|
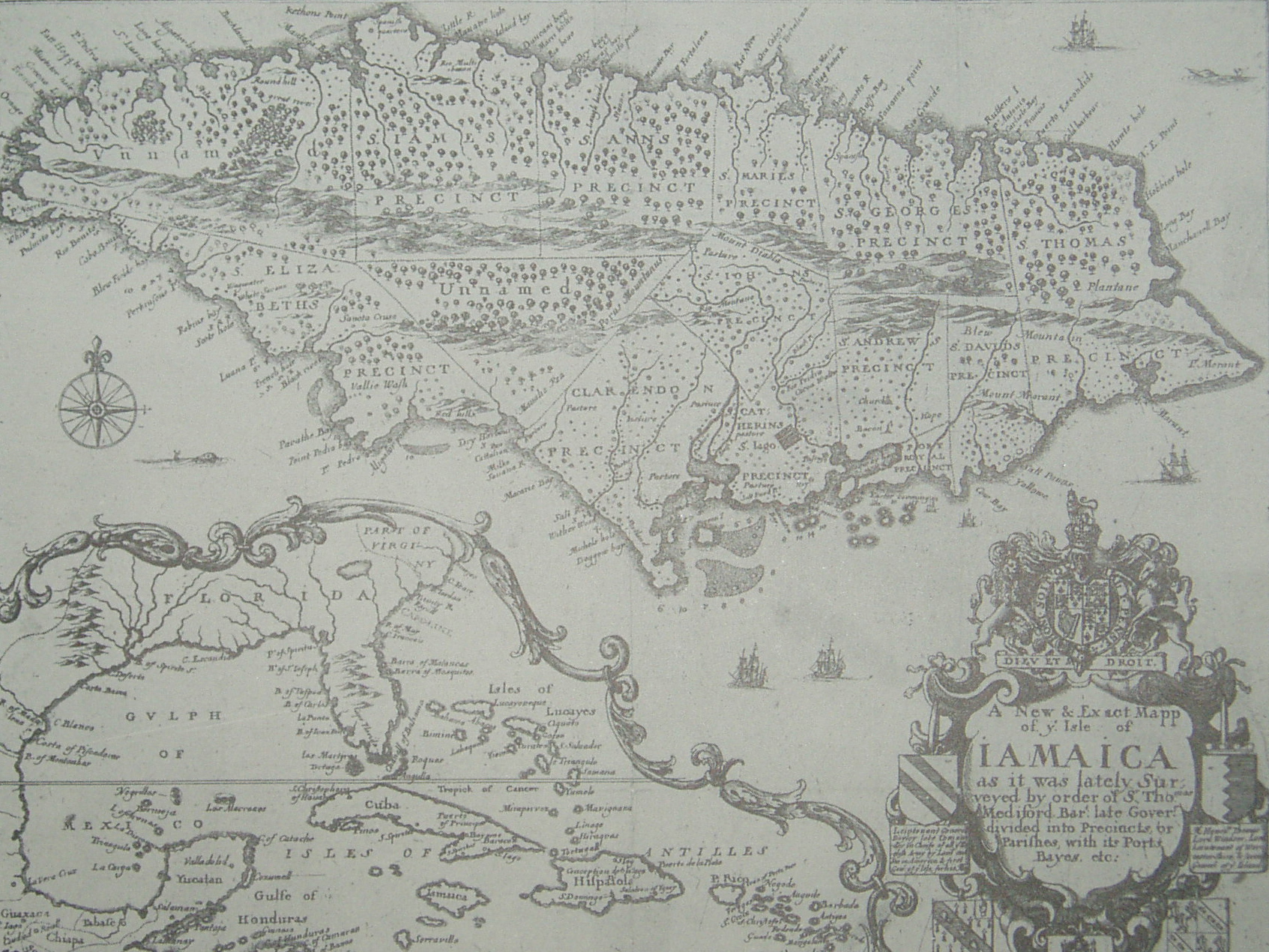
Treaty Of Madrid (1670)
The Treaty of Madrid, also known as the Godolphin Treaty, was a treaty between England and Spain that was agreed to in July 1670 "for the settlement of all disputes in America". The treaty officially ended the Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), war begun in 1654 in the Caribbean in which England had Invasion of Jamaica, conquered Jamaica.Pestana p. 185 The 1670 Treaty of Madrid was highly favourable to England, as its Adverse Possession in the Caribbean Sea and the rest of the Americas was confirmed and made legal by Spain. Before 1670, Spain had exclusively regarded the Americas as Spanish territory with the exception of Brazil, which was Portuguese according to the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas that had confirmed Christopher Columbus' claim of the New World for Spain since 12 October 1494.Padron pp.xiv-xxi Background The Anglo-Spanish War had begun in late 1654. In Europe, the conflict ended with the Treaty of the Pyrenees (between France and Spain) and King Charles II of England's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Godolphin (diplomat)
Sir William Godolphin (2 February 1635 – 11 July 1696) was an English diplomat for Charles II of England, Charles II and Member of Parliament. Biography Godolphin was third but eldest surviving son of Sir William Godolphin (Royalist), William Godolphin (1605–1663) of Spargor, Cornwall; the eldest son (by Judith Meredith) of John Godolphin (the younger brother of Sir William Godolphin (1567–1613)—and Ruth (died before 1658), daughter of Sir John Lambe of East Coulston, Wiltshire. Godolphin was baptised 2 February 1634, and was educated at Westminster School and Christ Church, Oxford, gaining the degrees of Master of Arts in 1661 and Doctor of Civil Law in 1663. He became a follower of Henry Bennet, 1st Earl of Arlington, Lord Arlington, and in 1665 he was elected in a by-election to Parliament as member for Camelford (UK Parliament constituency), Camelford, however as he went to Spain early the next year he probably never took up his seat. After 1662 he was exchanging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with their associated islands, the Americas cover 8% of Earth's total surface area and 28.4% of its land area. The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that runs the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon, St. Lawrence River–Great Lakes basin, Mississippi, and La Plata. Since the Americas extend from north to south, the climate and ecology vary widely, from the arctic tundra of Northern Canada, Greenland, and Alaska, to the tropical rain forests in Central America and South America. Humans first settled the Americas from Asia between 42,000 and 17,000 years ago. A second migration of Na-Dene speakers followed later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Madrid (1667)
The Treaty of Madrid, also known as The Earl of Sandwich's Treaty, was signed on 23 May, 1667 by England and Spain. It was one of a series of agreements made in response to French expansion under King Louis XIV. The parties agreed to commercial terms allowing English merchants trading privileges within the Spanish Empire that remained in place until superseded by the Treaty of Utrecht in 1714. They undertook not to assist each other's enemies, and England also agreed to mediate an end to the 1640-1668 Portuguese Restoration War, which resulted in the 1668 Treaty of Lisbon between Spain and Portugal. The issue of Spanish possessions captured by England in the Anglo-Spanish War (1654-1660) was settled by the 1670 Treaty of Madrid. Background The treaty was one of a series of agreements signed between 1662 and 1668 that were driven by changes in the European balance of power. They included the weakening of the relationship between France and the Dutch Republic, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the south of Cuba and northeast of Honduras, between Jamaica and Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The capital city is George Town on Grand Cayman, which is the most populous of the three islands. The Cayman Islands is considered to be part of the geographic Western Caribbean Zone as well as the Greater Antilles. The territory is a major world offshore financial centre for international businesses and wealthy individuals, largely as a result of the state not charging taxes on any income earned or stored. With a GDP per capita of $91,392, the Cayman Islands has the highest standard of living in the Caribbean. Immigrants from over 130 countries and territories reside in the Cayman Islands. History No archaeological evidence for an indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Modyford
Colonel Sir Thomas Modyford, 1st Baronet (c. 1620 – 1 September 1679) was a planter of Barbados and Governor of Jamaica from 1664 to 1671. Early life Modyford was the son of a mayor of Exeter with family connections to the Duke of Albemarle. Barbados Modyford emigrated to Barbados as a young man with other family members in 1647, in the opening stages of the English Civil War. He had £1,000 for a down payment on a plantation and £6,000 to commit in the next three years. Modyford soon was dominant in Barbados island politics, rising to be speaker of the House of Assembly in Barbados during the reign of King Charles II, and factor for the Royal Adventurers Trading to Africa, who had a monopoly in the slave trade to the islands. By 1647, Modyford had made a fortune from sugar and slavery. In 1651, Modyford sided with the Cavaliers under Lord Francis Willoughby, 5th Baron Willoughby of Parham, as they defied Oliver Cromwell, but when a force was despatched under the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Morgan
Sir Henry Morgan ( cy, Harri Morgan; – 25 August 1688) was a privateer, plantation owner, and, later, Lieutenant Governor of Jamaica. From his base in Port Royal, Jamaica, he raided settlements and shipping on the Spanish Main, becoming wealthy as he did so. With the prize money from the raids, he purchased three large sugar plantations on the island. Much of Morgan's early life is unknown. He was born in an area of Monmouthshire that is now part of the city of Cardiff. It is not known how he made his way to the West Indies, or how he began his career as a privateer. He was probably a member of a group of raiders led by Sir Christopher Myngs in the early 1660s during the Anglo-Spanish War. Morgan became a close friend of Sir Thomas Modyford, the Governor of Jamaica. When diplomatic relations between the Kingdom of England and Spain worsened in 1667, Modyford gave Morgan a letter of marque, a licence to attack and seize Spanish vessels. Morgan subsequently conducted succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Myngs
Vice Admiral Sir Christopher Myngs (sometimes spelled ''Mings'', 1625–1666) was an English naval officer and privateer. He came of a Norfolk family and was a relative of Admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell. Samuel Pepys' story of Myngs' humble birth, in explanation of his popularity, has now been evaluated by historians as to be mostly fictitious in nature. Life The date of Myngs's birth is uncertain, but probably somewhere between 1620 and 1625. It is probable that he saw a good deal of sea-service before 1648. He first appears prominently as the captain of the ''Elisabeth'', which after a sharp action during the First Anglo-Dutch War brought in a Dutch convoy with two men-of-war as prizes. From 1653 to 1655 he continued to command the ''Elisabeth'', high in favour with the council of state and recommended for promotion by the flag officers under whom he served. In 1655, he was appointed to the frigate ''Marston Moor'', the crew of which was on the verge of mutiny. His firm me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccaneers
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from the Restoration in 1660 until about 1688, during a time when governments were not strong enough and did not consistently attempt to suppress them. Originally the name applied to the landless hunters of wild boars and cattle in the largely uninhabited areas of Tortuga and Hispaniola. The meat they caught was smoked over a slow fire in little huts the French called ''boucans'' to make ''viande boucanée'' – ''jerked meat'' or ''jerky'' – which they sold to the corsairs who preyed on the (largely Spanish) shipping and settlements of the Caribbean. Eventually the term was applied to the corsairs and (later) privateers themselves, also known as the Brethren of the Coast. Though corsairs, also known as ''filibusters'' or ''freebooters'', were largely lawless, privateers were nomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Main
During the Spanish colonization of America, the Spanish Main was the collective term for the parts of the Spanish Empire that were on the mainland of the Americas and had coastlines on the Caribbean Sea or Gulf of Mexico. The term was used to distinguish those regions from the numerous islands Spain controlled in the Caribbean, which were known as the Spanish West Indies. Etymology The word "main" in the expression is a contraction of mainland.Online Etymology Dictionary: main (n.) Retrieved 20 August 2014 Composition The Spanish Main included and |
Siege Of Santo Domingo (1655)
The siege of Santo Domingo was fought between April23, 1655 and April30, 1655, at the Spanish Colony of Santo Domingo. A force of 2,400 Spanish troops led by Governor Don Bernardino Meneses y Bracamonte, Count of Peñalba successfully resisted a force of 13,120 soldiers led by General Robert Venables and 34 ships under Admiral Sir William Penn of the English Commonwealth. Background In 1655 the Commonwealth of England, under Oliver Cromwell, decided to declare war on Spain. Religious fanaticism played a role in this, as the puritans running the Commonwealth loathed the Catholicism of Spain. More practically, England had a large standing army with ambitious commanders and Cromwell wished to occupy them with a successful campaign, preferably far from home. In addition it was believed that war with Spain would be both easy and profitable. Command of an expedition to the Caribbean to capture Spanish colonies named the "Western Design" was given to General Robert Venables, with Admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restoration (England)
The Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland took place in 1660 when King Charles II returned from exile in continental Europe. The preceding period of the Protectorate and the civil wars came to be known as the Interregnum (1649–1660). The term ''Restoration'' is also used to describe the period of several years after, in which a new political settlement was established. It is very often used to cover the whole reign of King Charles II (1660–1685) and often the brief reign of his younger brother King James II (1685–1688). In certain contexts it may be used to cover the whole period of the later Stuart monarchs as far as the death of Queen Anne and the accession of the Hanoverian King George I in 1714. For example, Restoration comedy typically encompasses works written as late as 1710. The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of The Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees (french: Traité des Pyrénées; es, Tratado de los Pirineos; ca, Tractat dels Pirineus) was signed on 7 November 1659 on Pheasant Island, and ended the Franco-Spanish War that had begun in 1635. Negotiations were conducted on Pheasant Island, situated in the middle of the Bidasoa River on the border between the two countries, which has remained a French-Spanish condominium ever since. It was signed by Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain, as well as their chief ministers, Cardinal Mazarin and Don Luis Méndez de Haro. Background France entered the Thirty Years' War after the Spanish Habsburg victories in the Dutch Revolt in the 1620s and at the Battle of Nördlingen against Sweden in 1634. By 1640, France began to interfere in Spanish politics, aiding the revolt in Catalonia, while Spain responded by aiding the Fronde revolt in France in 1648. During the negotiations for the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, France gained the Sundgau and cut o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)