|
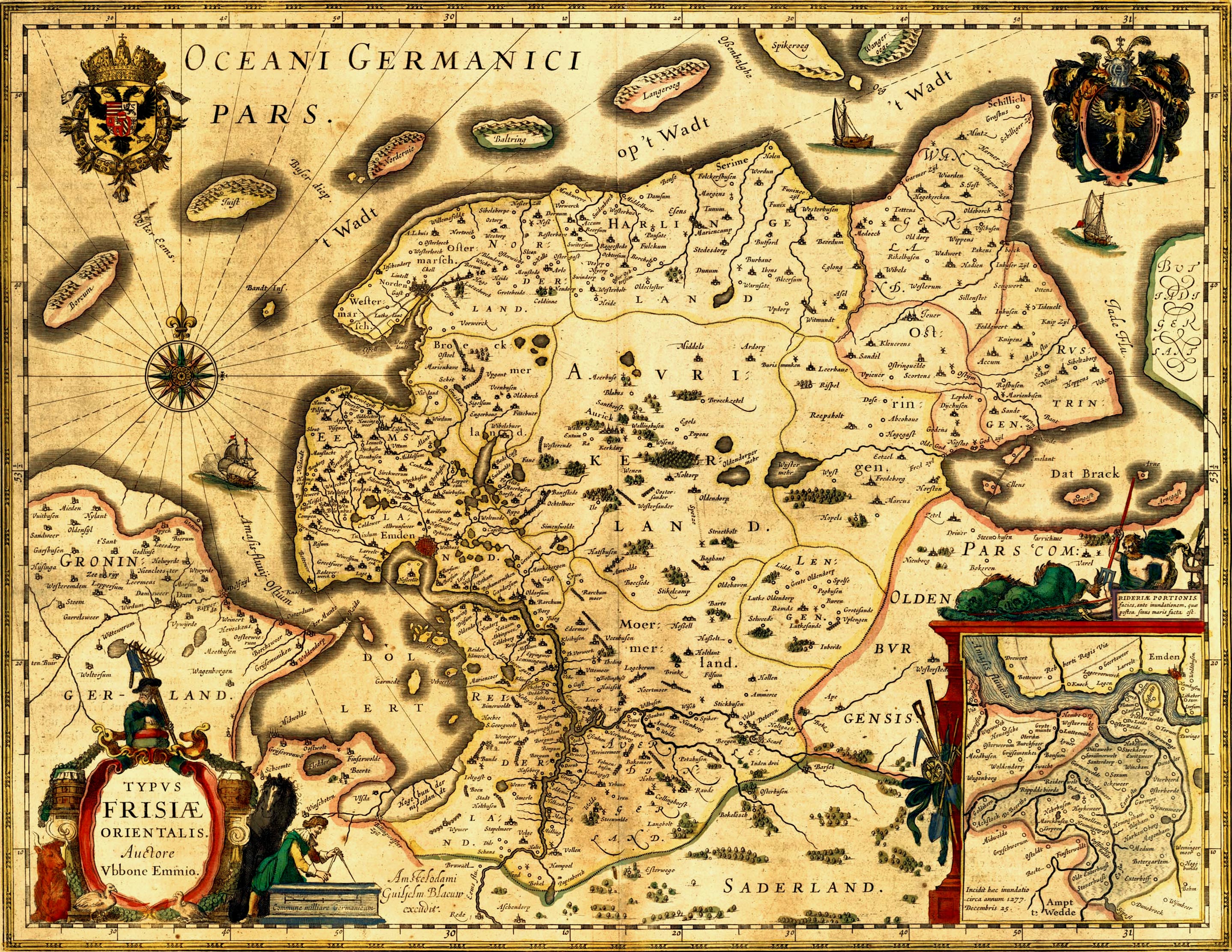
Treaty Of Berum
The Treaty of Berum was a treaty concluded on 28 January 1600 at Berum Castle between the Count Enno III of East Frisia and the County of Rietberg, which regulated the sale of the Harlingerland to East Frisia. Background With the death of Balthasar Oomkens von Esens in 1540, the Attena line of East Frisian chieftains ruling Harlingerland died out and the Harlingerland fell to the Counts of Rietberg, who were related to the Attenas. From 1540, Harlingerland was ruled by Count John II of Rietberg, the son of Balthasar's sister. After his death, the Harlingerland went to his second daughter, Walburgis. She married in 1581 Count Enno III of East Frisia. They had two daughters, who, by the Treaty of Berum, waived their right to inherit Harlingerland, in favour of Enno's son Rudolf Christian, from his first marriage. Contents Sabine Catharine and her sister Agnes sold the Lordships of Esens, Stedesdorf and Wittmund and thus the entire Harlingerland, to their father, for . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berum Castle
Berum Castle is located in the Berum district the East Frisian town of Hage in Germany. It is one of the most important sites in East Frisian history. History The castle is first mentioned in a document of 1310, as the seat of a member of the ''Syrtza'' (or ''Sytze'') family, who was a chieftain of the Norden area. It is not known exactly when the castle was built, or for how long that family had already resided at the location. In the 15th century, the castle was inherited by the Cirksena family. In 1443, Count Ulrich I of East Frisia expanded the castle to a château, consisting of a main castle with three wings, plus a front castle. On 1 June 1445, he celebrated his marriage to Theda Ukena, the granddaughter of his main rival, Focko Ukena, in Berum Castle. Since then, the castle has played a significant rôle in the history of East Frisia. Adolph, the son of Count Gerhard VI of Oldenburg, was held captive at Berum Castle from 1465 to 1481{{better source needed, Accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries. Geography The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present province of Gelderland (English also ''Guelders'') in the Netherlands occupies most of the area, the former duchy also comprised parts of the present Dutch province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg as well as those territories in the present-day German States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia that were acquired by Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in 1713. Four parts of the duchy had their own centres, as they were separated by rivers: * the quarter of Roermond, also called Upper Quarter or Upper Guelders – upstream on both sides of the Meuse (river), Maas, comprising the town of Geldern as well as Erkelenz, Goch, Nieuwstadt, Venlo and Straelen; spatially separated from the Lower Quarters (Gelde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of East Frisia
The history of East Frisia developed rather independently from the rest of Germany because the region was relatively isolated for centuries by large stretches of bog to the south, while at the same time its people were oriented towards the sea. Thus in East FrisiaThis article focusses on the historic region of East Frisia, which today comprises the town of Emden as well as the counties of Aurich, Leer and Wittmund; see the definition of the East Frisian landscapeStatute of the East Frisian Landscape Article I (Principles), Paragraph 2: "East Frisia includes the municipalities of Aurich, Leer and Wittmund as well as town of Emden." in the Middle Ages there was little feudalism, instead a system of fellowship under the so-called Friesian Freedom emerged. It was not until 1464, that the House of Cirksena was enfeoffed with the Imperial County of East Frisia. Nevertheless absolutism had been, and continued to be, unknown in East Frisia. In the two centuries after about 1500, the inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1600 Treaties
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: *16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * ''Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band *Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eberhard III, Duke Of Württemberg
Eberhard III, Duke of Württemberg (16 December 1614, in Stuttgart – 2 July 1674, in Stuttgart) ruled as Duke of Württemberg from 1628 until his death in 1674. Eberhard III became the heir under guardianship in 1628 during the Thirty Years' War at the age of 14 after the death of his father, Johann Frederick, 7th Duke of Württemberg. His guardian at first was his father's brother Louis Frederick, Duke of Württemberg-Montbéliard and after his death in 1631 Julius Frederick, Duke of Württemberg-Weiltingen. Württemberg lost around one third of its territory in 1629. Julius Frederick was removed as guardian in 1633 when Eberhard was declared of full age at which point he assumed full rule of the Duchy. Following a major defeat of Württemberg troops in the battle of Nördlingen on 6 September 1634, Württemberg was severely looted and plundered. Eberhard fled to Strasbourg where he married in 1637, returning to Württemberg in 1638 after long negotiations with Ferdinand II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States-General Of The Netherlands
The States General of the Netherlands ( nl, Staten-Generaal ) is the supreme bicameral legislature of the Netherlands consisting of the Senate () and the House of Representatives (). Both chambers meet at the Binnenhof in The Hague. The States General originated in the 15th century as an assembly of all the provincial states of the Burgundian Netherlands. In 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, the States General split as the northern provinces openly rebelled against Philip II, and the northern States General replaced Philip II as the supreme authority of the Dutch Republic in 1581. The States General were replaced by the National Assembly after the Batavian Revolution of 1795, only to be restored in 1814, when the country had regained its sovereignty. The States General was divided into a Senate and a House of Representatives in 1815, with the establishment of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. After the constitutional amendment of 1848, members of the House of Representatives w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sconce (fortification)
A sconce is a small protective fortification, such as an earthwork, often placed on a mound as a defensive work for artillery. It was used primarily in Northern Europe from the late Middle Ages until the 19th century. This type of fortification was common during the English Civil War, and the remains of one such structure can be seen on Fort Royal Hill in Worcester, England. During the Eighty Years' War for Dutch independence, the sconces (''schans'' in Dutch) were often used to defend strategic places, but were used also during sieges and in circumvallations. Several more or less intact sconces remain in the Netherlands. The Zaanse Schans, one of the top tourist locations in the Netherlands, derived its name from its original function as a sconce. Sconces played a major part in the Serbian Revolution, countering the numerical superiority of the Turkish army. Etymology The etymology of sconce is from the Latin ''absconsus'', via the French ''esconce'': a word of many meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liege Lord
Homage (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position (investiture). It was a symbolic acknowledgement to the lord that the vassal was, literally, his man (''homme''). The oath known as "fealty" implied lesser obligations than did "homage". Further, one could swear "fealty" to many different overlords with respect to different land holdings, but "homage" could only be performed to a single liege, as one could not be "his man" (i.e., committed to military service) to more than one "liege lord". There have been some conflicts about obligations of homage in history. For example, the Angevin monarchs of England were sovereign in England, i.e., they had no duty of homage regarding those holdings; but they were not sovereign regarding their French holdings. Henry II was king of England, but he was m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Christian, Prince Of East Frisia
George Christian (6 February 1634, Aurich – 6 June 1665, Aurich) was a member of the Cirksena family and succeeded his brother Enno Louis as ruler of East Frisia. He ruled from 1660 to 1665. Under his reign, the Cirksena family acquired on 18 April 1662 the hereditary title of Imperial Prince. George Christian grew up with his brother at the court in Aurich. After 1649, they received further education at the academies of Breda and Tübingen. In Tübingen he met his future wife, Christine Charlotte, a daughter of Duke Eberhard III of Württemberg from his first marriage to Anna Dorothea of Salm-Kyrburg. He could only marry her after had he received the hereditary title of Imperial Prince on 18 April 1662. This gave him the proper rank to marry a Princess of Württemberg (german: Ebenbürtigkeit), and so the marriage was finally performed on 10 May 1662 in the city of Stuttgart. The union produced only two short-lived daughters during George Christian's lifetime: Eberhardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gundakar, Prince Of Liechtenstein
Gundakar of Liechtenstein (30 January 1580 – 5 August 1658) (''Prince'' from 1623) was a member of the House of Liechtenstein and as such the owner of a large estate. He also served the Habsburg dynasty. Family He was the youngest son of Baron Hartmann II of Liechtenstein (1544–1585). His mother was Anna Maria (née Countess of Ortenburg). His brothers were Karl I and Maximilian. He received a careful education. He himself was married twice. In the first marriage, he married Agnes, a daughter of Count Enno III of East Frisia and in the second marriage Elizabeth Lucretia, a daughter of Duke Adam Wenceslaus of Cieszyn and herself a ruling Duchess of Cieszyn. He was the founder of the so-called Gundakar line of the House of Liechtenstein. In 1606, the brothers signed a familial treaty stipulating that the first-born of the eldest surviving line would be head of the House of Liechtenstein. In Habsburg service His father was a Lutheran and he had raised his children as Luth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Von Mansfeld
Peter Ernst, Graf von Mansfeld (german: Peter Ernst Graf von Mansfeld; c. 158029 November 1626), or simply Ernst von Mansfeld, was a German military commander who, despite being a Catholic, fought for the Protestants during the early years of the Thirty Years' War. He was one of the leading mercenary generals of the war. Biography Mansfeld was an illegitimate son of Count Peter Ernst von Mansfeld (1517–1604), a member of the comital House of Mansfeld and royal Spanish stadtholder. He was raised in the Catholic faith at his father's palace in Luxembourg. He gained his earliest military experiences during the Long War in Hungary, where his elder half-brother Charles (1543–1595), also a soldier of renown, held a high command in the imperial army. While his brother succumbed to an epidemic within short time, young Ernst stayed at the theatre of war for several years. In the War of the Jülich Succession he served under Archduke Leopold V of Austria, until that prince's ingra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |