|
Treaty Of Susa
The Treaty of Susa (also sometimes spelled Suza) refers to two separate peace treaties signed in 1629 at Susa (Italy), Susa in the Duchy of Savoy (now in the Italy, Italian Piedmont near the French border), recently occupied by France during the Thirty Years' War. Treaty between France and Savoy This treaty, signed on 11 March 1629, following the French capture of the city, was agreed between Louis XIII of France and Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy. Its terms allowed French military passage through Savoy to assist in relief of the siege of Casale Monferrato, Casale in the War of the Mantuan Succession, which was to be guaranteed by French occupation of Susa. The Duke was also to refrain from hostilities against the Duchy of Mantua. In return, France was to give Savoy Trino and other territory in Monferrat worth 15,000 crowns. Treaty between France and England and Scotland This treaty, signed on 14 April 1629 ended Anglo-French War (1627-1629), a war between England and Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa (Italy)
Susa ( lat, Segusio, french: Suse, frp, Suisa) is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Turin, Piedmont, Italy. In the middle of Susa Valley, it is situated on at the confluence of the Cenischia with the Dora Riparia, a tributary of the Po River, at the foot of the Cottian Alps, 51 km (32 mi) west of Turin. History Susa ( la, Segusio) was founded by the Ligures. It was the capital of the Segusini (also known as Cottii). In the late 1st century BC it became voluntarily part of the Roman Empire. Remains of the Roman city have been found in the excavations of the central square, the Piazza Savoia. Susa was the capital of the province of Alpes Cottiae. According to the medieval historian Rodulfus Glaber, Susa was "the oldest of Alpine towns". In the Middle and Modern ages, Susa remained important as a hub of roads connecting southern France to Italy. Taking part of the county or march of Turin (sometimes "march of Susa"). In 1167, Frederick I, Holy Roman Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Communauté métropolitaine de Québec, metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is the eleventhList of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, -largest city and the seventhList of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, -largest metropolitan area in Canada. It is also the List of towns in Quebec, second-largest city in the province after Montreal. It has a humid continental climate with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters. The Algonquian people had originally named the area , an Algonquin language, AlgonquinThe Algonquin language is a distinct language of the Algonquian languages, Algonquian language family, and is not a misspelling. word meaning "where the river narrows", because the Saint Lawrence River na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of England
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1629 In Scotland
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: *16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * '' Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band * Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1629 In England
Events from the 1620s in England. This decade sees a change of monarch. Incumbents * Monarch – James I (until 27 March 1625), then Charles I * Parliament – 3rd of King James I (starting 16 January 1621, until 8 February 1622), 4th of King James I (starting 12 February 1624, until 27 March 1625), Useless (starting 17 May, until 12 August 1625), 2nd of King Charles I (starting 6 February, until 15 June 1626), 3rd of King Charles I (starting 17 March 1628, until 10 March 1629) Events * 1620 **27 April – treaty with Spain arranges marriage between the Prince of Wales and Infanta Maria Anna of Spain in return for relaxation of laws concerning Roman Catholics. **3 July – Captain Andrew Shilling, on behalf of the Honourable East India Company, lays claim to Table Bay in Africa. **15 July – the armed merchant ship ''Mayflower'' embarks about 65 emigrants for New England at or near her home port of Rotherhithe on the Thames east of London. **c. 19 July – the ''Mayflow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1629 In France
Events from the year 1629 in France. Incumbents *Monarch: Louis XIII Events * * * * * * * * May 14–May 28 – Huguenot rebellions: After a Siege of Privas, 15-day siege, Louis XIII captures Privas. * June 17 – Huguenot rebellions: Alès surrenders after Siege of Alès, an intense siege. As a result, the leader of the Huguenot Rebellions, the Henri, Duke of Rohan, Duke of Rohan, surrenders. * June 28 – Huguenot rebellions: Louis XIII, King of France, signs in his camp at Lédignan the Peace of Alès, ending the Huguenot rebellions. The Huguenots are allowed religious freedom, but lose their political, territorial and military rights. * August 21 – Huguenot rebellions: Montauban, one of the last Huguenot strongholds, Redition of Montauban, surrenders without a fight to Cardinal Richelieu, Richelieu's troops. Births * * * * * * * * April 1 – Jean-Henri d'Anglebert, French harpsichordist and composer (d. 1691) Deaths * October 2 – Pier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Quebec
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia (also known as Mi'kma'ki and Acadia) is a Canadian province located in Canada's Maritimes. The region was initially occupied by Mi'kmaq. The colonial history of Nova Scotia includes the present-day Canadian Maritime provinces and the northern part of Maine ( Sunbury County, Nova Scotia), all of which were at one time part of Nova Scotia. In 1763 Cape Breton Island and St. John's Island (now Prince Edward Island) became part of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's Island became a separate colony. Nova Scotia included present-day New Brunswick until that province was established in 1784. (In 1765, the county of Sunbury was created, and included the territory of present-day New Brunswick and eastern Maine as far as the Penobscot River.) During the first 150 years of European settlement, the colony was primarily made up of Catholic Acadians, Maliseet and Mi'kmaq. During the latter seventy-five years of this time period, there were six colonial wars that took place in Nova Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1632)
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye was signed on March 29, 1632. It returned New France (Quebec, Acadia and Cape Breton Island) to French control after the English had seized it in 1629,"KIRKE, SIR DAVID, adventurer, trader, colonizer, leader of the expedition that captured Quebec in 1629, and later governor of Newfoundland" ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online'' after the had ended. On 19 July 1629, an English fleet under the command of |
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although the island is physically separated from the Nova Scotia peninsula by the Strait of Canso, the long Canso Causeway connects it to mainland Nova Scotia. The island is east-northeast of the mainland with its northern and western coasts fronting on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with its western coast forming the eastern limits of the Northumberland Strait. The eastern and southern coasts front the Atlantic Ocean with its eastern coast also forming the western limits of the Cabot Strait. Its landmass slopes upward from south to north, culminating in the highlands of its northern cape. One of the world's larger saltwater lakes, ("Arm of Gold" in French), dominates the island's centre. The total population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
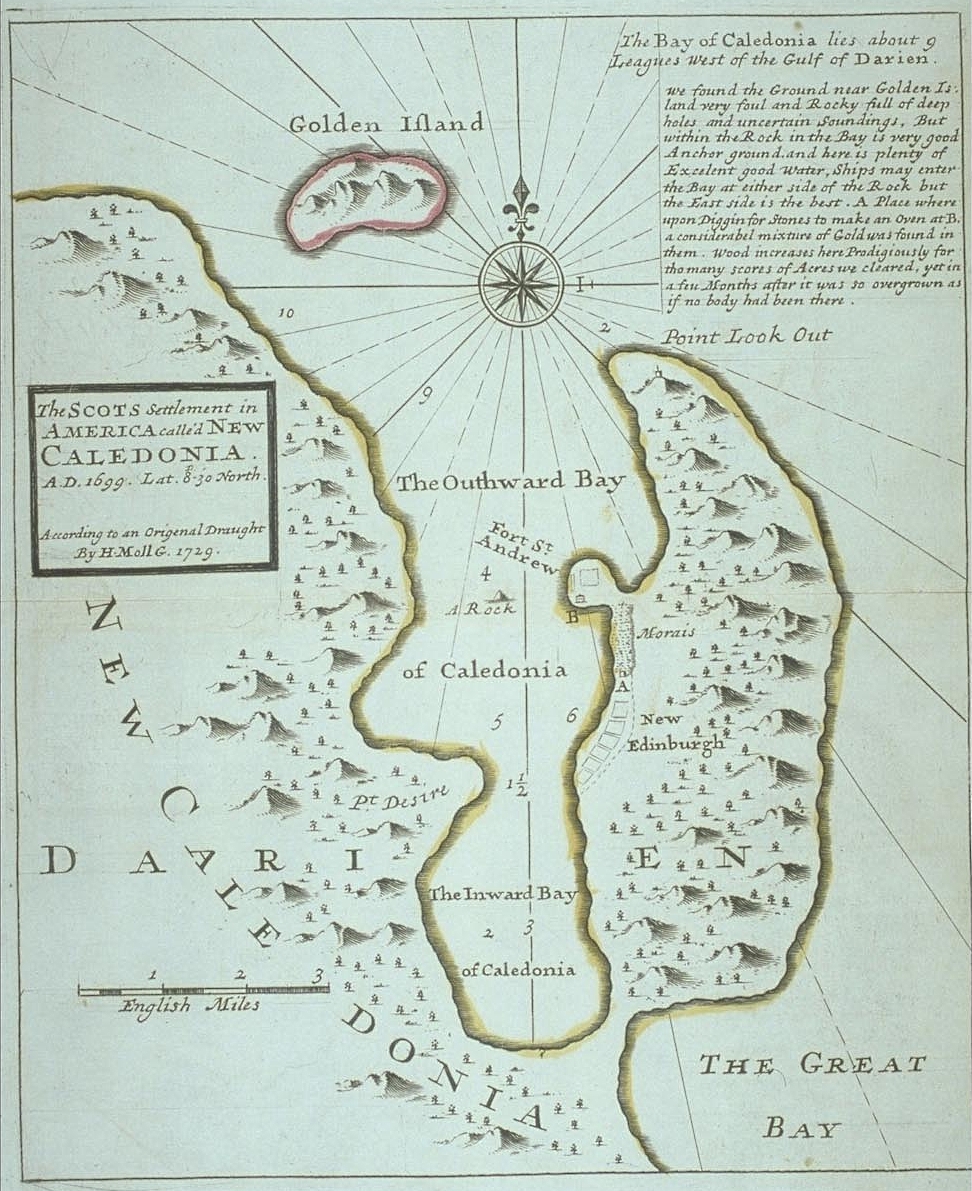
Scottish Colony
Scottish colonisation of the Americas comprised a number of failed or abandoned Scottish settlements in North America; a colony at Darien on the Isthmus of Panama; and a number of wholly or largely Scottish settlements made after the Acts of Union 1707, and those made by the enforced resettlement after the Battle of Culloden and the Highland Clearances. Nova Scotia (1621) The first documented Scottish settlement in the Americas was of Nova Scotia in 1629. On 29 September 1621, the charter for the foundation of a colony was granted by James VI of Scotland to Sir William Alexander. Between 1622 and 1628, Sir William launched four attempts to send colonists to Nova Scotia; all failed for various reasons. A successful settlement of Nova Scotia was finally achieved in 1629. The colony's charter, in law, made Nova Scotia (defined as all land between Newfoundland and New England; i.e., The Maritimes) a part of mainland Scotland; this was later used to get around the English na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |