|
Treaty Of Chudniv
Treaty of Chudnov or Treaty of Cudnów ( pl, Ugoda cudnowska, uk, Чуднівський трактат) was a treaty between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Cossacks, signed in Chudniv (Polish: Cudnów) on 17 October 1660 during the Chmielnicki Rebellion. It restored most of the provisions of the Treaty of Hadiach, except for the elevation of Ruthenia to the status equal of the Poland and Lithuania. It invalidated the Pereyaslav Articles. The treaty was signed following the Polish victory at the Battle of Chudnov. The treaty meant that the Cossacks withdrew their support from Russia in the Russo-Polish War (1654–67), and transferred it back to the Commonwealth. The war would eventually be concluded with the 1667 Treaty of Andrusovo. References 1658 in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Poland–Ukraine military relations 1660 treaties Chudnov Chudnov Chudniv ( ua, Чуднів, pl, Cudnów, yi, טשודנאוו, russian: Чу́днов) is a city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania ruled by a common Monarchy, monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and List of Lithuanian monarchs, Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish language, Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages. The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a ''de facto'' personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporozhtsi, translit-std=ungegn) were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids, the land also known historically as the Wild Fields in what is today central and eastern Ukraine. Much of this territory is now flooded by the waters of the Kakhovka Reservoir. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th century, the Zaporozhian Cossacks were a strong political and military force that challenged the authority of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Tsardom of Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chudniv
Chudniv ( ua, Чуднів, pl, Cudnów, yi, טשודנאוו, russian: Чу́днов) is a city in Zhytomyr Raion, Zhytomyr Oblast, Ukraine. Prior to 2020, it was the administrative center of the former Chudniv Raion. Population: History A significant battle of the Russo-Polish War (1654-1667) was fought near the town in 1660, followed by a treaty between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Cossacks, named after the city. In 1866 Polish Romantic-era novelist Henryk Rzewuski died in Chudniv. The Jewish population was important in the town. During World War II, the Germans occupied the town and kept the Jews imprisoned in a ghetto. In 1941, they were murdered in mass executions perpetrated by an Einsatzgruppen of Germans and Ukrainian policemen. Notable people from Chudniv * Alter Chudnover, AKA Yehiel Goyzman (1846–1912), virtuoso klezmer violinist * Menachem Ribalow - newspaper editor * Shloimke (Sam) Beckerman - early 20th century klezmer bandleader in New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chmielnicki Rebellion
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: восстание Богдана Хмельницкого also known as the Cossack–Polish War, the Chmielnicki Uprising, the Khmelnytsky massacre or the Khmelnytsky insurrection, was a Cossack rebellion that took place between 1648 and 1657 in the eastern territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which led to the creation of a Cossack Hetmanate in Ukraine. Under the command of Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky, the Zaporozhian Cossacks, allied with the Crimean Tatars and local Ukrainian peasantry, fought against Polish domination and Commonwealth forces. The insurgency was accompanied by mass atrocities committed by Cossacks against the civilian population, especially against the Roman Catholic clergy and the Jews, as well as savage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Hadiach
The Treaty of Hadiach ( pl, ugoda hadziacka; uk, гадяцький договір) was a treaty signed on 16 September 1658 in Hadiach (Hadziacz, Hadiacz, Гадяч) between representatives of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth ( representing Poland and representing Lithuania) and Zaporozhian Cossacks (represented by Hetman Ivan Vyhovsky and starshina Yuri Nemyrych, architect of the treaty, and Pavlo Teteria). It was designed to elevate the Cossacks and Ruthenians to the position equal to that of Poland and Lithuania in the Polish–Lithuanian union and in fact transforming the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth into a Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth (''Rzeczpospolita Trojga Narodów'', "Commonwealth of Three Nations"). Text The list of points and humble requests that are submitted at his mercy by Serene Hetman of Zaporizhian Host along with the whole Zaporizhian Host and Russian uthenianpeople to his royal mercy and the whole Rzecz Pospolita: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereyaslav Articles
The Pereyaslav Articles ( uk, Переяславські статті, translit=Pereiaslavski statti, russian: Переяславские статьи) were concluded on October 27, 1659 between Yurii Khmelnytsky, the son of Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and the Russian tsar. The treaty drastically limited the Ukrainian (Cossack) autonomy. This second treaty was an aftermath of the Treaty of Hadiach from 16 September 1658 between the Cossacks and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which granted many privileges to Cossacks and thus threatened Russian influence over Cossacks. The articles imposed severe restrictions on Cossack Hetmanate autonomy. The treaty Under the new articles, Ukraine was not allowed to conduct any foreign policy including military alliances.Pereiaslav Articles of 1659 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
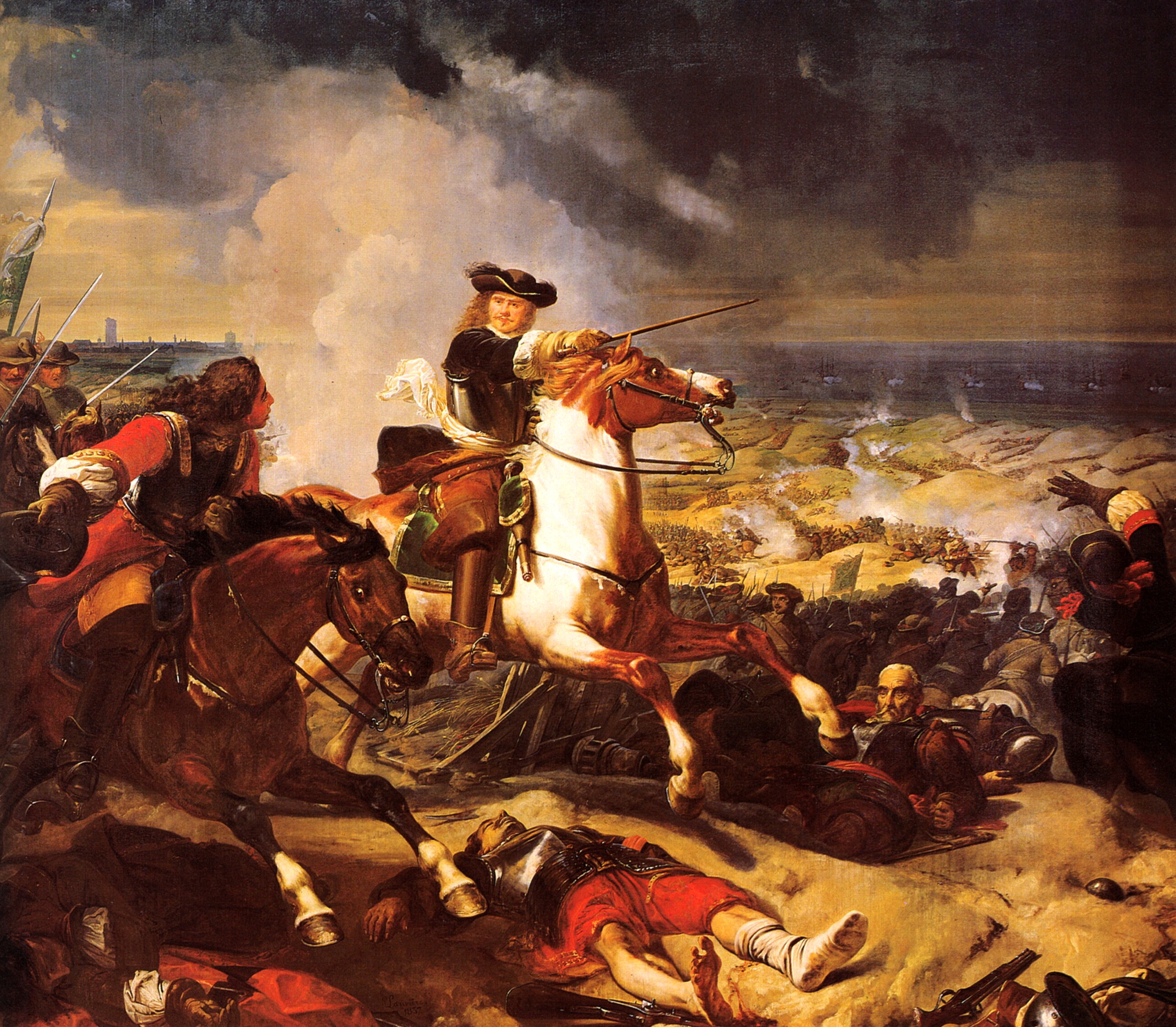
Battle Of Chudnov
The Battle of Chudnov (Chudniv, Cudnów) took place from 14 October to 2 November 1660, between the forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, allied with the Crimean Tatars, and the Tsardom of Russia, allied with the Cossacks. It ended with a decisive Polish victory, and the truce of Chudnov ( pl, Cudnów). The entire Russian army, including its commander, was taken into jasyr slavery by the Tatars. The battle was the largest and most important Polish victory over the Russian forces until the battle of Warsaw in 1920. Background In July 1660, tsar Alexis I of Russia ordered Vasily Sheremetev to resume the sporadic Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), and push the Poles west, taking Lwów (Lviv) and securing disputed Ukrainian territories for Russia. In September 1660, the commander of the Russian army, Sheremetev – acting on misleading information greatly underestimating the numerical strength of the Polish army – decided to seek out and destroy the Polish forces with w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
Armed conflicts between Poland (including the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and Russia (including the Soviet Union) include: Originally a Polish civil war that Russia, among others, became involved in. Originally a Hungarian revolution but was joined with Polish force on Hungarian side against Austria and Russia. Part of the broader Russian Revolution of 1905. See also * * * * * – in most of which Kingdom of Poland was allied with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ... * * * * * * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Russian War Lists of military conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which had fought the Russo-Polish War since 1654 over the territories of modern-day Ukraine and Belarus. Afanasy Ordin-Nashchokin (for Russia) and Jerzy Chlebowicz (for the Commonwealth) signed the truce on 30 January/9 February 1667 in the village of Andrusovo not far from Smolensk. Representatives of the Cossack Hetmanate were not allowed. Terms The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia (Muscovy) agreed on the following terms: * A truce was signed for 13.5 years during which both states were obligated to prepare the conditions for eternal peace. * Russia secured the territories of Left-bank Ukraine, Siever lands, and Smolensk. * Poland-Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1658 In The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Events January–March * January 13 – Edward Sexby, who had plotted against Oliver Cromwell, dies in the Tower of London. * January 30 – The " March Across the Belts" (''Tåget över Bält''), Sweden's use of winter weather to send troops across the waters of the Danish straits at a time when winter has turned them to ice, begins. Within 17 days, Sweden's King Karl X Gustav leads troops across the ice belts to capture six of Denmark's islands as Swedish territory. * February 5 – Prince Muhi al-Din Muhammad, one of the sons of India's Mughal, Emperor Shah Jahan, proclaims himself Emperor after Jahan names Muhi's older brother, Dara Shikoh, as regent, and departs from Aurangabad with troops. * February 6 – Swedish troops of Charles X Gustav of Sweden cross The Great Belt in Denmark, over frozen sea. * March 8 (February 26 OS) – The peace between Sweden and Denmark is concluded in Roskilde by the Treaty of Roskilde, under which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1660 Treaties
Year 166 ( CLXVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pudens and Pollio (or, less frequently, year 919 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 166 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Dacia is invaded by barbarians. * Conflict erupts on the Danube frontier between Rome and the Germanic tribe of the Marcomanni. * Emperor Marcus Aurelius appoints his sons Commodus and Marcus Annius Verus as co-rulers (Caesar), while he and Lucius Verus travel to Germany. * End of the war with Parthia: The Parthians leave Armenia and eastern Mesopotamia, which both become Roman protectorates. * A plague (possibly small pox) comes from the East and spreads throughout the Roman Empire, lasting for roughly twenty years. * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |