|
Transient Photocurrent
Transient photocurrent (TPC) is a measurement technique, typically employed in the physics of thin film semiconductors. TPC allows to study the time-dependent (on a microsecond time scale) extraction of Carrier generation and recombination, charges generated by photovoltaic effect in semiconductor devices, such as solar cells. A semiconductor is sandwiched between two extracting electrodes. When it is excited with a short pulse of light (as short as 100 femtoseconds), the photogenerated charges are extracted on the electrodes, resulting in a current, which is detected by an oscilloscope in form of voltage across a resistor. Since the excitation pulse is square, there are two ways to measure TPC: in a “light on” and a “light off” positions. In a “Light on”, the signal is recorded as soon as the excitation pulse is switched on, allowing to observe the build-up of charges on the electrode after the start of excitation. “Light off” measurements show how the charges deca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femtoseconds
A femtosecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10 or of a second; that is, one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth, of a second. For context, a femtosecond is to a second as a second is to about 31.71 million years; a ray of light travels approximately 0.3 μm (micrometers) in 1 femtosecond, a distance comparable to the diameter of a virus.Compared with overview in: Page 3 The word ''femtosecond'' is formed by the SI prefix ''femto'' and the SI unit ''second''. Its symbol is fs. A femtosecond is equal to 1000 attoseconds, or 1/1000 picosecond. Because the next higher SI unit is 1000 times larger, times of 10−14 and 10−13 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of femtoseconds. * Typical time steps for molecular dynamics simulations are on the order of 1 fs. * The periods of the waves of visible light have a duration of about 2 femtoseconds. = = 2.0 \times 10^~ The precise duration depends on the ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection–diffusion Equation
The convection–diffusion equation is a combination of the diffusion equation, diffusion and convection (advection equation, advection) equations, and describes physical phenomena where particles, energy, or other physical quantities are transferred inside a physical system due to two processes: diffusion and convection. Depending on context, the same equation can be called the advection–diffusion equation, drift velocity, drift–diffusion equation, or (generic) scalar transport equation. Equation General The general equation is \frac = \mathbf \cdot (D \mathbf c) - \mathbf \cdot (\mathbf c) + R where * is the variable of interest (species concentration for mass transfer, temperature for heat transfer), * is the diffusivity (also called diffusion coefficient), such as mass diffusivity for particle motion or thermal diffusivity for heat transport, * is the velocity field that the quantity is moving with. It is a function of time and space. For example, in advection, might be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Of States
In solid state physics and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of modes per unit frequency range. The density of states is defined as D(E) = N(E)/V , where N(E)\delta E is the number of states in the system of volume V whose energies lie in the range from E to E+\delta E. It is mathematically represented as a distribution by a probability density function, and it is generally an average over the space and time domains of the various states occupied by the system. The density of states is directly related to the dispersion relations of the properties of the system. High DOS at a specific energy level means that many states are available for occupation. Generally, the density of states of matter is continuous. In isolated systems however, such as atoms or molecules in the gas phase, the density distribution is discrete, like a spectral density. Local variations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an "open circuit", which is an infinite resistance between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same voltage. In an 'ideal' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Photovoltage
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program (signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:Given the 5 dialects that use the terms, UKUSA can be pronounced from "You-Q-SA" to "Oo-Coo-SA", AUSCANNZUKUS can be pronounced from "Oz-Can-Zuke-Us" to "Orse-Can-Zoo-Cuss". :From Talk:UKUSA Agreement: "Per documents officially released by both the Government Communications Headquarters and the National Security Agency, this agreement is referred to as the UKUSA Agreement. This name is subsequently used by media sources reporting on the story, as written in new references used for the article. The NSA press release provides a pronunciation guide, indicating that "UKUSA" should not be read as two separate entities.(National Security Agency)" Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, also known as the Five Eyes. Created in the late 1960s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
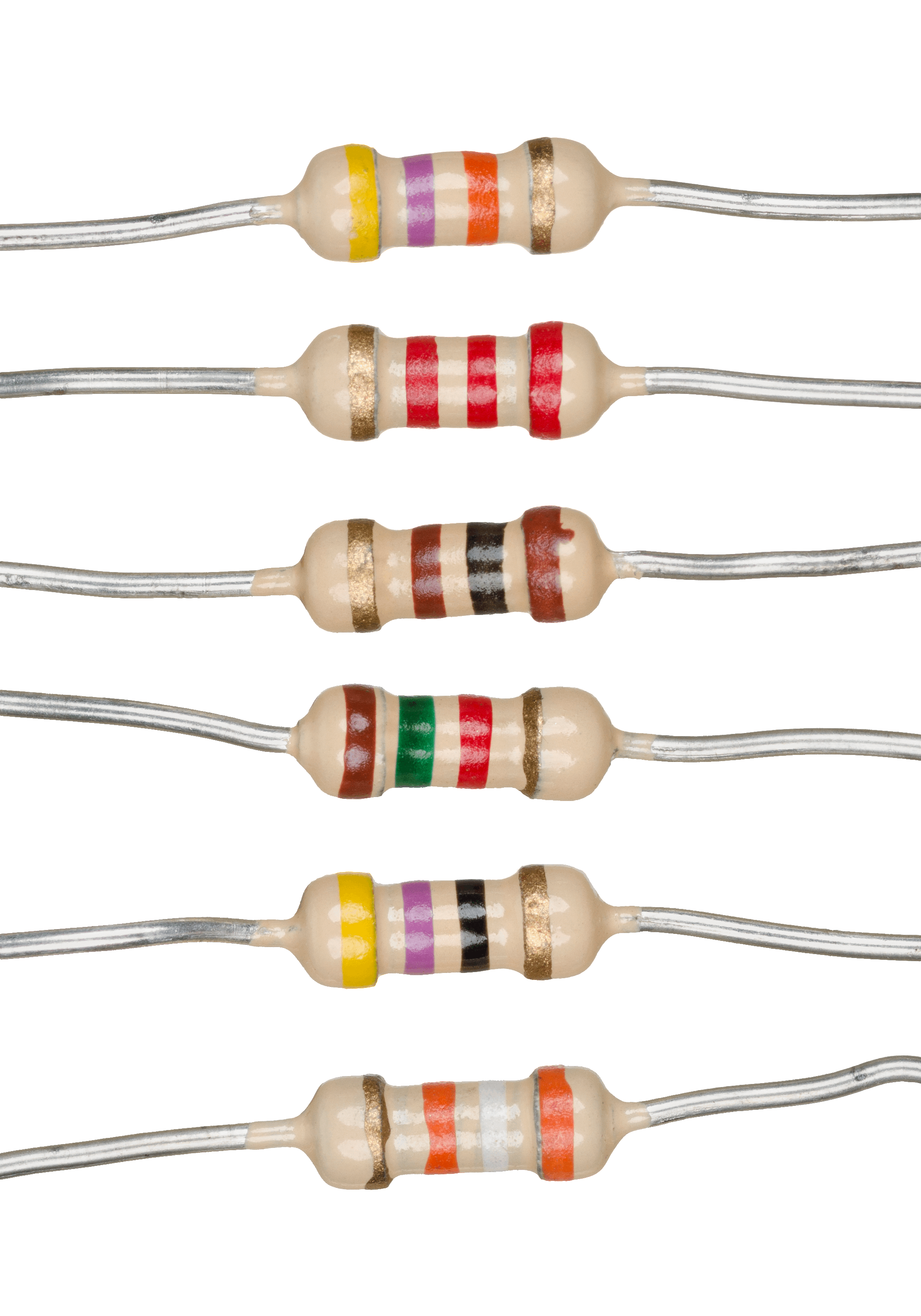
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named ''volt''. The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in generator, inductors, and transformers). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage between two points in a system. Often a common reference potential such as the ground of the system is used as one of the points. A voltage can represent either a source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (informally a scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying electrical voltages as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. The main purposes are to display repetitive or single waveforms on the screen that would otherwise occur too briefly to be perceived by the human eye. The displayed waveform can then be analyzed for properties such as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion, and others. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument. Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly. Oscilloscopes are used in the sciences, medicine, engineering, automotive and the telecommunications industry. General-purpose instruments are used for maintenance of electronic equipment and laboratory work. Special-purpose oscilloscopes may be used to analyze an automotive ign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. A familiar example is the household mirror, which typically has a thin metal coating on the back of a sheet of glass to form a reflective interface. The process of silvering was once commonly used to produce mirrors, while more recently the metal layer is deposited using techniques such as sputtering. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, integrated passive devices, LEDs, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage ( thin-film batteries). It is also being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodes
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery. The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery made was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes separated by brine-soaked paper disks. Due to fluctuation in the voltage provided by the voltaic cell it wasn't very practical. The first practical battery was invented in 1839 and named the Daniell cell after John Frederic Daniell. Still making use of the zinc–copper electrode combination. Since then many more batteries have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

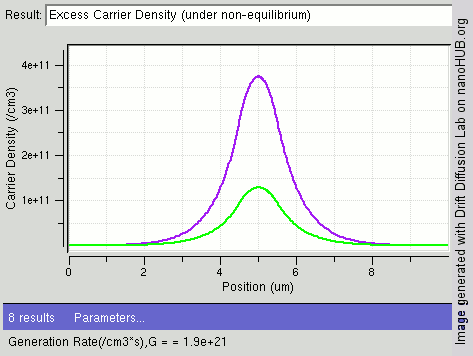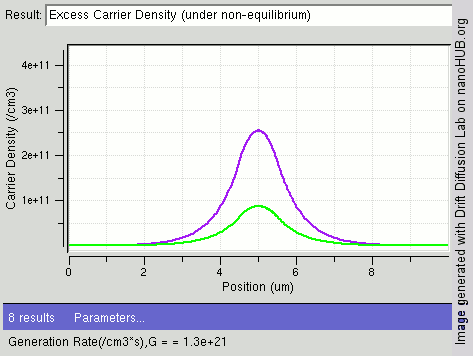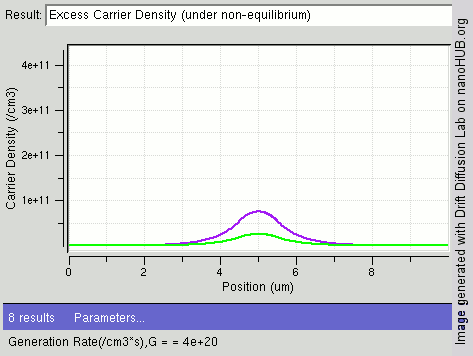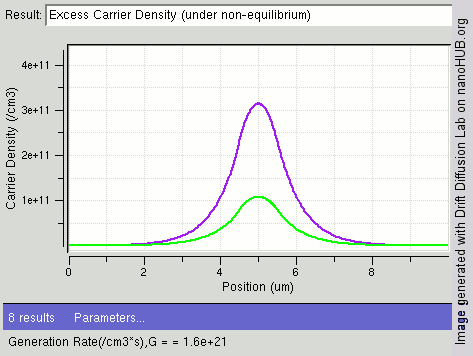



.jpg)
_250_nm_by_250_nm_image_of_one-atom-thick_silver_islands_grown_on_palladium_(111)_surface.png)
