|
Tram-train
A tram-train or dual-system tram is a type of light rail vehicle that both meets the standards of a light rail system, and also national mainline standards. Tramcars are adapted to be capable of running on streets like an urban tramway but also be permitted operation alongside mainline trains. This allows services that can utilise both existing urban light rail systems and mainline railway networks and stations. It combines the urban accessibility of a tram or light rail with a mainline train's greater speed in the suburbs. The modern tram-train concept was pioneered by the German city of Karlsruhe in the late 1980s, resulting in the creation of the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn. This concept is often referred to as the Karlsruhe model, and it has since been adopted in other cities such as Mulhouse in France and in Kassel, Nordhausen and Saarbrücken in Germany. An inversion of the concept is a train-tram – a mainline train adapted to run on-street in an urban tramway, also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulhouse Tramway
The Mulhouse tramway (; ) is a tram network in the France, French city of Mulhouse in Alsace, France. It commenced service in 2006, and now comprises three purely tram lines, plus one hybrid tram-train line. Tram services The three pure tram lines intersect at Porte Jeune stop in central Mulhouse, and comprise: * Line from Gare de Mulhouse, Gare Centrale to Châtaignier * Line from Nouveau Bassin to Coteaux (Mulhouse), Coteaux * Line from Gare Central to Lutterbach Lines 1 and 2 were put into service in 2006, whilst line 3 is a short working of the tram-train line and opened in December 2010 with that line. Extensions are planned for line 1, from Châtaignier to Bosquets du Roy, and for line 2, from Nouveau Bassin to Jonquilles. The network is electrified at using overhead power collection. Services are provided by a fleet of twenty-two Alstom Citadis, Alstom Citadis 302 trams. Both the network and the trams are operated by Soléa, who also operate the city's bus network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel RegioTram
The Kassel RegioTram is a tram-train light rail system in Kassel, Hesse, Germany. Kassel's tram-train system follows the Karlsruhe model, and has been in full operation since 2007. With special RegioTram tramcars, continuous trips between the Deutsche Bahn heavy rail network and Kassel's city tram network are easily possible, thus avoiding transfers requiring long walking distances between trains of the regional rail system and trams of the Kassel city system. The operator of the RegioTram network was, until December 2013, RegioTram mbH, a joint venture between Regionalbahn Kassel (RBK), a subsidiary of the Kasseler Verkehrs-Gesellschaft (KVG), and DB Regio. Since 9 December 2013, the RegioTram is operated by a consortium of the KVG and Hessische Landesbahn (HLB). The system is integrated in the Nordhessischer Verkehrsverbund (NVV). Concept The implementation of the RegioTram project includes various interlocking measures to improve local public transport in Kassel. The ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Nordhausen
The Nordhausen tramway () is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Nordhausen, a city in Thuringia, Germany. Opened in 1900, the network is currently operated by Verkehrsbetriebe Nordhausen and has three lines, including one linking Nordhausen with nearby Ilfeld which runs as a tram-train on tracks belonging to the Harz Narrow Gauge Railways. Tram-train Nordhausen also practices a unique model of tram-train operation, in which metre-gauge dual-power railcars operate using electric power in the town, and change to diesel-electric to operate on the Harzer Schmalspurbahnen (HSB) line to Ilfeld. On the centenary of the Harzquerbahn in 1999, HSB and Stadtwerke Nordhausen stated their intent to connect the railway and tram systems. A track along Oskar-Cohn-Straße connecting the Bahnhofsplatz tram stop to the Harzquerbahn sidings at Nordhausen Nord station opened on 28 April 2002, and since then HSB railcars have terminated at the tram stop i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Metrolink
Manchester Metrolink is a tram/light rail system in Greater Manchester, England. The network has List of Manchester Metrolink tram stops, 99 stops along of standard-gauge route, making it the Transport in the United Kingdom#Trams and light rail, most extensive light rail system in the United Kingdom. Over the 2023/24 Fiscal year, financial year 42 million passenger journeys were made on the system. Metrolink is owned by the public body Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM) and is part of the region's Bee Network. It is operated and maintained under contract by a Keolis/Amey plc, Amey consortium. The network consists of eight lines which radiate from Manchester city centre to termini at Altrincham, Ashton-under-Lyne, Bury, Greater Manchester, Bury, Didsbury, East Didsbury, Eccles, Greater Manchester, Eccles, Manchester Airport, Rochdale and the Trafford Centre. It runs on a mixture of Street running, on-street track shared with other traffic; reserved track sections segrega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlsruhe Stadtbahn
The Karlsruhe Stadtbahn is a German tram-train system combining Karlsruhe trams, tram lines in the city of Karlsruhe with railway lines in the surrounding countryside, serving the entire region of the middle upper Rhine valley and creating connections to neighbouring regions. The Stadtbahn combines an efficient urban railway in the city with an S-Bahn (suburban railway), overcoming the boundary between trams and trains. Its logo does not include the green and white S-Bahn symbol used in other German suburban rail systems and the symbol is only used at stops and stations outside the inner-city tram-operation area. The idea to link tram and railway lines with one another in order to be able to offer an attractive transport system for town and outskirts was developed in Karlsruhe and implemented gradually in the 1980s and 1990s, with the system commencing operation in 1992. This idea, known as the ''Karlsruhe model'' or ''tram-train'', has been adapted by other European cities. A new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Rail
Light rail (or light rail transit, abbreviated to LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit that uses rolling stock derived from tram technology National Conference of the Transportation Research Board while also having some features from heavy rapid transit. The term was coined in 1972 in the United States as an English equivalent for the German word ''Stadtbahn'', meaning "city railway". From: 9th National Light Rail Transit Conference Different definitions exist in some countries, but in the United States, light rail operates primarily along exclusive Right_of_way#Rail_right_of_way, rights-of-way and uses either individual tramcars or multiple units coupled together, with a lower capacity and speed than a long heavy rail passenger train or rapid transit system. Narrowly defined, light rail transit uses rolling stock that is similar to that of a traditional tram, while operating at a higher capacity and speed, often on an exclusive right-of-way. In broader usage, light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombardier M5000
The Bombardier M5000 is a model of high-floor passenger light rail vehicles. It is part of the Flexity Swift range of vehicles, built specifically as a high-floor, articulated bi-directional tram to operate solely on the Manchester Metrolink system in England. The Metrolink system is the only tram network in the United Kingdom capable of running services made up of numerous tram sets, and consequently, the M5000s can operate as either a single vehicle or coupled together to form a "double" unit. A total of 147 trams were ordered between 2007 and 2018, with the first M5000 entering service on 16 December 2009. Following the withdrawal of the last T-68 and T-68A trams in May 2014, the M5000s have operated all Metrolink services. History In April 2007, eight Bombardier Flexity Swift trams were ordered by the Greater Manchester Passenger Transport Executive for Metrolink; these were intended to supplement the existing T-68/T-68A fleet and increase capacity on the Bury-Altrincha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrosassari
Metrosassari, also called ''Sassari tramway'', ''Sassari tram-train'' or ''Sassari metro-tramway'' ( or ) is the commercial name of a tram-train line in Sassari, Sardinia, Italy, operated by the regional public transport company ARST (''Azienda Regionale Sarda Trasporti''). Despite having been built in the early 2000s, in the urban section the line was built with single track and narrow gauge, to connect with the same gauge used in the secondary railway lines in Sardinia. Rolling stock Tram vehicles were designed by Pininfarina and built by AnsaldoBreda " Sirio ". Route The tramway part of the line ('' Stazione'' - ''Emiciclo Garibaldi'') opened in October 2006, linking the railway station with the city centre via the hospital district. On 27 September 2009 the line was extended into the peripheral district of Santa Maria di Pisa, running on the electrified portion of the Sassari–Sorso railway. ''Tram oltre Sassari''. In: ″I Treni″ Nr. 320 (November 2009), p. 8. Proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlsruhe Model
The Karlsruhe model is a tram-train system which consists of tram/light rail trains and commuter/regional rail trains running on the same set of tracks, generally between or outside of urban areas. It was initially developed and implemented in the city of Karlsruhe, Germany, by the local transit authority, ''Karlsruher Verkehrsverbund'' (KVV). Overview Commencing service in 1992, the system in Karlsruhe has provided a connection between the regular railway network and the city's local tram network. The whole system is now called the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn. Passengers may travel from distant towns such as Baden-Baden directly into the city centre of Karlsruhe, bridging the inconvenient distance between the main station and the city centre. For most trips, the number of train transfers has been reduced significantly. This model has led to the creation of similar tram-train systems in other locations. Other examples A similar model has been connecting the city of Vienna with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include segments on segregated Right-of-way (property access), right-of-way. The tramlines or tram networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Because of their close similarities, trams are commonly included in the wider term ''light rail'', which also includes systems separated from other traffic. Tram vehicles are usually lighter and shorter than Main line (railway), main line and rapid transit trains. Most trams use electrical power, usually fed by a Pantograph (transport), pantograph sliding on an overhead line; older systems may use a trolley pole or a bow collector. In some cases, a contact shoe on a third rail is used. If necessary, they may have dual power systems—electricity in city stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interurban
The interurban (or radial railway in Canada) is a type of electric railway, with tram-like electric self-propelled railcars which run within and between cities or towns. The term "interurban" is usually used in North America, with other terms used outside it. They were very prevalent in many parts of the world before the Second World War and were used primarily for passenger travel between cities and their surrounding suburban and rural communities. Interurban as a term encompassed the companies, their infrastructure, their cars that ran on the rails, and their service. In the United States, the early 1900s interurban was a valuable economic institution, when most roads between towns, many town streets were unpaved, and transportation and haulage was by horse-drawn carriages and carts. The interurban provided reliable transportation, particularly in winter weather, between towns and countryside. In 1915, of interurban railways were operating in the United States and, for a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
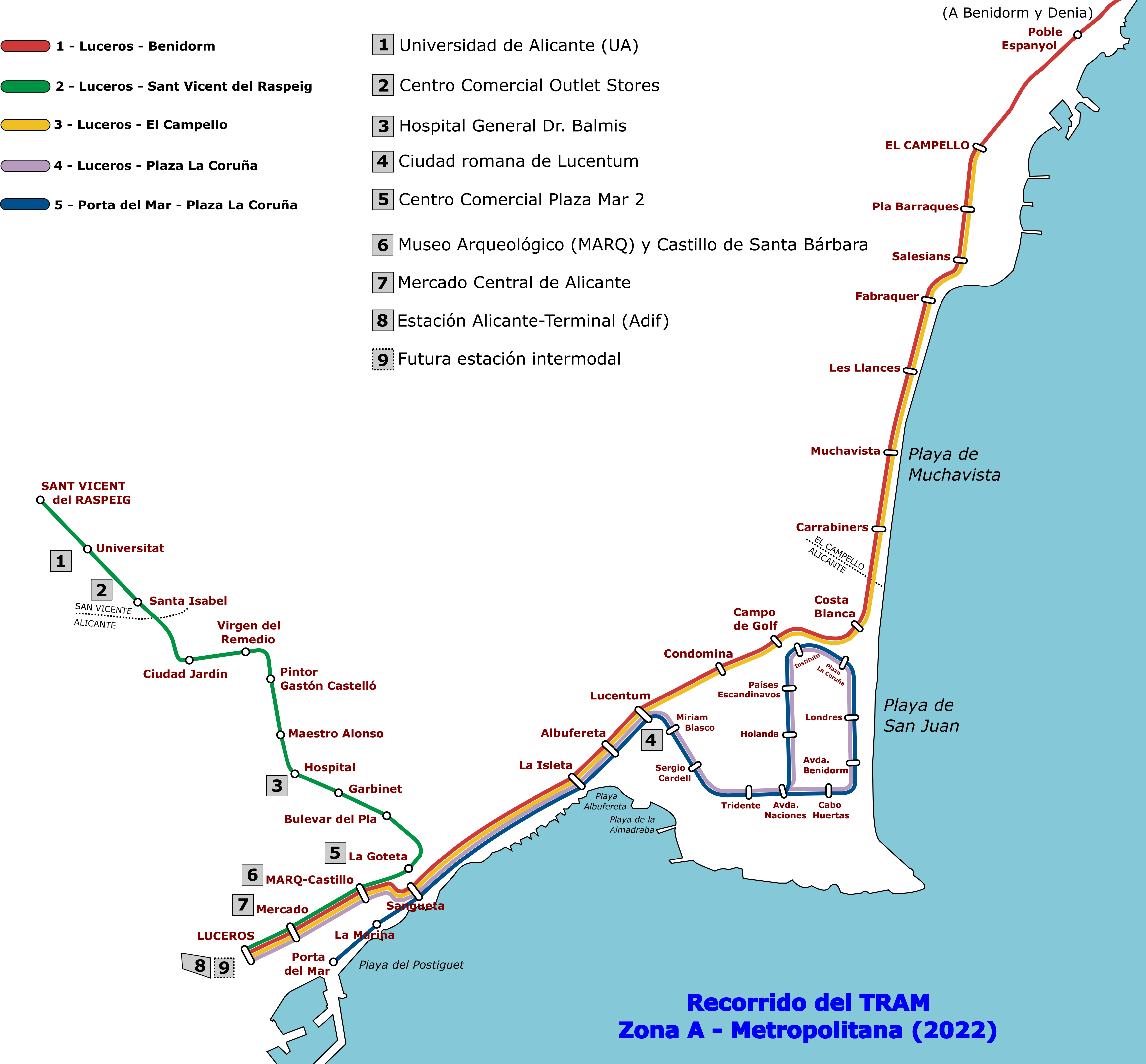
Alicante Tram
The Alicante Tram, trademarked as Alicante Metropolitan TRAM (, ), operates in the Spain, Spanish city of Alicante (Valencian Community) and its surrounding area. Like other narrow gauge railways in the Valencian Community, it is run by Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat Valenciana (FGV). It was inaugurated on 15 August 2003 replacing narrow-gauge diesel trains between Alicante and El Campello. The Alicante Metropolitan Tram light rail combines different modes of rail services: a partially semi-metro, underground tram way through Alicante city centre, a tram-train from Alicante to Benidorm, and conventional commuter rail from Benidorm to Altea, Calp and Dénia. History There has been a long history of urban rail service in Alicante. The tram service began on 13 July 1893 and the network was rapidly expanding to Mutxamel (1902), Elche and Crevillent (1905) and San Vicente del Raspeig (1906). Initially, the streetcars were horse-drawn. From 1903 the trams were powered by steam engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |