|
Transport In Australia
There are many forms of transport in Australia. Australia is highly dependent on road transport. There are more than 300 airports with paved runways. Passenger rail transport includes widespread commuter networks in the major capital cities with more limited intercity and interstate networks. The Australian mining sector is reliant upon rail to transport its product to Australia's ports for export. Road transport Road transport is an essential element of the Australian transport network, and an enabler of the Australian economy. There is a heavy reliance on road transport due to Australia's large area and low population density in considerable parts of the country. Australia's road network experiences excessive demand during peak periods and very weak demand overnight. Another reason for the reliance upon roads is that the Australian rail network has not been sufficiently developed for a lot of the freight and passenger requirements in most areas of Australia. This has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
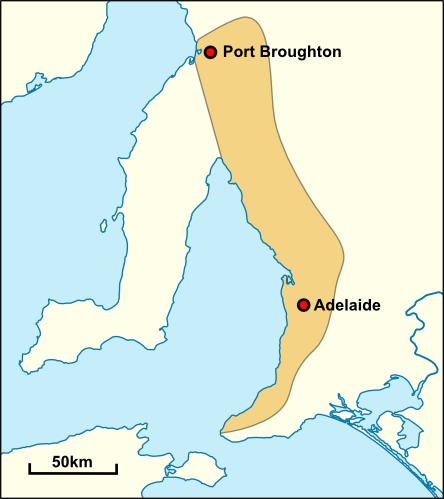
Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0402 Chatswood, 2019 (01)
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinia Road 2012-07-22 03
{{disambig, geo ...
Cardinia may refer to: * Cardinia, Victoria, Australia * Shire of Cardinia, Victoria, Australia * Cardinia Creek, Australia ** Cardinia Reservoir ** Cardinia Dam Power Station * Cardinia Transit, a bus and coach operator in Melbourne, Australia See also * Kardinya, a suburb of Perth, Western Australia Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet ( Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Duty
Stamp duty is a tax that is levied on single property purchases or documents (including, historically, the majority of legal documents such as cheques, receipts, military commissions, marriage licences and land transactions). A physical revenue stamp had to be attached to or impressed upon the document to show that stamp duty had been paid before the document was legally effective. More modern versions of the tax no longer require an actual stamp. The duty is thought to have originated in Venice in 1604, being introduced (or re-invented) in Spain in the 1610s, the Spanish Netherlands in the 1620s, France in 1651, Denmark in 1657, Prussia in 1682 and England in 1694. Usage by country Australia The Australian Federal Government does not levy stamp duty. However, stamp duties are levied by the Australian states on various instruments (written documents) and transactions. Stamp duty laws can differ significantly between all eight jurisdictions. The rates of stamp duty also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-emission Vehicle
A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions. This is because under cold-start conditions for example, internal combustion engines tend to produce the maximum amount of pollutants. In a number of countries and states, transport is cited as the main source of greenhouse gases (GHG) and other pollutants. The desire to reduce this is thus politically strong. Terminology Harmful pollutants to the health and the environment include particulates (soot), hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ozone, lead, and various oxides of nitrogen. Although not considered emission pollutants by the original California Air Resources Board (CARB) or U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) definitions, the most recent common use of the term also includes volatile organic compounds, several air toxics (most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes charged by solar panels, or by converting fuel to electricity using fuel cells or a generator). EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft. For road vehicles, together with other emerging automotive technologies such as autonomous driving, connected vehicles and shared mobility, EVs form a future mobility vision called Connected, Autonomous, Shared and Electric (CASE) Mobility. EVs first came into existence in the late 19th century, when electricity was among the preferred methods for motor vehicle propulsion, providing a level of comfort and ease of operation that could not be achieved by the gasoline cars of the time. Internal combustion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Electric Vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) to store electrical power within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which then powers the electric motor and contributes to propelling the wheels. PEV is a subset of electric vehicles, and includes all-electric/battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs). ''See definition on pp. 2.'' Sales of the first series production plug-in cars began in December 2008 with the introduction of the plug-in hybrid BYD F3DM, and then with the all-electric Mitsubishi i-MiEV in July 2009, but global retail sales only gained traction after the introduction of the mass production all-electric Nissan Leaf and the plug-in hybrid Chevrolet Volt in December 2010. Plug-in electric cars have several benefits compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. All-electric vehicles have lower oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |