|
Treaty Of Berwick (1560)
The Treaty of Berwick was negotiated on 27 February 1560 at Berwick-upon-Tweed. It was an agreement made by the representative of Queen Elizabeth I of England, the Duke of Norfolk, and the group of Scottish nobles known as the Scottish Lords of the Congregation. The purpose was to agree the terms under which an English fleet and army would come to Scotland to expel the French troops who were defending the Regency of Mary of Guise. The Lords were trying both to expel the French and to effect the Scottish Reformation, and this led to rioting and armed conflict. England and the Scottish Lords of the Congregation The leader of the Lords of the Congregation was the Duke of Chatelherault. He had formerly been Regent, but in this treaty was described as "second person", meaning that he was heir to the throne after Mary, Queen of Scots. His representatives at Berwick were James Stewart, 1st Earl of Moray, Patrick, Lord Ruthven, Sir John Maxwell of Terregles, William Maitland younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hamilton (Earl Of Arran)
James Hamilton may refer to: Dukes *James Hamilton, 1st Duke of Hamilton (1606–1649), heir to the throne of Scotland *James Hamilton, 4th Duke of Hamilton (1658–1712), Scottish nobleman *James Hamilton, 5th Duke of Hamilton (1703–1743), Scottish nobleman *James Hamilton, 6th Duke of Hamilton (1724–1758), Scottish nobleman *James Hamilton, 7th Duke of Hamilton (1755–1769), Scottish nobleman *James Hamilton, 1st Duke of Abercorn (1811–1885), twice served as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland *James Hamilton, 2nd Duke of Abercorn (1838–1913), British nobleman and diplomat *James Hamilton, 3rd Duke of Abercorn (1869–1953), first Governor of Northern Ireland *James Hamilton, 4th Duke of Abercorn (1904–1979), Northern Irish senator *James Hamilton, 5th Duke of Abercorn (born 1934), Northern Irish politician Marquesses *James Hamilton, 2nd Marquess of Hamilton (1589–1625), 4th Earl of Arran, Scottish nobleman Earls *James Hamilton, 1st Earl of Arran (c. 1475–1529), Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyemouth
Eyemouth ( sco, Heymooth) is a small town and civil parish in Berwickshire, in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland. It is east of the main north–south A1 road and north of Berwick-upon-Tweed. The town's name comes from its location at the mouth of the Eye Water river. The Berwickshire coastline consists of high cliffs over deep clear water with sandy coves and picturesque harbours. A fishing port, Eyemouth holds a yearly Herring Queen Festival. Notable buildings in the town include Gunsgreen House and a cemetery watch-house built to stand guard against the Resurrectionists (body snatchers). Many of the features of a traditional fishing village are preserved in the narrow streets and ' vennels'. Eyemouth is not far from the small villages of Ayton, Reston, St Abbs, Coldingham, and Burnmouth, all in Berwickshire. The coast offers opportunities for birdwatching, walking, fishing and diving. Accommodation includes several hotels, B&Bs and a holiday park. History Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
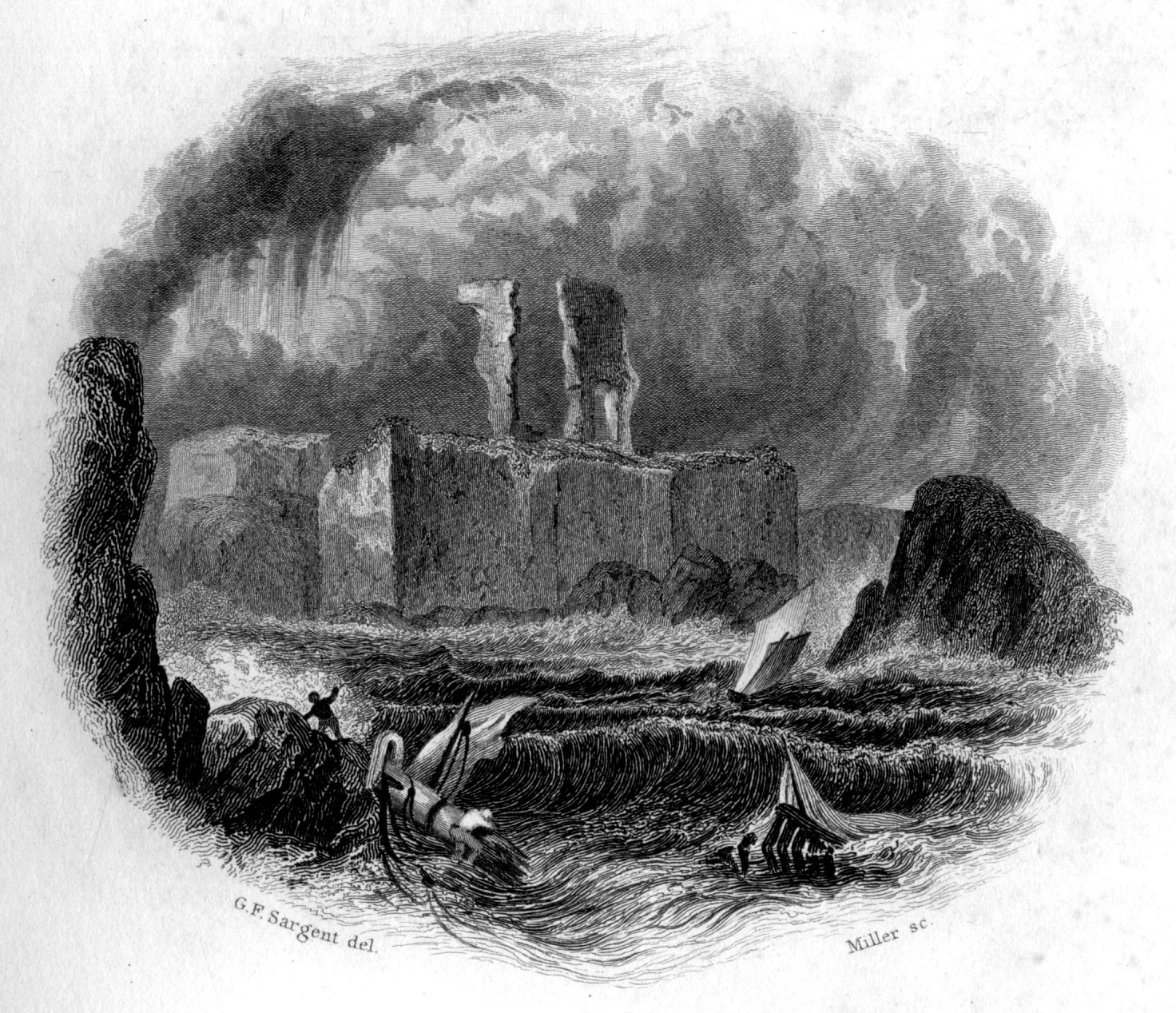
Dunbar Castle
Dunbar Castle was one of the strongest fortresses in Scotland, situated in a prominent position overlooking the harbour of the town of Dunbar, in East Lothian. Several fortifications were built successively on the site, near the English-Scottish border. The last was slighted in 1567; it is a ruin today. Structure The body of buildings measured in excess of one hundred and sixty five feet from east to west, and in some places up to two hundred and ten feet from north to south. The South Battery, which Grose supposes to have been the citadel or keep, is situated on a detached perpendicular rock, only accessible on one side, seventy two feet high, and is connected to the main part of the castle by a passage of masonry measuring sixty nine feet. The interior of the citadel measures fifty four feet by sixty within the walls. Its shape is octagonal. Five of the gun-ports remain, which are called the 'arrow-holes'. They measure four feet at the mouth and only sixteen inches at the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world. The earliest surviving historical references are in the royal charter authorising the construction of Holyrood Abbey in 1128 in which it is termed ''Inverlet'' (Inverleith). After centuries of control by Edinburgh, Leith was made a separate burgh in 1833 only to be merged into Edinburgh in 1920. Leith is located on the southern coast of the Firth of Forth and lies within the City of Edinburgh Council area; since 2007 it has formed one of 17 multi-member wards of the city. History As the major port serving Edinburgh, Leith has seen many significant events in Scottish history. First settlement The earliest evidence of settlement in Leith comes from several archaeological digs undertaken in The Shore area in the late 20th century. Amongst the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Edinburgh
The Treaty of Edinburgh (also known as the Treaty of Leith) was a treaty drawn up on 5 July 1560 between the Commissioners of Queen Elizabeth I of England with the assent of the Scottish Lords of the Congregation, and the French representatives of King Francis II of France (husband of Mary Queen of Scots) to formally conclude the siege of Leith and replace the Auld Alliance with France with a new Anglo-Scottish accord, while maintaining the peace between England and France agreed by the Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis. French and English troops in Scotland The rule of Mary of Guise in Scotland was supported by French troops. Scottish Protestants challenged her rule in the Reformation Crisis. During the ensuing Siege of Leith, French troops fortified the port and town of Leith against an English and Scottish Protestant force. The English army was invited into Scotland by the Treaty of Berwick made by the Lords of the Congregation. The treaty was concluded on 6 July 1560 just short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Leith
The siege of Leith ended a twelve-year encampment of French troops at Leith, the port near Edinburgh, Scotland. The French troops arrived by invitation in 1548 and left in 1560 after an English force arrived to attempt to assist in removing them from Scotland. The town was not taken by force and the French troops finally left peacefully under the terms of a treaty signed by Scotland, England and France.Knight, p. 120 Background The Auld Alliance and Reformation of religion Scotland and France had long been allies under the "Auld Alliance", first established in the 13th century. However, during the 16th century, divisions appeared between a pro-French faction at Court and Protestant reformers. The Protestants saw the French as a Catholic influence and, when conflict broke out between the two factions, called on English Protestants for assistance in expelling the French from Scotland. In 1542, King James V of Scotland died, leaving only a week-old daughter who was proclaimed Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Lothian
East Lothian (; sco, East Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area. The county was called Haddingtonshire until 1921. In 1975, the historic county was incorporated for local government purposes into Lothian Region as East Lothian District, with some slight alterations of its boundaries. The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 later created East Lothian as one of 32 modern council areas. East Lothian lies south of the Firth of Forth in the eastern central Lowlands of Scotland. It borders Edinburgh to the west, Midlothian to the south-west and the Scottish Borders to the south. Its administrative centre and former county town is Haddington while the largest town is Musselburgh. Haddingtonshire has ancient origins and is named in a charter of 1139 as ''Hadintunschira'' and in another of 1141 as ''Hadintunshire''. Three of the county's towns were designated as roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestongrange
Prestongrange is a place in East Lothian, Scotland, United Kingdom, situated between Musselburgh to the west, and Prestonpans to the east. The place name derives from "Preston", meaning "priest's town", and a grange (or granary) which was worked by the Cistercian monks of Newbattle Abbey. In the early 17th century, Mark Ker took possession of the lands from the abbey, and after the Grant Suttie family took over, the Prestongrange Colliery was no longer productive and fell into disuse. In 1830, Sir George Grant Suttie leased Prestongrange Colliery to Matthias Dunn, the Inspector of Mines. Prestongrange House This fine mansion-house was partly rebuilt by Mark Kerr and Helen Leslie. It passed through marriage to John Morison of Saughton Hall around 1600. Laters owners included Alexander Morison, Lord Prestongrange who extended it in 1620. In the early 19th century it was greatly extended by the architect William Henry Playfair.Colin McWilliam, ''The Buildings of Scotl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newbattle Abbey
Newbattle Abbey ( gd, Abaid a' Bhatail Nuaidh) was a Cistercian monastery near the village of Newbattle in Midlothian, Scotland, which subsequently become a stately home and then an educational institution. Monastery It was founded in 1140 by monks from Melrose Abbey. The patron was King David I of Scotland (with his son Henry). Its church was dedicated in 1234. The abbey was burned by English royal forces in 1385 and once more in 1544. It became a secular lordship for the last commendator, Mark Kerr (Ker) in 1587. Newbattle Abbey was a filiation of Melrose Abbey (itself a daughter of Rievaulx Abbey) and was situated, according to Cistercian usages, in a beautiful valley along the River South Esk. Rudolph, its first abbot, a strict and severe observer of the rule, devoted himself energetically to the erection of proper buildings. The church, cruciform in shape, was 240 feet in length, and the other buildings in proportion; at one period the community numbered as many as 80 monk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrison's Haven
Morrison's Haven is a harbour at Prestongrange, East Lothian, Scotland, UK, on the B1348, close to Levenhall Links, Prestongrange Industrial Heritage Museum, Prestonpans, and Prestongrange House. The name comes from the Morisons of Prestongrange. A part of Prestongrange were purchased by John Morison from the Kerr family in 1609. He was a burgess of Edinburgh, a bailie (1581) and treasurer of Edinburgh (1588). His son Sir Alexander Morison, a Lord of Session, developed the harbour. The property was purchased in 1746 from William Morrison by William Grant. History In 1526, the Cistercian monks of Holyrood Abbey and Newbattle Abbey received permission from King James V for the construction of a port in place called "Gilbertis-draucht". The Abbot leased the port to Alexander Atkinsoun or Achesoun, and the port was known as Acheson's Haven and sometimes "New Haven" until the 17th century. The monks could also collect "port monies, customs and duties". There was at least one mill, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halidon Hill
Halidon Hill is a summit, about west of the centre of Berwick-upon-Tweed, on the border of England and Scotland. It reaches 600 feet (180 m) high. The name of the hill indicates that it once had a fortification on its top. At the Battle of Halidon Hill in 1333, Edward III of England used longbowmen on the heights of the hill to defeat the Scottish army led by Archibald the "Tyneman" Douglas, Regent of Scotland. An English army camped at Halidon Hill on 27 March 1560. The soldiers were sent into Scotland to help at the siege of Leith during the Scottish Reformation. Mary, Queen of Scots came to Halidon Hill to view Berwick on 15 November 1566 and met John Foster, Marshal of Berwick. When James VI visited Halidon Hill near on 27 April 1588 there was a cannon salute and he spoke with members of the garrison. He gave the English commanding officers a gift of 100 gold crowns and to the porters (officers of lesser rank) 40 crowns described as "drinksilver". In April 1595 Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |