|
Train Mountain Railroad
Train Mountain Railroad is the world's largest miniature hobbyist railroad near Chiloquin, Oregon, in Klamath County, which is in the south central region of Oregon. It is situated between Klamath Falls, Oregon, approximately to the south, and Crater Lake National Park to the north. Physical Location: 36941 South Chiloquin Road, Chiloquin, OR 97624, USA. Geography The approximately property borders Highway 97 on the east side, Highway 62 (Crater Lake Highway) on the west side, and Highway 422 on the north. The track and facilities which are not obscured by trees are clearly visible on public satellite images. The elevation at Train Mountain varies from at South Meadow, at Central Station, at Ward Passing Track (the highest point accessible by train), to at Steiger Butte, the highest point on Train Mountain property. Longest miniature hobby railroad In the 2004 Guinness World Records, Train Mountain is recognized as the “Longest Miniature Hobby Railroad”. At the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
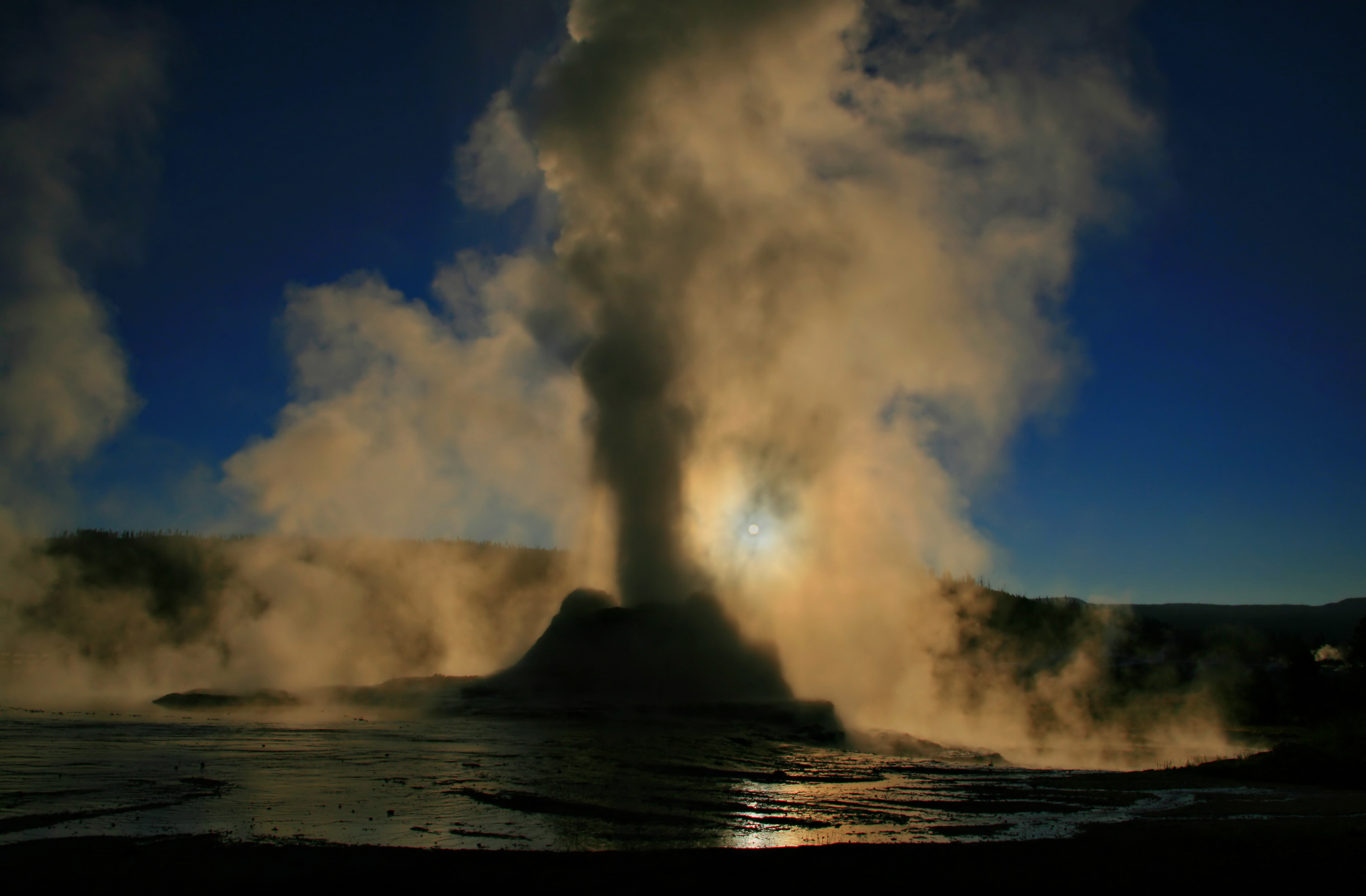
20110707 Central Station Train Mtn 013
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Scale
Large scale or G scale (, G gauge) is a track gauge for model railways which is often used for outdoor garden railways because of its size and durability. G scale trains use a fixed track gauge of to accommodate a range of rail transport modelling scales between narrow gauge ( ~1:13‒ 1:19‒ 1:20), metre gauge ( 1:22.5), Playmobil trains ( ~1:24), and standard gauge (~1:29– 1:32). G-scale LGB (, "Lehmann's Big Train") was introduced in 1968 by Ernst Paul Lehmann Patentwerk in Germany. LGB products were intended for indoor and outdoor use; so the "G" became interpreted as "garden scale". Most track is made of brass which can remain outside in all weather. Track can also be obtained in less expensive aluminium as well as oxidation-resistant, though more expensive, stainless steel. Like other scales, large scale is sometimes used for model trains that run indoors on a track mounted against the wall near the ceiling. G scale versus G gauge G gauge track has a spacing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transportation In Oregon
Rail transportation is an important element of the transportation network in the U.S. state of Oregon. Rail transportation has existed in Oregon in some form since 1855, and the state was a pioneer in development of electric railway systems. While the automobile has displaced many uses of rail in the state (as elsewhere), rail remains a key means of moving passengers and freight, both within the state and to points beyond its borders. History The first railway in Oregon was proposed by Byron J. Pengra, Surveyor General of Oregon, along the Oregon Central Military Wagon Road in 1864, but Oregon's first railroad ended up being the Oregon Portage Railroad. Henry Villard's Oregon Railway and Navigation Company established transcontinental rail lines with Northern Pacific in 1880, then with Union Pacific in 1881 (through the latter's Oregon Short Line). Twenty-first century network As of 2004, the state of Oregon has over (route-miles) of track, and of railroad right-of-way after p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transportation Museums In Oregon
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Museums In Oregon
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Museums In The United States
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Steam
Live steam is steam under pressure, obtained by heating water in a boiler. The steam is used to operate stationary or moving equipment. A live steam machine or device is one powered by steam, but the term is usually reserved for those that are replicas, scale models, toys, or otherwise used for heritage, museum, entertainment, or recreational purposes, to distinguish them from similar devices powered by electricity, internal combustion, or some other more convenient method but designed to look as if they are steam-powered. Revenue-earning steam-powered machines such as mainline and narrow gauge steam locomotives, full-sized steamships, and the worldwide electric power-generating industry steam turbines are not normally referred to as "live steam". Steamrollers and traction engines are popular, in 1:4 or 1:3 scale, as are model stationary steam engines, ranging from pocket-size to 1:2 scale. Railroads or railways Ridable, large-scale live steam railroading on a backyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport Modelling
Railway modelling (UK, Australia, New Zealand, and Ireland) or model railroading (US and Canada) is a hobby in which rail transport systems are modelled at a reduced Scale (ratio), scale. The scale models include locomotives, rolling stock, streetcars, rail tracks, tracks, Railway signal, signalling, Crane (machine), cranes, and landscapes including: countryside, roads, bridges, buildings, vehicles, harbors, urban landscape, model figures, lights, and features such as rivers, hills, tunnels, and canyons. The earliest model railways were the 'carpet railways' in the 1840s. The first documented model railway was the Railway of the Prince Imperial (French: Chemin de fer du Prince impérial) built in 1859 by emperor Napoleon III for his then 3-year-old son, also Napoleon, in the grounds of the Château de Saint-Cloud in Paris. It was powered by clockwork and ran in a figure-of-eight. Electric trains appeared around the start of the 20th century, but these were crude likenesses. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
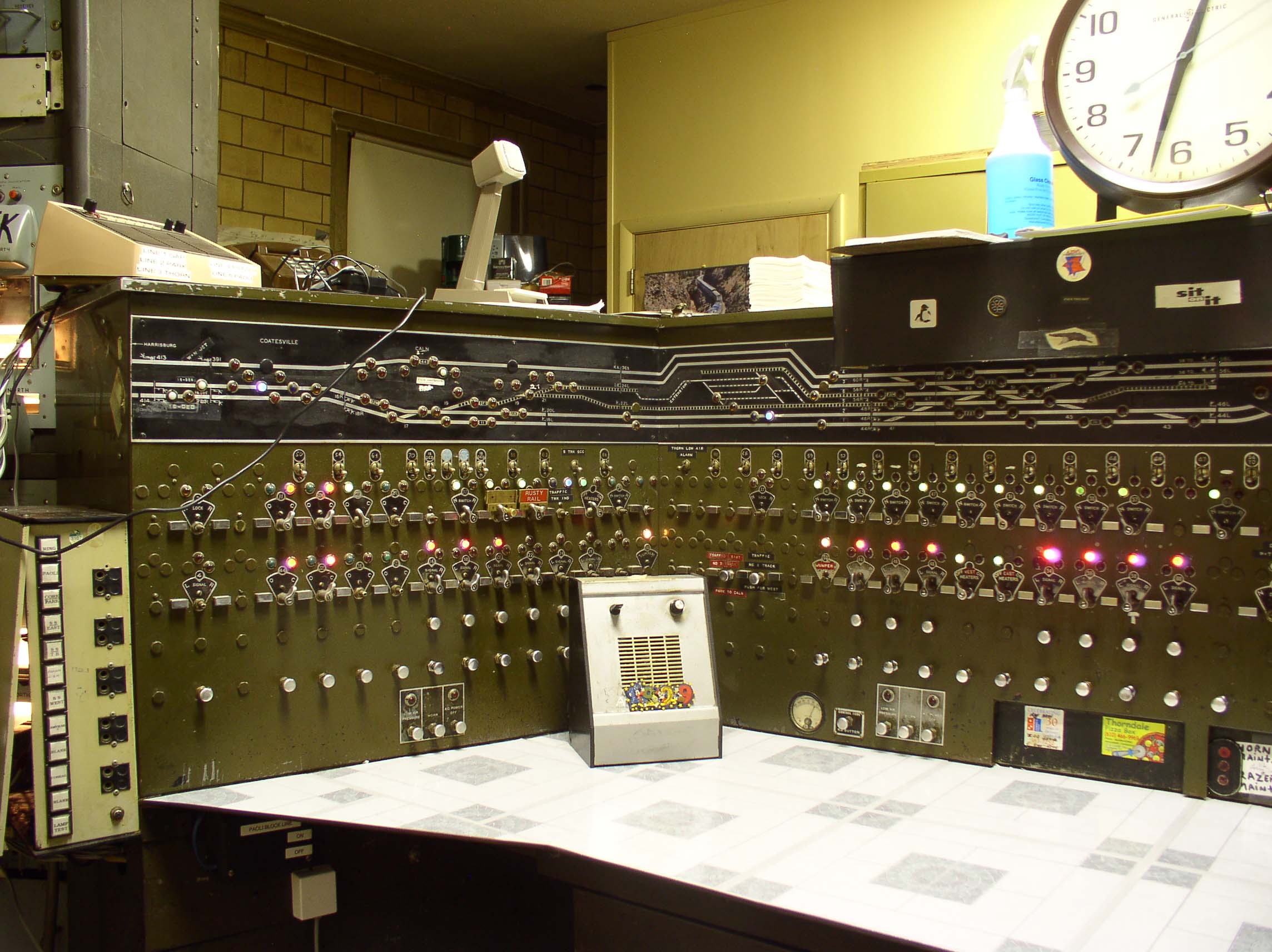
Centralized Traffic Control
Centralized traffic control (CTC) is a form of railway signalling that originated in North America. CTC consolidates train routing decisions that were previously carried out by local signal operators or the train crews themselves. The system consists of a centralized train dispatcher's office that controls railroad interlockings and traffic flows in portions of the rail system designated as CTC territory. One hallmark of CTC is a control panel with a graphical depiction of the railroad. On this panel, the dispatcher can keep track of trains' locations across the territory that the dispatcher controls. Larger railroads may have multiple dispatcher's offices and even multiple dispatchers for each operating division. These offices are usually located near the busiest yards or stations, and their operational qualities can be compared to air traffic towers. Background Key to the concept of CTC is the notion of ''traffic control'' as it applies to railroads. Trains moving in opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Snowplow
A rotary snowplow (American English) or rotary snowplough is a piece of railroad snow removal equipment with a large circular set of blades on its front end that rotate to cut through the snow on the track ahead of it. The precursor to the rotary snowplow was the wedge snowplow. History The rotary was invented in Toronto, Canada, by dentist J.W. Elliot in 1869. He never built a working model or prototype. Orange Jull of Orangeville, Ontario, expanded on Elliot's design, building working models he tested with sand. During the winter of 1883–84, Jull contracted with the Leslie Brothers of Toronto to build a full-size prototype that proved successful. Jull later sold his design rights to Leslie Brothers, who formed the Rotary Steam Shovel Manufacturing Company in Paterson, New Jersey. Leslie Brothers contracted with Cooke Locomotive & Machine Works in Paterson to do the actual construction. Another inventor is said to be Colonel Lewis P. Campbell. He is listed in US patent 184855 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
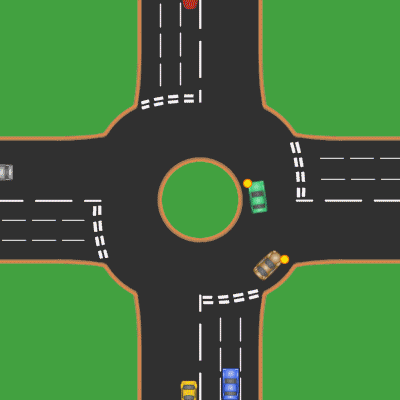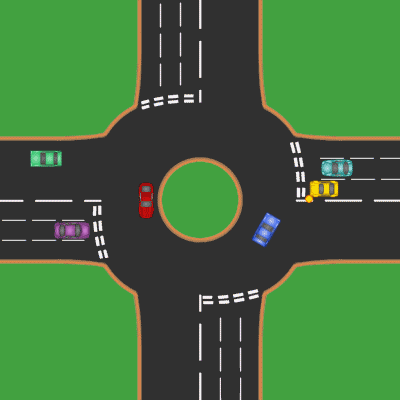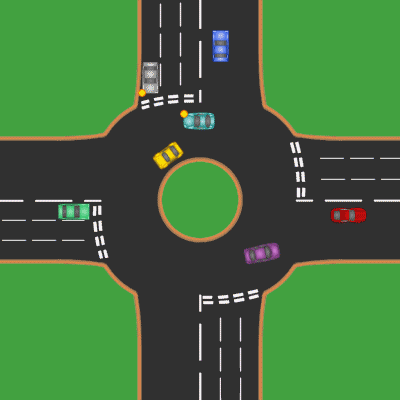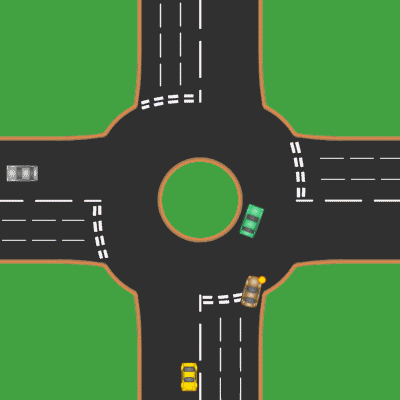
Roundabouts
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.''The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary,'' Volume 2, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993), page 2632 Engineers use the term modern roundabout to refer to junctions installed after 1960 that incorporate various design rules to increase safety. Both modern and non-modern roundabouts, however, may bear street names or be identified colloquially by local names such as rotary or traffic circle. Compared to stop signs, traffic signals, and earlier forms of roundabouts, modern roundabouts reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions greatly by reducing traffic speeds and minimizing T-bone and head-on collisions. Variations on the basic concept include integration with tram or train lines, two-way flow, higher speeds and many others. For pedestrians, traffic exiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |