|
Trapezoidal Rule
In calculus, the trapezoidal rule (or trapezium rule in British English) is a technique for numerical integration, i.e., approximating the definite integral: \int_a^b f(x) \, dx. The trapezoidal rule works by approximating the region under the graph of the function f(x) as a trapezoid and calculating its area. It follows that \int_^ f(x) \, dx \approx (b-a) \cdot \tfrac(f(a)+f(b)). The integral can be even better approximated by Partition of an interval, partitioning the integration interval, applying the trapezoidal rule to each subinterval, and summing the results. In practice, this "chained" (or "composite") trapezoidal rule is usually what is meant by "integrating with the trapezoidal rule". Let \ be a partition of [a,b] such that a=x_0 < x_1 < \cdots < x_ < x_N = b and be the length of the -th subinterval (that is, ), then |
Trapezoidal Rule Illustration
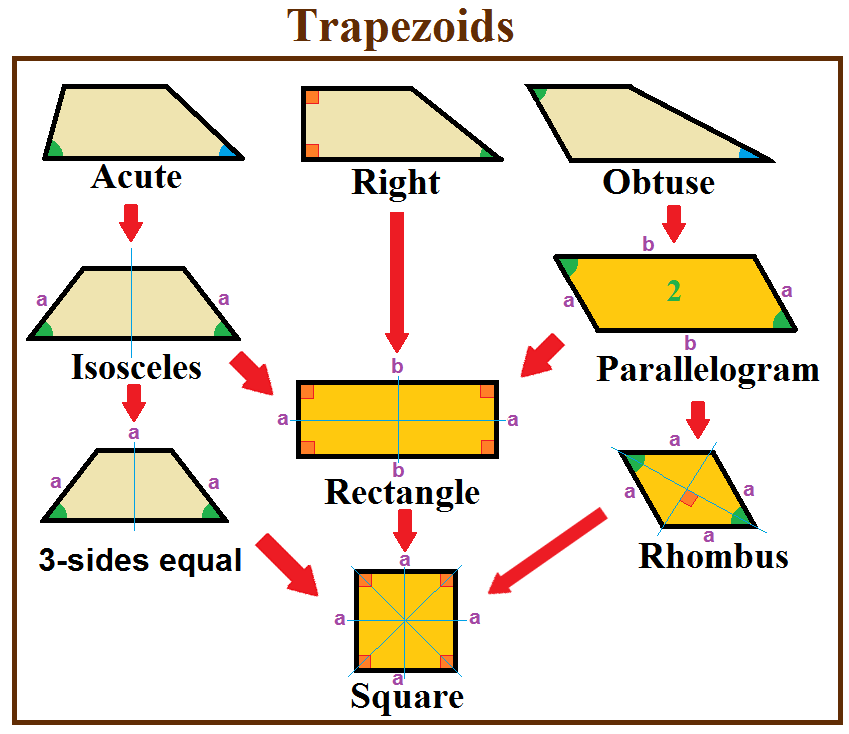
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of Parallel (geometry), parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' or ''lateral sides''. (If the trapezoid is a parallelogram, then the choice of bases and legs is arbitrary.) A trapezoid is usually considered to be a Convex polygon, convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also Crossed polygon, crossed cases. If ''ABCD'' is a convex trapezoid, then ''ABDC'' is a crossed trapezoid. The metric formulas in this article apply in convex trapezoids. Definitions ''Trapezoid'' can be defined exclusively or inclusively. Under an exclusive definition a trapezoid is a quadrilateral having pair of parallel sides, with the other pair of opposite sides non-parallel. Parallelograms including rhombi, rectangles, and squares are then not considered to be trapez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezoid
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' or ''lateral sides''. (If the trapezoid is a parallelogram, then the choice of bases and legs is arbitrary.) A trapezoid is usually considered to be a convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also crossed cases. If ''ABCD'' is a convex trapezoid, then ''ABDC'' is a crossed trapezoid. The metric formulas in this article apply in convex trapezoids. Definitions ''Trapezoid'' can be defined exclusively or inclusively. Under an exclusive definition a trapezoid is a quadrilateral having pair of parallel sides, with the other pair of opposite sides non-parallel. Parallelograms including rhombi, rectangles, and squares are then not considered to be trapezoids. Under an inclusive definition, a trapezoid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflection Point
In differential calculus and differential geometry, an inflection point, point of inflection, flex, or inflection (rarely inflexion) is a point on a smooth plane curve at which the curvature changes sign. In particular, in the case of the graph of a function, it is a point where the function changes from being concave (concave downward) to convex (concave upward), or vice versa. For the graph of a function of differentiability class (its first derivative , and its second derivative , exist and are continuous), the condition can also be used to find an inflection point since a point of must be passed to change from a positive value (concave upward) to a negative value (concave downward) or vice versa as is continuous; an inflection point of the curve is where and changes its sign at the point (from positive to negative or from negative to positive). A point where the second derivative vanishes but does not change its sign is sometimes called a point of undulation or und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midpoint Rule
In mathematics, a Riemann sum is a certain kind of approximation of an integral by a finite sum. It is named after nineteenth century German mathematician Bernhard Riemann. One very common application is in numerical integration, i.e., approximating the area of functions or lines on a graph, where it is also known as the rectangle rule. It can also be applied for approximating the length of curves and other approximations. The sum is calculated by partitioning the region into shapes (rectangles, trapezoids, parabolas, or cubics—sometimes infinitesimally small) that together form a region that is similar to the region being measured, then calculating the area for each of these shapes, and finally adding all of these small areas together. This approach can be used to find a numerical approximation for a definite integral even if the fundamental theorem of calculus does not make it easy to find a closed-form solution. Because the region by the small shapes is usually not exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton–Cotes Formulas
In numerical analysis, the Newton–Cotes formulas, also called the Newton–Cotes quadrature rules or simply Newton–Cotes rules, are a group of formulas for numerical integration (also called ''quadrature'') based on evaluating the integrand at equally spaced points. They are named after Isaac Newton and Roger Cotes. Newton–Cotes formulas can be useful if the value of the integrand at equally spaced points is given. If it is possible to change the points at which the integrand is evaluated, then other methods such as Gaussian quadrature and Clenshaw–Curtis quadrature are probably more suitable. Description It is assumed that the value of a function defined on [a, b] is known at n + 1 equally spaced points: a \leq x_0 < x_1 < \dots < x_n \leq b. There are two classes of Newton–Cotes quadrature: they are called "closed" when and , i.e. they use the function values at the interval endpoints, and "open" when |
Smoothness
In mathematical analysis, the smoothness of a function is a property measured by the number of continuous derivatives (''differentiability class)'' it has over its domain. A function of class C^k is a function of smoothness at least ; that is, a function of class C^k is a function that has a th derivative that is continuous in its domain. A function of class C^\infty or C^\infty-function (pronounced C-infinity function) is an infinitely differentiable function, that is, a function that has derivatives of all orders (this implies that all these derivatives are continuous). Generally, the term smooth function refers to a C^-function. However, it may also mean "sufficiently differentiable" for the problem under consideration. Differentiability classes Differentiability class is a classification of functions according to the properties of their derivatives. It is a measure of the highest order of derivative that exists and is continuous for a function. Consider an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson's Rule
In numerical integration, Simpson's rules are several approximations for definite integrals, named after Thomas Simpson (1710–1761). The most basic of these rules, called Simpson's 1/3 rule, or just Simpson's rule, reads \int_a^b f(x) \, dx \approx \frac \left (a) + 4f\left(\frac\right) + f(b)\right In German and some other languages, it is named after Johannes Kepler, who derived it in 1615 after seeing it used for wine barrels (barrel rule, ). The approximate equality in the rule becomes exact if is a polynomial up to and including 3rd degree. If the 1/3 rule is applied to ''n'' equal subdivisions of the integration range 'a'', ''b'' one obtains the composite Simpson's 1/3 rule. Points inside the integration range are given alternating weights 4/3 and 2/3. Simpson's 3/8 rule, also called Simpson's second rule, requires one more function evaluation inside the integration range and gives lower error bounds, but does not improve the order of the error. If the 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Proceedings Of The Cambridge Philosophical Society
''Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society'' is a mathematical journal published by Cambridge University Press for the Cambridge Philosophical Society. It aims to publish original research papers from a wide range of pure and applied mathematics. The journal, titled ''Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society'' before 1975, has been published since 1843. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in *MathSciNet *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus *ZbMATH Open See also *Cambridge Philosophical Society The Cambridge Philosophical Society (CPS) is a scientific society at the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1819. The name derives from the medieval use of the word philosophy to denote any research undertaken outside the fields of law ... External linksofficial website References Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies Cambridge University Press academic journals Mathematics e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponentially Modified Gaussian Distribution
In probability theory, an exponentially modified Gaussian distribution (EMG, also known as exGaussian distribution) describes the sum of independent Normal distribution, normal and Exponential distribution, exponential random variables. An exGaussian random variable ''Z'' may be expressed as , where ''X'' and ''Y'' are independent, ''X'' is Gaussian with mean ''μ'' and variance ''σ''2, and ''Y'' is exponential of rate ''λ''. It has a characteristic positive skew from the exponential component. It may also be regarded as a weighted function of a shifted exponential with the weight being a function of the normal distribution. Definition The probability density function (pdf) of the exponentially modified Gaussian distribution is :f(x;\mu,\sigma,\lambda) = \frac \exp \left[\frac (2 \mu + \lambda \sigma^2 - 2 x)\right] \operatorname \left(\frac\right), where erfc is the complementary error function defined as :\begin \operatorname(x) & = 1-\operatorn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
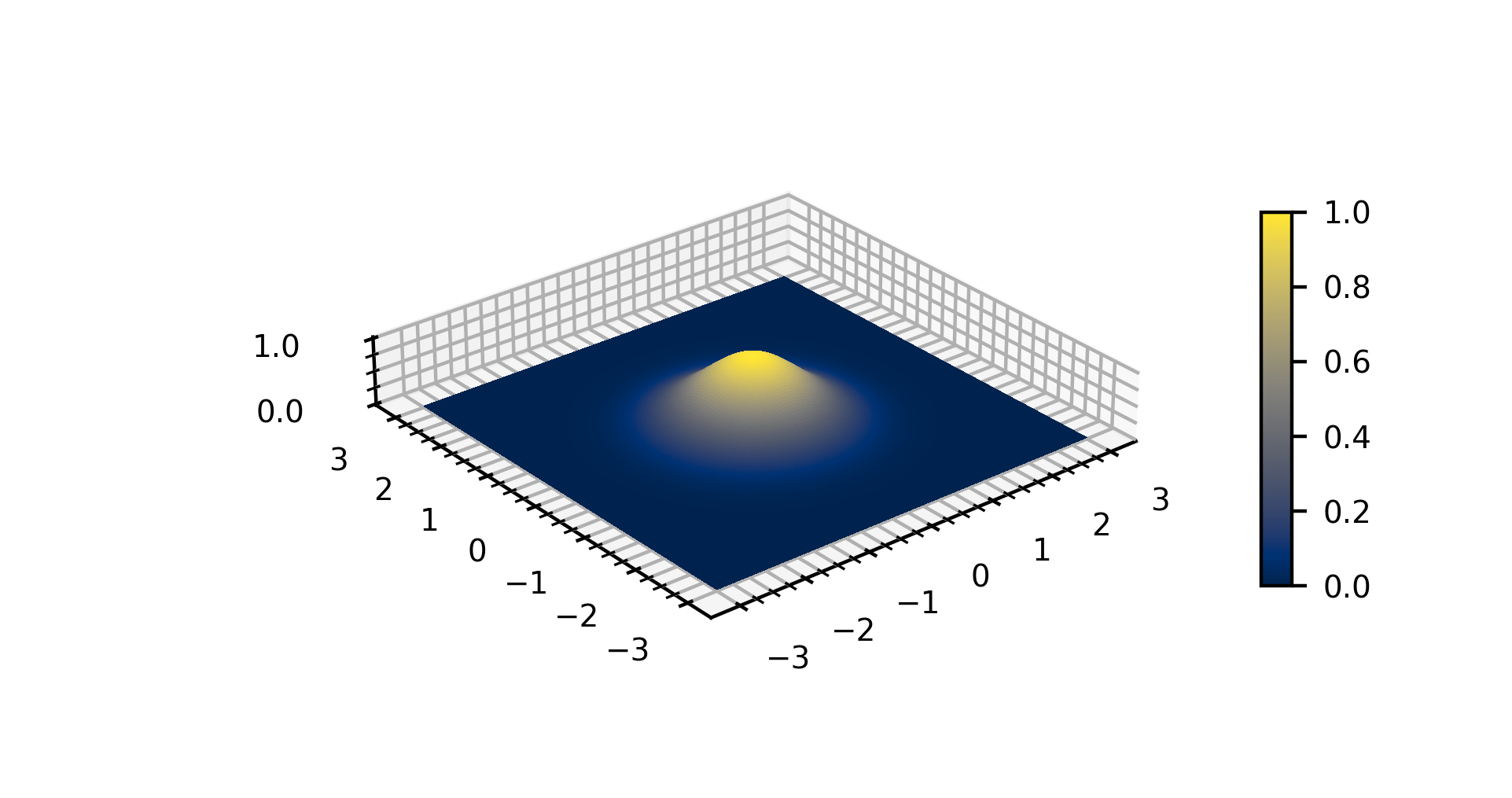
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function (mathematics), function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real number, real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a function, graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "Normal distribution, bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian Root mean square, RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normal distribution, normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |