|
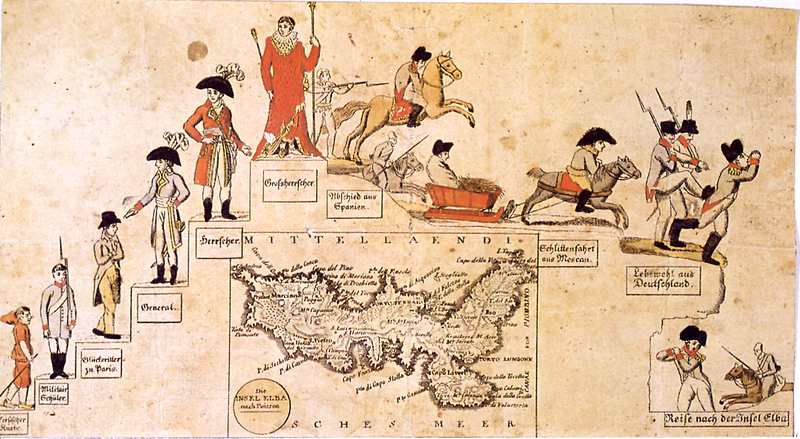
Treaty Of Fontainebleau (1814)
The Treaty of Fontainebleau was an agreement established in Fontainebleau, France, on 11 April 1814 between Napoleon and representatives of Austrian Empire, Austria, Russian Empire, Russia and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. The treaty was signed in Paris on 11 April by the Plenipotentiary, plenipotentiaries of both sides and ratified by Napoleon on 13 April. With this treaty, the allies ended Napoleon's rule as emperor of the First French Empire, French and sent him into exile on Elba. Prelude In the War of the Sixth Coalition (1812–1814), a coalition of Austrian Empire, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and a number of Confederation of the Rhine, German states drove Napoleon out of Germany in 1813. In 1814, while the United Kingdom, History of Spain (1814–73), Spain and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal Campaign in south-west France (1814), invaded France across the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouchot - Napoléon Signe Son Abdication à Fontainebleau 11 Avril 1814
''For people with the surname, see Bouchot (surname).'' The Bouchot is a river in the France, French region of Grand Est which flows in the Vosges (département), Vosges department. It is a right tributary of the Moselotte, and thus a sub-tributary of the Rhine via the Moselotte and the Moselle. It is long. Geography The Bouchot rises in the Massif des Vosges, on a flank of the ''Tête de Grouvelin'', a peak located within the commune of Gérardmer in the ''Bas-Rupts'' section. The Bouchot is thus also known as the ''ruisseau des Hauts-Rupts'' from its source to its confluence with the ''ruisseau des Bas-Rupts''. It flows through Rochesson, follows Gerbamont, then flows into Sapois, Vosges, Sapois where the ''ruisseau de Menaurupt'' joins its right bank. After flowing through Vagney, it joins the right bank of the Moselotte. At Gerbamont, it cascades at the ''Saut du Bouchot'', a waterfall that is high. Hydrology The discharge (hydrology), hydrological discharge of the Bouc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaign In North-east France (1814)
The 1814 campaign in north-east France was Napoleon's final campaign of the War of the Sixth Coalition. Following their victory at Leipzig in 1813, the Austrian, Prussian, Russian, and other German armies of the Sixth Coalition invaded France. Despite the disproportionate forces in favour of the Coalition, Napoleon managed to inflict some defeats, especially during the Six Days' Campaign. However, the campaign ended in total defeat for Napoleon as the Coalition kept advancing towards Paris as Napoleon was out of position to defend the capital, which capitulated in late March 1814. When Napoleon proposed the army march on Paris, his Marshals decided to unanimously overrule Napoleon in order to save the city from further destruction. As a result, the victorious Coalition negotiated the Treaty of Paris, under which Napoleon was exiled to the island of Elba and the borders of France were returned to where they had been in 1792. Background Following defeats in the Wars of the Fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francs
The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription ''francorum rex'' (King of the Franks) used on early French coins and until the 18th century, or from the French ''franc'', meaning "frank" (and "free" in certain contexts, such as ''coup franc'', "free kick"). The countries that use francs today include Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and most of Francophone Africa. The Swiss franc is a major world currency today due to the prominence of Swiss financial institutions. Before the introduction of the euro in 1999, francs were also used in France, Belgium and Luxembourg, while Andorra and Monaco accepted the French franc as legal tender (Monégasque franc). The franc was also used within the French Empire's colonies, including Algeria and Cambodia. The franc is sometimes Italianised or Hispanicised as the ''franco'', for instance in Luccan franco. Origins The franc was originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Guastalla
The Duchy of Guastalla was an Italian state which existed between 1621 and 1748. It was bordered by the Duchy of Modena and Reggio and the Po River to the north, on the opposite bank of the Duchy of Mantua. History On 2 July 1621, Emperor Ferdinand II elevated the County of Guastalla to the rank of a duchy. Ferrante II Gonzaga became the first duke of the city, hoping to succeed in the future to the great Duchy of Mantua. Ferrante II died of plague in 1630 and was succeeded by his son, Cesare II. With him, Guastalla expanded its territory with the annexation of the lands of Dosolo, Luzzara and Reggiolo, until then owned by Mantua. In 1632, his son Ferrante III ascended to the throne. Having no male heir, he bequeathed the Duchy of Guastalla to his daughter's husband Ferdinand Charles, Duke of Mantua. Meanwhile, Guastalla modernized its defenses, owing to the frequent wars which swept over Italy at this time. Between 1689 and 1690, the city was attacked by the Spaniards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Parma, Piacenza E Guastalla
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna. Originally a realm of the Farnese family after Pope Paul III made it a hereditary duchy for his son, Pier Luigi Farnese, it was ruled by the dynasty until 1731, when the last duke, Antonio Farnese, died without direct heirs. It was invaded by Napoleon and annexed by France, having its sovereignty restored in 1814 after Napoleon’s defeat. Napoleon's wife, Marie Louise (''Maria Luigia''), then ruled as its duchess until her death. Parma was restored to Bourbon rule in 1847, and in 1859, the duchy was formally abolished as it was integrated into the new Italian state. History The Duchy of Parma was created in 1545 from parts of the Duchy of Milan south of the Po River, which had been conquered by the Papal States in 1512. These territories, centered on the city of Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Parma
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna. Originally a realm of the Farnese family after Pope Paul III made it a hereditary duchy for his son, Pier Luigi Farnese, it was ruled by the dynasty until 1731, when the last duke, Antonio Farnese, died without direct heirs. It was invaded by Napoleon and annexed by France, having its sovereignty restored in 1814 after Napoleon’s defeat. Napoleon's wife, Marie Louise (''Maria Luigia''), then ruled as its duchess until her death. Parma was restored to Bourbon rule in 1847, and in 1859, the duchy was formally abolished as it was integrated into the new Italian state. History The Duchy of Parma was created in 1545 from parts of the Duchy of Milan south of the Po River, which had been conquered by the Papal States in 1512. These territories, centered on the city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Fontainebleau (1814)
The Treaty of Fontainebleau was an agreement established in Fontainebleau, France, on 11 April 1814 between Napoleon and representatives of Austrian Empire, Austria, Russian Empire, Russia and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. The treaty was signed in Paris on 11 April by the Plenipotentiary, plenipotentiaries of both sides and ratified by Napoleon on 13 April. With this treaty, the allies ended Napoleon's rule as emperor of the First French Empire, French and sent him into exile on Elba. Prelude In the War of the Sixth Coalition (1812–1814), a coalition of Austrian Empire, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and a number of Confederation of the Rhine, German states drove Napoleon out of Germany in 1813. In 1814, while the United Kingdom, History of Spain (1814–73), Spain and Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal Campaign in south-west France (1814), invaded France across the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Marmont
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont (20 July 1774 – 22 March 1852) was a French general and nobleman who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire and was awarded the title (french: duc de Raguse). In the Peninsular War Marmont succeeded the disgraced André Masséna in the command of the French army in northern Spain, but lost decisively at the Battle of Salamanca. At the close of the War of the Sixth Coalition, Marmont went over to the Restoration, and remained loyal to the Bourbons through the Hundred Days. This gave Marmont a reputation as a traitor among the remaining Bonapartists, and in French society more broadly. He led the royalist Paris garrison during the July Revolution in 1830, but his efforts proved incapable of quelling the revolution, leading King Charles X to accuse Marmont of betraying the Bourbons as he had betrayed the Bonapartes. Marmont departed France with Charles's entourage and never returned to France. Spending his exile mostly in Vienna and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Louise, Duchess Of Parma
french: Marie-Louise-Léopoldine-Françoise-Thérèse-Josèphe-Lucie it, Maria Luigia Leopoldina Francesca Teresa Giuseppa Lucia , house = Habsburg-Lorraine , father = Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor , mother = Maria Theresa of Naples and Sicily , religion = Roman Catholicism , signature = Signatur Marie-Louise von Österreich.PNG Marie Louise (12 December 1791 – 17 December 1847) was an Austrian archduchess who reigned as Duchess of Parma from 11 April 1814 until her death. She was Napoleon's second wife and as such Empress of the French and Queen of Italy from their marriage on 1 April 1810 until his abdication on 6 April 1814. As the eldest child of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor and Emperor of Austria, and his second wife, Maria Theresa of Naples and Sicily, Marie Louise grew up during a period of continuous conflict between Austria and revolutionary France. A series of military defeats at the hands of Napoleon Bonaparte had inflicted a heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Fontainebleau
Palace of Fontainebleau (; ) or Château de Fontainebleau, located southeast of the center of Paris, in the commune of Fontainebleau, is one of the largest French royal châteaux. The medieval castle and subsequent palace served as a residence for the French monarchs from Louis VII to Napoleon III. Francis I and Napoleon were the monarchs who had the most influence on the palace as it stands today. It became a national museum in 1927 and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1981 for its unique architecture and historical importance. History Medieval palace (12th century) The earliest record of a fortified castle at Fontainebleau dates to 1137. It became a favorite residence and hunting lodge of the Kings of France because of the abundant game and many springs in the surrounding forest. It took its name from one of the springs, the fountain de Bliaud, located now in the English garden, next to the wing of Louis XV. It was used by King Louis VII, for whom Thomas B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Invasion Of Russia
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Napoleon's invasion of Russia is one of the best studied military campaigns in history and is listed among the most lethal military operations in world history. It is characterized by the massive toll on human life: in less than six months nearly a million soldiers and civilians died. On 24 June 1812 and the following days, the first wave of the multinational crossed the Niemen into Russia. Through a series of long forced marches, Napoleon pushed his army of almost half a million people rapidly through Western Russia, now Belarus, in an attempt to destroy the separated Russian armies of Barclay de Tolly and Pyotr Bagration who amounted to around 180,000–220,000 at this time. Within six weeks, Napoleon lost ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |