|
Treaty Of Canandaigua
The Treaty of Canandaigua (or Konondaigua, as spelled in the treaty itself) also known as the Pickering Treaty and the Calico Treaty, is a treaty signed after the American Revolutionary War between the Grand Council of the Six Nations and President George Washington representing the United States of America. It was signed at Canandaigua, New York on November 11, 1794, by fifty sachems () and war chiefs representing the Grand Council of the Six Nations of the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee) Confederacy (including the Cayuga, Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Seneca and Tuscarora tribes), and by Timothy Pickering, official agent of President George Washington. Background of the treaty The Treaty of Canandaigua arose out of a combination of geo-political tensions. In the aftermath of its defeat in the American Revolutionary War, Great Britain was forced to relinquish its land east of the Mississippi River to the United States. However, Great Britain’s original rights to this territory were un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Pickering
Timothy Pickering (July 17, 1745January 29, 1829) was the third United States Secretary of State under Presidents George Washington and John Adams. He also represented Massachusetts in both houses of Congress as a member of the Federalist Party. In 1795, he was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society. Born in Salem in the Province of Massachusetts Bay, Pickering began a legal career after graduating from Harvard University. He won election to the Massachusetts General Court and served as a county judge. He also became an officer in the colonial militia and served in the siege of Boston during the early stages of the American Revolutionary War. Later in the war, he was Adjutant General and Quartermaster General of the Continental Army. After the war, Pickering moved to the Wyoming Valley of Pennsylvania and took part in the then colony's 1787 ratifying convention for the United States Constitution. President Washington appointed Pickering to the position of Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
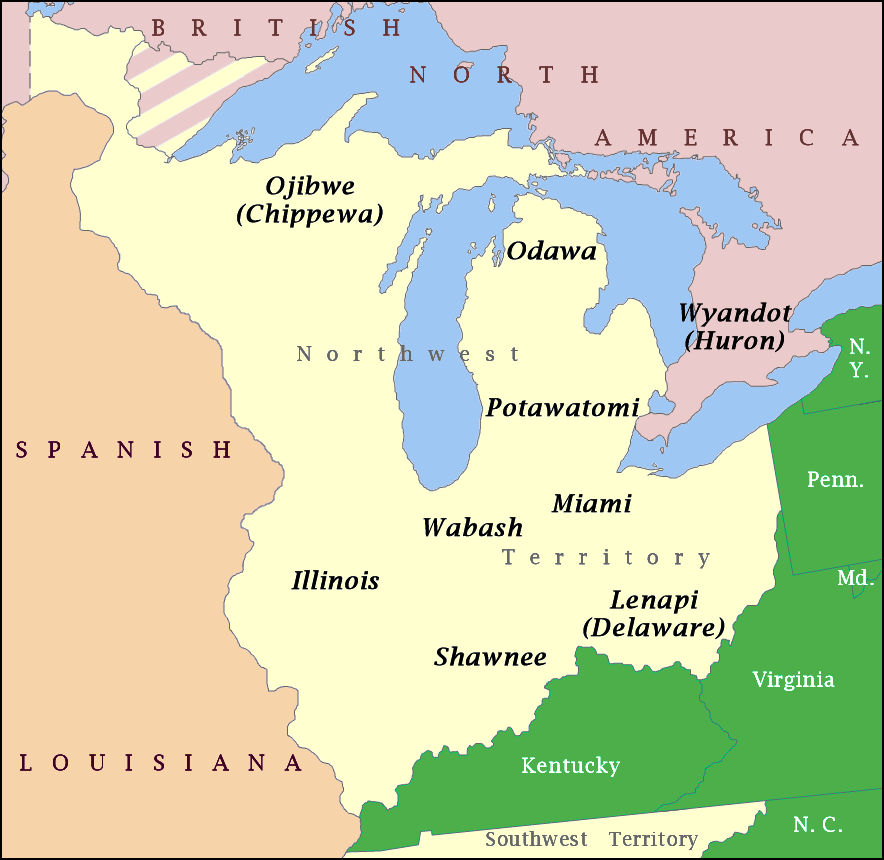
Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars. Following centuries of conflict for control of this region, it was granted to the new United States by the Kingdom of Great Britain in article 2 of the Treaty of Paris, which ended the American Revolutionary War. The treaty used the Great Lakes as a border between British territory and the United States. This granted significant territory to the United States, initially known as the Ohio Country and the Illinois Country, which had previously been prohibited to new settlements. However, numerous Native American peoples inhabited this region, and the British maintained a military presence and continued policies that supported their Native allies. With t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handsome Lake
Handsome Lake (Cayuga language: Sganyadái:yo, Seneca language: Sganyodaiyo) (Θkanyatararí•yau• in Tuscarora) (1735 – 10 August 1815) was a Seneca religious leader of the Iroquois people. He was a half-brother to Cornplanter, a Seneca war chief. Handsome Lake, a leader and prophet, played a major role in reviving traditional religion among the Haudenosaunee (People of the Longhouse), or Six Nations Iroquois Confederacy. He preached a message that combined traditional Haudenosaunee religious beliefs with a revised code meant to revive traditional consciousness to the Haudenosaunee after a long period of cultural disintegration following colonization. This message was eventually published as the " Code of Handsome Lake" and is still practiced today. Early life Handsome Lake was born as Hadawa'ko ("Shaking Snow") around 1735 in the Seneca village of Canawaugus, on the Genesee River near present-day Avon, New York. Very little is known of his parents; his mother, Gahonnone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornplanter
John Abeel III (born between 1732 and 1746–February 18, 1836), known as Gaiänt'wakê (''Gyantwachia'' – "the planter") or Kaiiontwa'kon (''Kaintwakon'' – "By What One Plants") in the Seneca language and thus generally known as Cornplanter, was a Dutch-Seneca war chief and diplomat of the Wolf clan. As a chief warrior, Cornplanter fought in the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. In both wars, the Seneca and three other Iroquois nations were allied with the British. After the war Cornplanter led negotiations with the United States and was a signatory of the Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1784). He helped gain Iroquois neutrality during the Northwest Indian War. In the postwar years, Cornplanter worked to learn more about European-American ways and invited Quakers to establish schools in Seneca territory. Disillusioned by his people's poor reaction to European-American society, he had the schools closed and followed his half-brother Handsome Lake's movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneida Nation Of Wisconsin
The Oneida Nation is a federally recognized tribe of Oneida people in Wisconsin. The tribe's Indian reservation, reservation spans parts of two counties west of the Green Bay, Wisconsin, Green Bay metropolitan area. The reservation was established by treaty in 1838, and was allotted to individual New York Oneida tribal members as part of an agreement with the U.S. government. The land was individually owned until the tribe was formed under the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934. Under the Dawes Act, the land was allotted in 1892 to individual households. The nation kept control of most of the land until sales were allowed in the early 20th century, when members were often tricked out of their property. They used the land for farming and harvesting timber. As of 2010, the nation controlled about 35 percent of the land within its reservation and is working to reacquire the rest. In 1988 the nation established the state's first modern lottery, known as Big Green. Since the late 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Evening Independent
The ''Evening Independent'' was St. Petersburg, Florida's first daily newspaper. The sister evening newspaper of the ''St. Petersburg Times'', it was launched as a weekly newspaper in March 1906 under the ownership of Willis B. Powell. In November 1907, it became a daily paper as the ''St. Petersburg Evening Independent''. The newspaper was known for its "Sunshine Offer", which was first enacted in 1910 by Lew Brown as a way to publicize St. Petersburg as "The Sunshine City". The paper offered copies free following days without sunshine in St. Petersburg. From 1910 until the paper folded in 1986, the ''Evening Independent'' made good on its offer 296 times. The ''Evening Independent'' was acquired by the ''Times'' in 1962, when its previous owner, the Thomson newspaper chain, threatened to close it down. Roy Thomson had originally bought the ''Independent'' so he would have a place to moor his yacht. The ''Evening Independent'' was merged into the ''Times'' in November 1986, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phelps And Gorham Purchase
The Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the purchase in 1788 of of land in what is now western New York State from the Commonwealth of Massachusetts for $1,000,000 ( £300,000), to be paid in three annual installments, and the pre-emptive right to the title on the land from the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy for $5000 (£12,500). A syndicate formed by Oliver Phelps and Nathaniel Gorham bought preemptive rights to the parcel - larger than six present U.S. states: Vermont, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Connecticut, Delaware, and Rhode Island - in New York, west of Seneca Lake between Lake Ontario and the Pennsylvania border, from the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Phelps and Gorham then negotiated with the Seneca nation and other Iroquois tribes to obtain clear title for the entire parcel. They acquired title to only about east of the Genesee River plus the by Mill Yard Tract along the river's northwestern bank. Within a year, monetary values rose and, in combination with po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in northeast North America/Turtle Island (Native American folklore), Turtle Island. They were known during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English people, English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk people, Mohawk, Oneida people, Oneida, Onondaga people, Onondaga, Cayuga people, Cayuga, and Seneca people, Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by The Great Peacem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca Nation Territory 1794
Seneca may refer to: People and language * Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname * Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America ** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people Places Extraterrestrial * Seneca (crater), a lunar crater * 2608 Seneca, an asteroid Water features in the United States * Seneca Creek (North Fork South Branch Potomac River), West Virginia * Seneca Creek (Potomac River), Maryland * Seneca Lake (New York), the largest of the Finger Lakes * Senecaville Lake or Seneca Lake, Ohio, a reservoir * Seneca River (New York), the outlet of Seneca Lake * Seneca River (South Carolina) Communities in the United States and Canada * Seneca, California, an unincorporated community * Seneca, Illinois, a village * Seneca, Kansas, a city * Seneca, Keweenaw County, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Seneca, Maryland, an unincorporated community * Seneca, Missouri, a city * Seneca, Nebraska, a village * Seneca, Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States. The composition and powers of the Senate are established by Article One of the United States Constitution. The Senate is composed of senators, each of whom represents a single state in its entirety. Each of the 50 states is equally represented by two senators who serve staggered terms of six years, for a total of 100 senators. The vice president of the United States serves as presiding officer and president of the Senate by virtue of that office, despite not being a senator, and has a vote only if the Senate is equally divided. In the vice president's absence, the president pro tempore, who is traditionally the senior member of the party holding a majority of seats, presides over the Senate. As the upper chamber of Congress, the Senate has several powers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)