan, Will. 2006. Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society. Bulletin of the Eastern Native Tree Society, Volume 1, Number 1, Summer 2006. pp. 3–10. These are summaries of how to measure trees are also presented by various groups involved in documenting big trees around the world. These include among oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen C
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclinometer
An inclinometer or clinometer is an measuring instrument, instrument used for measuring angles of slope, elevation, or depression (geology), depression of an object with respect to gravity's direction. It is also known as a ''tilt indicator'', ''tilt sensor'', tiltmeter, ''tilt meter'', ''slope alert'', ''slope gauge'', ''gradient meter'', ''gradiometer'', ''level gauge'', ''level meter'', ''declinometer'', and ''pitch & roll indicator''. Clinometers measure both inclines and declines using three different units of measure: degree (angle), degrees, percentage points, and topos. The Astrolabes, astrolabe is an example of an inclinometer that was used for celestial navigation and location of astronomical objects from ancient history, ancient times to the Renaissance. A ''tilt sensor'' can measure the wikt:tilt, tilting in often two axes of a reference plane in two axes. In contrast, a full motion would use at least three axes and often additional sensors. One way to measure tilt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter or laser distance meter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used instead. Laser rangefinders are sometimes classified as type of handheld scannerless lidar. Pulse The pulse may be coded to reduce the chance that the rangefinder can be jammed. It is possible to use Doppler effect techniques to judge whether the object is moving towards or away from the rangefinder, and if so, how fast. Precision The precision of an instrument is correlated with the rise time, divergence, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocular
A monocular is a compact refracting telescope used to magnify images of distant objects, typically using an optical prism to ensure an erect image, instead of using relay lenses like most telescopic sights. The volume and weight of a monocular are typically less than half of a pair of binoculars with similar optical properties, making it more portable and also less expensive. This is because binoculars are essentially a pair of monoculars packed together — one for each eye. As a result, monoculars only produce two-dimensional images, while binoculars can use two parallaxed images (each for one eye) to produce binocular vision, which allows stereopsis and depth perception. Monoculars are ideally suited to those applications where three-dimensional perception is not needed, or where compactness and low weight are important (e.g. hiking). Monoculars are also sometimes preferred where difficulties occur using both eyes through binoculars due to significant eyesight variation ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Station
A total station or total station theodolite is an electronic/optical instrument used for surveying and building construction. It is an electronic transit theodolite integrated with electronic distance measurement (EDM) to measure both vertical and horizontal angles and the slope distance from the instrument to a particular point, and an on-board computer to collect data and perform triangulation calculations. Robotic or motorized total stations allow the operator to control the instrument from a distance via remote control. In theory, this eliminates the need for an assistant staff member, as the operator holds the retroreflector and controls the total station from the observed point. In practice, however, an assistant surveyor is often needed when the surveying is being conducted in busy areas such as on a public carriageway or construction site. This is to prevent people from disrupting the total station as they walk past, which would necessitate resetting the tripod and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
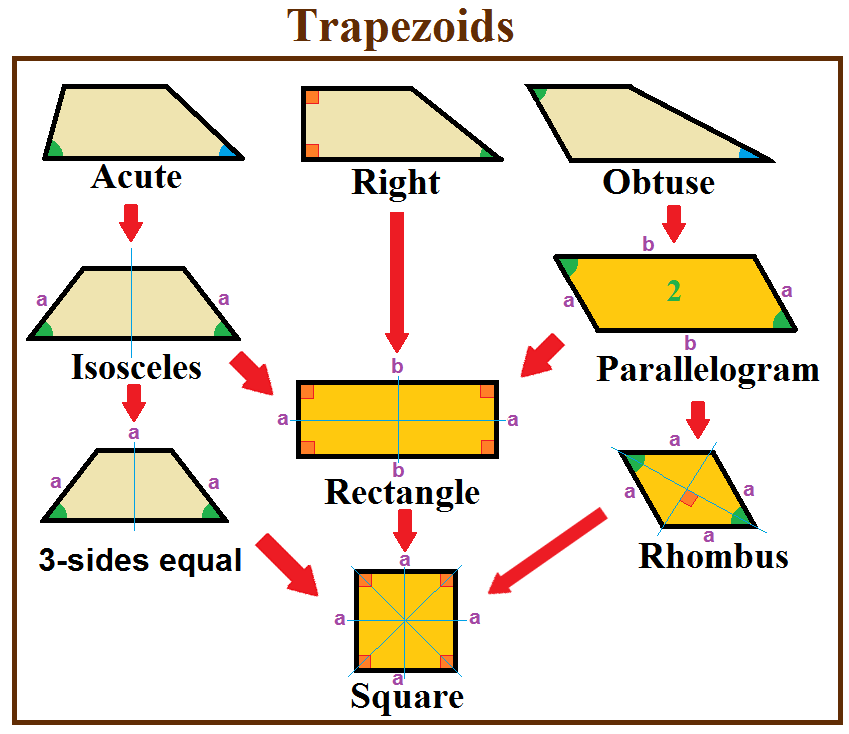
Trapezoid
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' or ''lateral sides''. (If the trapezoid is a parallelogram, then the choice of bases and legs is arbitrary.) A trapezoid is usually considered to be a convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also crossed cases. If ''ABCD'' is a convex trapezoid, then ''ABDC'' is a crossed trapezoid. The metric formulas in this article apply in convex trapezoids. Definitions ''Trapezoid'' can be defined exclusively or inclusively. Under an exclusive definition a trapezoid is a quadrilateral having pair of parallel sides, with the other pair of opposite sides non-parallel. Parallelograms including rhombi, rectangles, and squares are then not considered to be trapezoids. Under an inclusive definition, a trapezoid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it extends only into roots. The pith is encircled by a ring of xylem; the xylem, in turn, is encircled by a ring of phloem. While new pith growth is usually white or pale in color, as the tissue ages it commonly darkens to a deeper brown color. In trees pith is generally present in young growth, but in the trunk and older branches the pith often gets replaced – in great part – by xylem. In some plants, the pith in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate, resulting in a hollow stem. A few plants, such as walnuts, have distinctive chambered pith with numerous short cavities (see image at middle right). The cells in the peripheral parts of the pith may, in some plants, develop to be different from cells in the rest of the pith. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Dominance
In botany, apical dominance is the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of the plant is dominant over (i.e., grows more strongly than) other side stems; on a branch the main stem of the branch is further dominant over its own side twigs. Plant physiology describes apical dominance as the control exerted by the terminal bud (and shoot apex) over the outgrowth of lateral buds. Overview Apical dominance occurs when the shoot apex inhibits the growth of lateral buds so that the plant may grow vertically. It is important for the plant to devote energy to growing upward so that it can get more light to undergo photosynthesis. If the plant utilizes available energy for growing upward, it may be able to outcompete other individuals in the vicinity. Plants that were capable of outcompeting neighboring plants likely had higher fitness. Apical dominance is therefore most likely adaptive. Typically, the end of a shoot contains an apical bud, which is the location where shoot gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a Line (mathematics), line is a number that describes the direction (geometry), direction of the line on a plane (geometry), plane. Often denoted by the letter ''m'', slope is calculated as the ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change ("rise over run") between two distinct points on the line, giving the same number for any choice of points. The line may be physical – as set by a Surveying, road surveyor, pictorial as in a diagram of a road or roof, or Pure mathematics, abstract. An application of the mathematical concept is found in the grade (slope), grade or gradient in geography and civil engineering. The ''steepness'', incline, or grade of a line is the absolute value of its slope: greater absolute value indicates a steeper line. The line trend is defined as follows: *An "increasing" or "ascending" line goes from left to right and has positive slope: m>0. *A "decreasing" or "descending" line goes from left to right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Top Measurement
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated Plant stem, stem, or trunk (botany), trunk, usually supporting Branch, branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only Bark (botany), woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller Arecaceae, palms, Cyatheales, tree ferns, Musa (genus), bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a Monophyletic group, monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that Convergent evolution, have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |