|
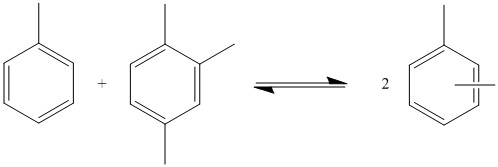
Transalkylation
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particular value in the petrochemical industry to manufacture p-xylene, styrene, and other aromatic compounds. Motivation for using transalkylation reactions is based on a difference in production and demand for benzene, toluene, and xylenes. Transalkylation can convert toluene, which is overproduced, into benzene and xylene, which are under-produced. Zeolites are often used as catalysts in transalkylation reactions. Disproportionation Transalkylation, as used by the petrochemical industry, is often used to convert toluene into benzene and xylenes. This is achieved through a disproportionation reaction of toluene in which one toluene molecule transfers its methyl group to another one. The reaction is not selective, and the xylene produced ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transalkylation
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particular value in the petrochemical industry to manufacture p-xylene, styrene, and other aromatic compounds. Motivation for using transalkylation reactions is based on a difference in production and demand for benzene, toluene, and xylenes. Transalkylation can convert toluene, which is overproduced, into benzene and xylene, which are under-produced. Zeolites are often used as catalysts in transalkylation reactions. Disproportionation Transalkylation, as used by the petrochemical industry, is often used to convert toluene into benzene and xylenes. This is achieved through a disproportionation reaction of toluene in which one toluene molecule transfers its methyl group to another one. The reaction is not selective, and the xylene produced ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedel–Crafts Reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Alkylation With alkyl halides Friedel–Crafts alkylation involves the alkylation of an aromatic ring. Traditionally, the alkylating agents are alkyl halides. Many alkylating agents can be used instead of alkyl halides. For example, enones and epoxides can be used in presence of protons. Traditionally also, the reaction employs a strong Lewis acid, such as aluminium chloride as catalyst. This reaction suffers from the disadvantage that the product is more nucleophilic than the reactant because alkyl groups are activators for the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Consequently, overalkylation can occur. Steric hindrance can be exploited to limit the number of alkylations, as in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Tert-butylphenol
4-''tert''-Butylphenol is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CC6H4OH. It is one of three isomeric ''tert''-butyl phenols. It is a white solid with a distinct phenolic odor. It dissolves in basic water. Manufacture It can be prepared by acid-catalyzed alkylation of phenol with isobutene, 2-''tert''-butylphenol being the major side product. It can be produced by diverse transalkylation reactions. Uses It major uses are in the production of epoxy resins and curing agents and also in polycarbonate resins. It has also found use in the production of phenolic resins. Another use is in the production of para tertiary butylphenol formaldehyde resin. It has also found use as a plasticizer. Bisphenol A is difunctional and used to produce epoxy resin and polycarbonate. 4-''tert''-Butylphenol is monofunctional and so in polymer science terms, bisphenol A is a polymer chain extender but 4-''tert''-butylphenol is a chain stopper or sometimes called endcapper. It is thus use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylene
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula . They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value. The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical empirical formulas . Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods. Occurrence and production Xylenes are an important petrochemical produced by catalytic reforming and also by coal carbonisation in the manufacture of coke fuel. They also occur in crude oil in concentrations of about 0.5–1%, depending on the source. Small quantities occur in gasoline and aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrodealkylation
Hydrodealkylation is a chemical reaction that often involves reacting an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as toluene, in the presence of hydrogen gas to form a simpler aromatic hydrocarbon devoid of functional groups. An example is the conversion of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene to xylene. This chemical process usually occurs at high temperature, at high pressure, or in the presence of a catalyst. These are predominantly transition metals, such as chromium or molybdenum. Examples * Toluene hydrodealkylation to benzene * Transalkylation In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particul ... References {{reaction-stub Addition reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTX (chemistry)
In the Oil refinery, petroleum refining and petrochemical industries, the initialism BTX refers to mixtures of benzene, toluene, and the three Xylene, xylene isomers, all of which are aromatic hydrocarbons. The xylene isomers are distinguished by the designations ''ortho'' – (or ''o'' –), ''meta'' – (or ''m'' –), and ''para'' – (or ''p'' –) as indicated in the adjacent diagram. If ethylbenzene is included, the mixture is sometimes referred to as BTEX. The BTX aromatics are very important petrochemical materials. Global consumption of benzene, estimated at more than 40,000,000 tons in 2010, showed an unprecedented growth of more than 3,000,000 tons from the level seen in 2009. Likewise, the para-xylene consumption showed unprecedented growth in 2010, growing by 2,800,000 tons, a full ten percent growth from 2009. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylation
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new coval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Diisopropylbenzene Via Transalkylation
1,3-Diisopropylbenzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H4(CHMe2)2 (Me = CH3). It is one of three isomeric diisopropylbenzenes. This colorless liquid is prepared by thermal isomerization of 1,4-diisopropylbenzene over a solid acid catalyst. It is the principal industrial precursor to resorcinol Resorcinol (or resorcin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or '' meta''-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble i ... via the Hock rearrangement. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Diisopropylbenzene, 1,3- Alkylbenzenes Isopropyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resorcinol
Resorcinol (or resorcin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or '' meta''-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether, but insoluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide. Production Resorcinol is produced in several steps from benzene, starting with dialkylation with propylene to give 1,3-diisopropylbenzene. Oxidation and Hock rearrangement of this disubstituted arene gives acetone and resorcinol. Resorcinol is an expensive chemical, produced in only a very few locations around the world (to date only four commercial plants are known to be operative: in the United States, Germany,China and Japan), and as such it is the determining factor in the cost of PRF adhesives. Many additional routes exist for resorcinol. It was formerly produced by disulfonation of benzene followed by hydrolysis of the 1,3-disulfonate. This meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Diisopropylbenzene
1,3-Diisopropylbenzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H4(CHMe2)2 (Me = CH3). It is one of three isomeric diisopropylbenzenes. This colorless liquid is prepared by thermal isomerization of 1,4-diisopropylbenzene over a solid acid catalyst. It is the principal industrial precursor to resorcinol via the Hock rearrangement. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Diisopropylbenzene, 1,3- Alkylbenzenes Isopropyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hock Rearrangement or Hock tide, an English holiday consisting of Hock Monday and Hock Tuesday
{{disambig ...
Hock may refer to: Common meanings: * Hock (wine), a type of wine * Hock (anatomy), part of an animal's leg * To leave an item with a pawnbroker People: * Hock (surname) * Richard "Hock" Walsh (1948-1999), Canadian blues singer Other uses: * A type of wine bottle used primarily for German or Alsatian wine See also * Hock Mountain, a summit in Washington state * Hocktide Hocktide, Hock tide or Hoke Day is a very old term used to denote the Monday and Tuesday in the second week after Easter. It was an English medieval festival; both the Tuesday and the preceding Monday were the Hock-days. Together with Whitsuntid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |